Biomaterials Translational ›› 2022, Vol. 3 ›› Issue (1): 24-30.doi: 10.12336/biomatertransl.2022.01.004
• REVIEW • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xuechen Zhang1, Ana Justo Caetano1, Paul T. Sharpe1,2,*( ), Ana Angelova Volponi1,*(
), Ana Angelova Volponi1,*( )
)
Received:2021-12-11
Revised:2022-03-09
Accepted:2022-03-12
Online:2022-03-28
Published:2022-03-28
Contact:
Paul T. Sharpe,paul.sharpe@kcl.ac.uk;Ana Angelova Volponi,ana.angelova@kcl.ac.uk.
About author:Paul T. Sharpe, paul.sharpe@kcl.ac.uk;Zhang, X.; Caetano, A. J.; Sharpe, P. T.; Volponi, A. A.Oral stem cells, decoding and mapping the resident cells populations. Biomater Transl. 2022, 3(1), 24-30.
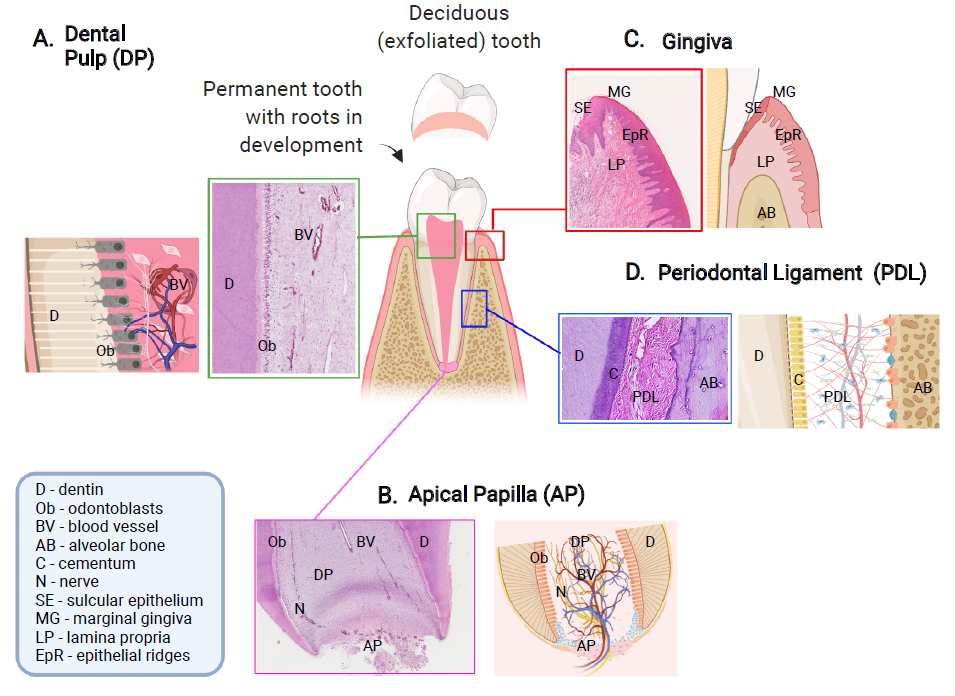
Figure 1. Teeth and their supporting tissues provide an easily accessible source of oral stem cells. These different stem cell populations reside within stem cell niches and can be obtained from: dental pulp tissue of deciduous and permanent teeth (A), apical papilla tissue (B), gingival tissue (C) and periodontal ligament (D). Created with BioRender.com.
| 1. | Nanci, A. Ten Cate’s oral histology: development, structure, and function. 8th ed.; Elsevier: St. Louis, 2012. |
| 2. |
Gronthos, S.; Mankani, M.; Brahim, J.; Robey, P. G.; Shi, S. Postnatal human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000, 97, 13625-13630.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.240309797 URL |
| 3. |
Gronthos, S.; Brahim, J.; Li, W.; Fisher, L. W.; Cherman, N.; Boyde, A.; DenBesten, P.; Robey, P. G.; Shi, S. Stem cell properties of human dental pulp stem cells. J Dent Res. 2002, 81, 531-535.
doi: 10.1177/154405910208100806 URL |
| 4. |
Jo, Y. Y.; Lee, H. J.; Kook, S. Y.; Choung, H. W.; Park, J. Y.; Chung, J. H.; Choung, Y. H.; Kim, E. S.; Yang, H. C.; Choung, P. H. Isolation and characterization of postnatal stem cells from human dental tissues. Tissue Eng. 2007, 13, 767-773.
doi: 10.1089/ten.2006.0192 URL |
| 5. |
Huang, G. T.; Gronthos, S.; Shi, S. Mesenchymal stem cells derived from dental tissues vs. those from other sources: their biology and role in regenerative medicine. J Dent Res. 2009, 88, 792-806.
doi: 10.1177/0022034509340867 URL |
| 6. |
Balic, A.; Aguila, H. