Biomaterials Translational ›› 2021, Vol. 2 ›› Issue (3): 177-187.doi: 10.12336/biomatertransl.2021.03.002
• REVIEW • Previous Articles Next Articles
Hongtao Yang1,2, Wenjiao Lin3,4, Yufeng Zheng1,*(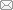 )
)
Received:2021-05-30
Revised:2021-07-16
Accepted:2021-07-21
Online:2021-09-28
Published:2021-09-28
Contact:
Yufeng Zheng
E-mail:yfzheng@pku.edu.cn
About author:Yufeng Zheng, yfzheng@pku.edu.cn.
Yang, H.; Lin, W.; Zheng, Y. Advances and perspective on the translational medicine of biodegradable metals. Biomater Transl. 2021, 2(3), 177-187.
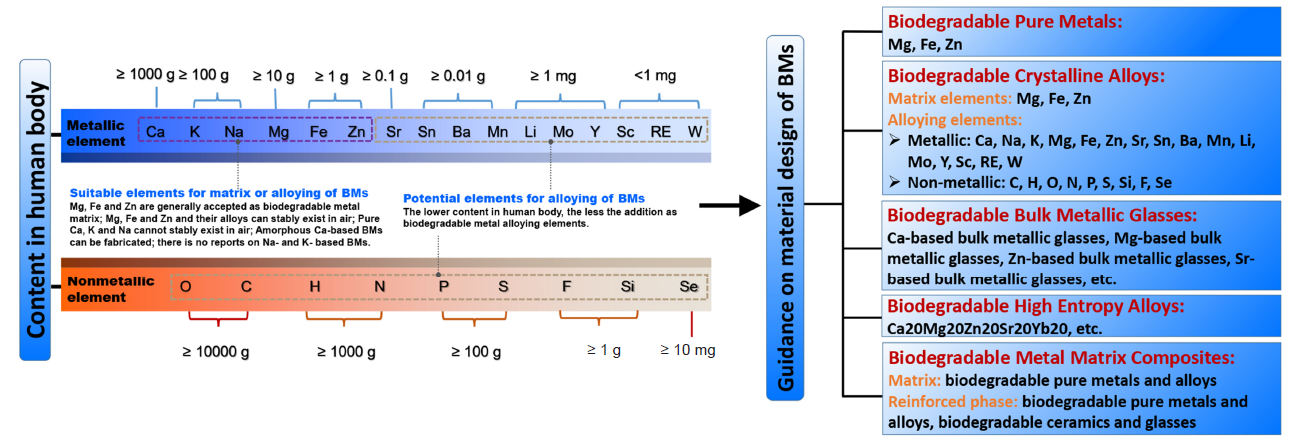
Figure 1. Design of biodegradable metals based on the criteria of “biodegradability” and “biocompatibility”. BM: biodegradable metal. Reprinted with permission from Liu et al.11 Copyright 2019 WILEY‐VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
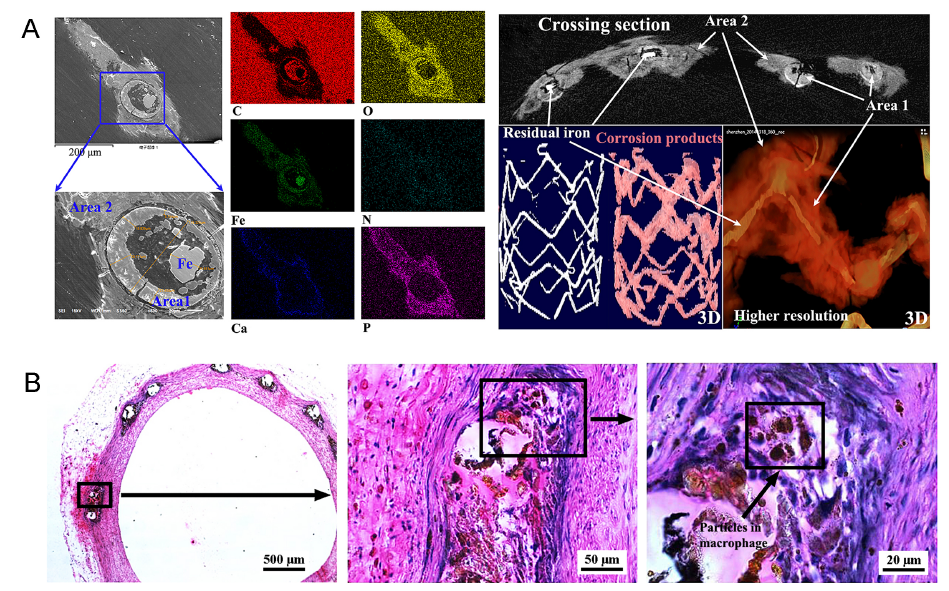
Figure 2. (A) Scanning electron microscopic images and corresponding chemical element distribution of one iron strut, and micro-computed tomographic image of a representative iron-based scaffold with residual iron backbone and corrosion products at 6 months after implantation in the rabbit abdominal aorta. Scale bars: 200 μm (scanning electron microscopic images). 3D: three-dimensional. Reprinted from Lin et al.33 Copyright 2016, with permission from Elsevier. (B) Macrophages engulf the insoluble corrosion products of an iron-based scaffold in rabbit abdominal aorta within 12 months. Right images are magnifications of black rectangles in left images. Scale bars: 500 μm (left), 50 μm (middle), 20 μm (right). Reprinted Lin et al.34 Copyright 2017, with permission from Elsevier.
Figure 3. Schematic diagrams showing evolution of the degradation mechanism of a zinc (Zn) stent associated with the conversion of degradation microenvironments during the healing process. a-d indicates representative time points during vascular healing, which are described by images above from left to right. Scale bars: 10 μm or 3 μm. Reprinted from Yang et al.42 Copyright 2017, with permission from Elsevier.
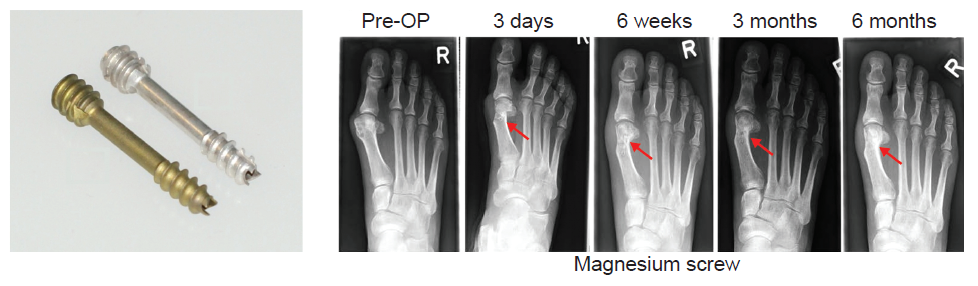
Figure 4. MAGNEAIX® compression screws for Hallux valgus surgery. Red arrows indicate implantation sites. OP: operative; R: right. Reprinted from Windhagen et al.45; licensee BioMed Central Ltd.
| [1] | National Bureau of Statistics. The main data of the seventh national census, National Bureau of Statistics of China. http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/zxfb/202105/t20210510_1817176.html . Accessed by May, 2021. |
| [2] |
Navarro, M.; Michiardi, A.; Castaño, O.; Planell, J. A. Biomaterials in orthopaedics. J R Soc Interface. 2008, 5, 1137-1158.
doi: 10.1098/rsif.2008.0151 URL |
| [3] |
Li, C.; Guo, C.; Fitzpatrick, V.; Ibrahim, A.; Zwierstra, M. J.; Hanna, P.; Lechtig, A.; Nazarian, A.; Lin, S. J.; Kaplan, D. L. Design of biodegradable, implantable devices towards clinical translation. Nat Rev Mater. 2020, 5, 61-81.
doi: 10.1038/s41578-019-0150-z URL |
| [4] | Haseeb, M.; Butt, M. F.; Altaf, T.; Muzaffar, K.; Gupta, A.; Jallu, A. Indications of implant removal: A study of 83 cases. Int J Health Sci (Qassim). 2017, 11, 1-7. |
| [5] |
Reith, G.; Schmitz-Greven, V.; Hensel, K. O.; Schneider, M. M.; Tinschmann, T.; Bouillon, B.; Probst, C. Metal implant removal: benefits and drawbacks a patient survey. BMC Surg. 2015, 15, 96.
doi: 10.1186/s12893-015-0081-6 URL |
| [6] |
Wentzel, J. J.; Whelan, D. M.; van der Giessen, W. J.; van Beusekom, H. M.; Andhyiswara, I.; Serruys, P. W.; Slager, C. J.; Krams, R. Coronary stent implantation changes 3-D vessel geometry and 3-D shear stress distribution. J Biomech. 2000, 33, 1287-1295.
doi: 10.1016/S0021-9290(00)00066-X URL |
| [7] |
Han, H. S.; Loffredo, S.; Jun, I.; Edwards, J.; Kim, Y. C.; Seok, H. K.; Witte, F.; Mantovani, D.; Glyn-Jones, S. Current status and outlook on the clinical translation of biodegradable metals. Mater Today. 2019, 23, 57-71.
doi: 10.1016/j.mattod.2018.05.018 URL |
| [8] |
Zhao, D.; Witte, F.; Lu, F.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Qin, L. Current status on clinical applications of magnesium-based orthopaedic implants: A review from clinical translational perspective. Biomaterials. 2017, 112, 287-302.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2016.10.017 URL |
| [9] |
Venezuela, J.; Dargusch, M. S. The influence of alloying and fabrication techniques on the mechanical properties, biodegradability and biocompatibility of zinc: a comprehensive review. Acta Biomater. 2019, 87, 1-40.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.01.035 URL |
| [10] |
Hench, L. L.; Polak, J. M. Third-generation biomedical materials. Science. 2002, 295, 1014-1017.
doi: 10.1126/science.1067404 URL |
| [11] |
Liu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, X. H.; Yang, J. A.; Pan, H.; Chen, D.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, D.; Wu, S.; Yeung, K. W. K.; Zeng, R. C.; Han, Y.; Guan, S. Fundamental theory of biodegradable metals—definition, criteria, and design. Adv Funct Mater. 2019, 29, 1805402.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v29.18 URL |
| [12] | Williams, D. The williams dictionary of biomaterials. Liverpool University Press: 1999. |
| [13] |
Tamada, J. A.; Langer, R. Erosion kinetics of hydrolytically degradable polymers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993, 90, 552-556.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.552 URL |
| [14] |
Hench, L. L. The future of bioactive ceramics. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2015, 26, 86.
doi: 10.1007/s10856-015-5425-3 URL |
| [15] |
Williams, D. F. On the mechanisms of biocompatibility. Biomaterials. 2008, 29, 2941-2953.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2008.04.023 URL |
| [16] |
Aykul, S.; Martinez-Hackert, E. Determination of half-maximal inhibitory concentration using biosensor-based protein interaction analysis. Anal Biochem. 2016, 508, 97-103.
doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2016.06.025 URL |
| [17] |
Zbinden, G.; Flury-Roversi, M. Significance of the LD50-test for the toxicological evaluation of chemical substances. Arch Toxicol. 1981, 47, 77-99.
doi: 10.1007/BF00332351 URL |
| [18] |
Zoroddu, M. A.; Aaseth, J.; Crisponi, G.; Medici, S.; Peana, M.; Nurchi, V. M. The essential metals for humans: a brief overview. J Inorg Biochem. 2019, 195, 120-129.
doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2019.03.013 URL |
| [19] |
Li, H. F.; Zheng, Y. F. Recent advances in bulk metallic glasses for biomedical applications. Acta Biomater. 2016, 36, 1-20.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.03.047 URL |
| [20] |
Virtanen, S. Biodegradable Mg and Mg alloys: corrosion and biocompatibility. Mater Sci Eng B. 2011, 176, 1600-1608.
doi: 10.1016/j.mseb.2011.05.028 URL |
| [21] |
Hermawan, H. Updates on the research and development of absorbable metals for biomedical applications. Prog Biomater. 2018, 7, 93-110.
doi: 10.1007/s40204-018-0091-4 URL |
| [22] |
Ye, X.; Chen, M.; Yang, M.; Wei, J.; Liu, D. In vitro corrosion resistance and cytocompatibility of nano-hydroxyapatite reinforced Mg-Zn-Zr composites. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2010, 21, 1321-1328.
doi: 10.1007/s10856-009-3954-3 URL |
| [23] |
Witte, F.; Feyerabend, F.; Maier, P.; Fischer, J.; Störmer, M.; Blawert, C.; Dietzel, W.; Hort, N. Biodegradable magnesium-hydroxyapatite metal matrix composites. Biomaterials. 2007, 28, 2163-2174.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2006.12.027 URL |
| [24] |
Narita, K.; Tian, Q.; Johnson, I.; Zhang, C.; Kobayashi, E.; Liu, H. Degradation behaviors and cytocompatibility of Mg/β-tricalcium phosphate composites produced by spark plasma sintering. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2019, 107, 2238-2253.
doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.v107.7 URL |
| [25] |
Wong, H. M.; Wu, S.; Chu, P. K.; Cheng, S. H.; Luk, K. D.; Cheung, K. M.; Yeung, K. W. Low-modulus Mg/PCL hybrid bone substitute for osteoporotic fracture fixation. Biomaterials. 2013, 34, 7016-7032.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.05.062 URL |
| [26] |
Lei, T.; Tang, W.; Cai, S. H.; Feng, F. F.; Li, N. F. On the corrosion behaviour of newly developed biodegradable Mg-based metal matrix composites produced by in situ reaction. Corros Sci. 2012, 54, 270-277.
doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2011.09.027 URL |
| [27] | Yang, H. T.; Wang, Z. H.; Li, H. F.; Zheng, Y. F.; Li, Y. W.; Li, R. In vitro study on novel Zn-ZnO composites with tunable degradation rate. Eur Cell Mater. 2014, 25, S5. |
| [28] |
Esmaily, M.; Svensson, J. E.; Fajardo, S.; Birbilis, N.; Frankel, G. S.; Virtanen, S.; Arrabal, R.; Thomas, S.; Johansson, L. G. Fundamentals and advances in magnesium alloy corrosion. Prog Mater Sci. 2017, 89, 92-193.
doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2017.04.011 URL |
| [29] |
Lee, J. W.; Han, H. S.; Han, K. J.; Park, J.; Jeon, H.; Ok, M. R.; Seok, H. K.; Ahn, J. P.; Lee, K. E.; Lee, D. H.; Yang, S. J.; Cho, S. Y.; Cha, P. R.; Kwon, H.; Nam, T. H.; Han, J. H.; Rho, H. J.; Lee, K. S.; Kim, Y. C.; Mantovani, D. Long-term clinical study and multiscale analysis of in vivo biodegradation mechanism of Mg alloy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016, 113, 716-721.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1518238113 URL |
| [30] |
Bennett, J.; De Hemptinne, Q.; McCutcheon, K. Magmaris resorbable magnesium scaffold for the treatment of coronary heart disease: overview of its safety and efficacy. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2019, 16, 757-769.
doi: 10.1080/17434440.2019.1649133 URL |
| [31] |
Wittchow, E.; Adden, N.; Riedmüller, J.; Savard, C.; Waksman, R.; Braune, M. Bioresorbable drug-eluting magnesium-alloy scaffold: design and feasibility in a porcine coronary model. EuroIntervention. 2013, 8, 1441-1450.
doi: 10.4244/EIJV8I12A218 URL |
| [32] | Ahmad, Z. Principles of corrosion engineering and corrosion control. Elsevier: 2006. |
| [33] |
Lin, W. J.; Zhang, D. Y.; Zhang, G.; Sun, H. T.; Qi, H. P.; Chen, L. P.; Liu, Z. Q.; Gao, R. L.; Zheng, W. Design and characterization of a novel biocorrodible iron-based drug-eluting coronary scaffold. Mater Des. 2016, 91, 72-79.
doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2015.11.045 URL |
| [34] |
Lin, W.; Qin, L.; Qi, H.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, G.; Gao, R.; Qiu, H.; Xia, Y.; Cao, P.; Wang, X.; Zheng, W. Long-term in vivo corrosion behavior, biocompatibility and bioresorption mechanism of a bioresorbable nitrided iron scaffold. Acta Biomater. 2017, 54, 454-468.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2017.03.020 URL |
| [35] | Thomas, S.; Birbilis, N.; Venkatraman, M. S.; Cole, I. S. Corrosion of zinc as a function of pH. Corrosion. 2012, 68:015009-1-015009-9. |
| [36] |
Yang, H.; Jia, B.; Zhang, Z.; Qu, X.; Li, G.; Lin, W.; Zhu, D.; Dai, K.; Zheng, Y. Alloying design of biodegradable zinc as promising bone implants for load-bearing applications. Nat Commun. 2020, 11, 401.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-14153-7 URL |
| [37] |
Yang, H.; Qu, X.; Wang, M.; Cheng, H.; Jia, B.; Nie, J.; Dai, K.; Zheng, Y. Zn-0.4Li alloy shows great potential for the fixation and healing of bone fractures at load-bearing sites. Chem Eng J. 2021, 417, 129317.
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.129317 URL |
| [38] |
He, J.; Fang, J.; Wei, P.; Li, Y.; Guo, H.; Mei, Q.; Ren, F. Cancellous bone-like porous Fe@Zn scaffolds with core-shell-structured skeletons for biodegradable bone implants. Acta Biomater. 2021, 121, 665-681.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.11.032 URL |
| [39] |
Yang, H.; Qu, X.; Lin, W.; Chen, D.; Zhu, D.; Dai, K.; Zheng, Y. Enhanced osseointegration of Zn-Mg composites by tuning the release of Zn ions with sacrificial Mg-rich anode design. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2019, 5, 453-467.
doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.8b01137 URL |
| [40] |
Bowen, P. K.; Drelich, J.; Goldman, J. Zinc exhibits ideal physiological corrosion behavior for bioabsorbable stents. Adv Mater. 2013, 25, 2577-2582.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201300226 URL |
| [41] |
Drelich, A. J.; Zhao, S.; Guillory, R. J., 2nd; Drelich, J. W.; Goldman, J. Long-term surveillance of zinc implant in murine artery: Surprisingly steady biocorrosion rate. Acta Biomater. 2017, 58, 539-549.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2017.05.045 URL |
| [42] |
Yang, H.; Wang, C.; Liu, C.; Chen, H.; Wu, Y.; Han, J.; Jia, Z.; Lin, W.; Zhang, D.; Li, W.; Yuan, W.; Guo, H.; Li, H.; Yang, G.; Kong, D.; Zhu, D.; Takashima, K.; Ruan, L.; Nie, J.; Li, X.; Zheng, Y. Evolution of the degradation mechanism of pure zinc stent in the one-year study of rabbit abdominal aorta model. Biomaterials. 2017, 145, 92-105.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.08.022 URL |
| [43] |
Zhou, C.; Li, H. F.; Yin, Y. X.; Shi, Z. Z.; Li, T.; Feng, X. Y.; Zhang, J. W.; Song, C. X.; Cui, X. S.; Xu, K. L.; Zhao, Y. W.; Hou, W. B.; Lu, S. T.; Liu, G.; Li, M. Q.; Ma, J. Y.; Toft, E.; Volinsky, A. A.; Wan, M.; Yao, X. J.; Wang, C. B.; Yao, K.; Xu, S. K.; Lu, H.; Chang, S. F.; Ge, J. B.; Wang, L. N.; Zhang, H. J. Long-term in vivo study of biodegradable Zn-Cu stent: A 2-year implantation evaluation in porcine coronary artery. Acta Biomater. 2019, 97, 657-670.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.08.012 URL |
| [44] | Huse, E. C. A new ligature?. Chicago Med J Exam. 1878, 172, 11. |
| [45] |
Windhagen, H.; Radtke, K.; Weizbauer, A.; Diekmann, J.; Noll, Y.; Kreimeyer, U.; Schavan, R.; Stukenborg-Colsman, C.; Waizy, H. Biodegradable magnesium-based screw clinically equivalent to titanium screw in hallux valgus surgery: short term results of the first prospective, randomized, controlled clinical pilot study. Biomed Eng Online. 2013, 12, 62.
doi: 10.1186/1475-925X-12-62 URL |
| [46] |
Erbel, R.; Di Mario, C.; Bartunek, J.; Bonnier, J.; de Bruyne, B.; Eberli, F. R.; Erne, P.; Haude, M.; Heublein, B.; Horrigan, M.; Ilsley, C.; Böse, D.; Koolen, J.; Lüscher, T. F.; Weissman, N.; Waksman, R.; PROGRESS-AMS (Clinical Performance and Angiographic Results of Coronary Stenting with Absorbable Metal Stents) Investigators. Temporary scaffolding of coronary arteries with bioabsorbable magnesium stents: a prospective, non-randomised multicentre trial. Lancet. 2007, 369, 1869-1875.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60853-8 URL |
| [47] |
Campos, C. M.; Muramatsu, T.; Iqbal, J.; Zhang, Y. J.; Onuma, Y.; Garcia-Garcia, H. M.; Haude, M.; Lemos, P. A.; Warnack, B.; Serruys, P. W. Bioresorbable drug-eluting magnesium-alloy scaffold for treatment of coronary artery disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2013, 14, 24492-24500.
doi: 10.3390/ijms141224492 URL |
| [48] |
Haude, M.; Ince, H.; Abizaid, A.; Toelg, R.; Lemos, P. A.; von Birgelen, C.; Christiansen, E. H.; Wijns, W.; Neumann, F. J.; Kaiser, C.; Eeckhout, E.; Lim, S. T.; Escaned, J.; Onuma, Y.; Garcia-Garcia, H. M.; Waksman, R. Sustained safety and performance of the second-generation drug-eluting absorbable metal scaffold in patients with de novo coronary lesions: 12-month clinical results and angiographic findings of the BIOSOLVE-II first-in-man trial. Eur Heart J. 2016, 37, 2701-2709.
doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw196 URL |
| [49] |
Haude, M.; Ince, H.; Abizaid, A.; Toelg, R.; Lemos, P. A.; von Birgelen, C.; Christiansen, E. H.; Wijns, W.; Neumann, F. J.; Kaiser, C.; Eeckhout, E.; Lim, S. T.; Escaned, J.; Garcia-Garcia, H. M.; Waksman, R. Safety and performance of the second-generation drug-eluting absorbable metal scaffold in patients with de-novo coronary artery lesions (BIOSOLVE-II): 6 month results of a prospective, multicentre, non-randomised, first-in-man trial. Lancet. 2016, 387, 31-39.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00447-X URL |
| [50] |
Haude, M.; Ince, H.; Kische, S.; Abizaid, A.; Tölg, R.; Alves Lemos, P.; Van Mieghem, N. M.; Verheye, S.; von Birgelen, C.; Christiansen, E. H.; Barbato, E.; Garcia-Garcia, H. M.; Waksman, R. Safety and clinical performance of a drug eluting absorbable metal scaffold in the treatment of subjects with de novo lesions in native coronary arteries: Pooled 12-month outcomes of BIOSOLVE-II and BIOSOLVE-III. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2018, 92, E502-E511.
doi: 10.1002/ccd.v92.7 URL |
| [51] |
Peuster, M.; Hesse, C.; Schloo, T.; Fink, C.; Beerbaum, P.; von Schnakenburg, C. Long-term biocompatibility of a corrodible peripheral iron stent in the porcine descending aorta. Biomaterials. 2006, 27, 4955-4962.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2006.05.029 URL |
| [52] |
Waksman, R.; Pakala, R.; Baffour, R.; Seabron, R.; Hellinga, D.; Tio, F. O. Short-term effects of biocorrodible iron stents in porcine coronary arteries. J Interv Cardiol. 2008, 21, 15-20.
doi: 10.1111/joic.2008.21.issue-1 URL |
| [53] | Shen, D.; Qi, H.; Lin, W.; Zhang, W.; Bian, D.; Shi, X.; Qin, L.; Zhang, G.; Fu, W.; Dou, K.; Xu, B.; Yin, Z.; Rao, J.; Alwi, M.; Wang, S.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, D.; Gao, R. PDLLA-Zn-nitrided Fe bioresorbable scaffold with 53-μm-thick metallic struts and tunable multistage biodegradation function. Sci Adv. 2021, 7, eabf0614. |
| [54] | Bian, D.; Qin, L.; Lin, W.; Shen, D.; Qi, H.; Shi, X.; Zhang, G.; Liu, H.; Yang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, D.; Zheng, Y. Magnetic resonance (MR) safety and compatibility of a novel iron bioresorbable scaffold. Bioact Mater. 2020, 5, 260-274. |
| [55] | Lin, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, W.; Qi, H.; Zhang, G.; Qian, J.; Li, X.; Qin, L.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Qiu, H.; Shi, X.; Zheng, W.; Zhang, D.; Gao, R.; Ding, J. In vivo degradation and endothelialization of an iron bioresorbable scaffold. Bioact Mater. 2021, 6, 1028-1039. |
| [56] | Caputo, R.; Kirwan, J.; Green, S.; Ebner, A. TCT-233 first in man experience with a large bore (≥14 FR) bio-corrodable vascular closure device. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017, 70, B97. |
| [57] |
Jafari, S.; Raman, R. K. S.; Davies, C. H. J.; Hofstetter, J.; Uggowitzer, P. J.; Löffler, J. F. Stress corrosion cracking and corrosion fatigue characterisation of MgZn1Ca0.3 (ZX10) in a simulated physiological environment. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2017, 65, 634-643.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2016.09.033 URL |
| [58] |
Khakpour, M.; Vafai, K. Critical assessment of arterial transport models. Int J Heat Mass Transfer. 2008, 51, 807-822.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2007.04.021 URL |
| [59] |
Liu, X.; Yang, H.; Xiong, P.; Li, W.; Huang, H. H.; Zheng, Y. Comparative studies of Tris-HCl, HEPES and NaHCO3/CO2 buffer systems on the biodegradation behaviour of pure Zn in NaCl and SBF solutions. Corros Sci. 2019, 157, 205-219.
doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2019.05.018 URL |
| [60] |
Yadav, A. P.; Nishikata, A.; Tsuru, T. Oxygen reduction mechanism on corroded zinc. J Electroanal Chem. 2005, 585, 142-149.
doi: 10.1016/j.jelechem.2005.08.007 URL |
| [61] | Zheng, Y. F.; Gu, X. N.; Witte, F. Biodegradable metals. Mater Sci Eng RRep. 2014, 77, 1-34. |
| [62] |
Li, Z.; Gu, X.; Lou, S.; Zheng, Y. The development of binary Mg-Ca alloys for use as biodegradable materials within bone. Biomaterials. 2008, 29, 1329-1344.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2007.12.021 URL |
| [63] |
Liu, X.; Sun, J.; Zhou, F.; Yang, Y.; Chang, R.; Qiu, K.; Pu, Z.; Li, L.; Zheng, Y. Micro-alloying with Mn in Zn-Mg alloy for future biodegradable metals application. Mater Des. 2016, 94, 95-104.
doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2015.12.128 URL |
| [64] |
Li, Y.; Pavanram, P.; Zhou, J.; Lietaert, K.; Bobbert, F. S. L.; Kubo, Y.; Leeflang, M. A.; Jahr, H.; Zadpoor, A. A. Additively manufactured functionally graded biodegradable porous zinc. Biomater Sci. 2020, 8, 2404-2419.
doi: 10.1039/C9BM01904A URL |
| [65] |
Gu, X. N.; Zhou, W. R.; Zheng, Y. F.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y. X. Degradation and cytotoxicity of lotus-type porous pure magnesium as potential tissue engineering scaffold material. Mater Lett. 2010, 64, 1871-1874.
doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2010.06.015 URL |
| [66] |
Yan, T.; Tan, L.; Xiong, D.; Liu, X.; Zhang, B.; Yang, K. Fluoride treatment and in vitro corrosion behavior of an AZ31B magnesium alloy. Mater Sci Eng C. 2010, 30, 740-748.
doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2010.03.007 URL |
| [67] |
Xu, X.; Lu, P.; Guo, M.; Fang, M. Cross-linked gelatin/nanoparticles composite coating on micro-arc oxidation film for corrosion and drug release. Appl Surf Sci. 2010, 256, 2367-2371.
doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2009.10.069 URL |
| [68] |
Einhorn, T. A.; Gerstenfeld, L. C. Fracture healing: mechanisms and interventions. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015, 11, 45-54.
doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2014.164 URL |
| [69] |
Chen, Z.; Klein, T.; Murray, R. Z.; Crawford, R.; Chang, J.; Wu, C.; Xiao, Y. Osteoimmunomodulation for the development of advanced bone biomaterials. Mater Today. 2016, 19, 304-321.
doi: 10.1016/j.mattod.2015.11.004 URL |
| [70] |
Kim, S. E.; Song, S. H.; Yun, Y. P.; Choi, B. J.; Kwon, I. K.; Bae, M. S.; Moon, H. J.; Kwon, Y. D. The effect of immobilization of heparin and bone morphogenic protein-2 (BMP-2) to titanium surfaces on inflammation and osteoblast function. Biomaterials. 2011, 32, 366-373.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.09.008 URL |
| [71] | Zhou, L.; Lin, Z.; Ding, J.; Huang, W.; Chen, J.; Wu, D. Inflammatory and biocompatibility evaluation of antimicrobial peptide GL13K immobilized onto titanium by silanization. Colloids Surf BBiointerfaces. 2017, 160, 581-588. |
| [72] |
Luu, T. U.; Gott, S. C.; Woo, B. W.; Rao, M. P.; Liu, W. F. Micro- and nanopatterned topographical cues for regulating macrophage cell shape and phenotype. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015, 7, 28665-28672.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.5b10589 URL |
| [73] |
Jayant, R. D.; McShane, M. J.; Srivastava, R. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of anti-inflammatory agents using nanoengineered alginate carriers: towards localized implant inflammation suppression. Int J Pharm. 2011, 403, 268-275.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2010.10.035 URL |
| [74] |
Kzhyshkowska, J.; Gudima, A.; Riabov, V.; Dollinger, C.; Lavalle, P.; Vrana, N. E. Macrophage responses to implants: prospects for personalized medicine. J Leukoc Biol. 2015, 98, 953-962.
doi: 10.1189/jlb.5VMR0415-166R URL |
| [75] |
Simon-Walker, R.; Romero, R.; Staver, J. M.; Zang, Y.; Reynolds, M. M.; Popat, K. C.; Kipper, M. J. Glycocalyx-inspired nitric oxide-releasing surfaces reduce platelet adhesion and activation on titanium. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2017, 3, 68-77.
doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.6b00572 URL |
| [1] | Ying Luo, Jue Wang, Michael Tim Yun Ong, Patrick Shu-hang Yung, Jiali Wang, Ling Qin. Update on the research and development of magnesium-based biodegradable implants and their clinical translation in orthopaedics [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2021, 2(3): 188-196. |
| [2] | Jing Long, Bin Teng, Wei Zhang, Long Li, Ming Zhang, Yingqi Chen, Zhenyu Yao, Xiangbo Meng, Xinluan Wang, Ling Qin, Yuxiao Lai. Preclinical evaluation of acute systemic toxicity of magnesium incorporated poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) porous scaffolds by three-dimensional printing [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2021, 2(3): 272-284. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||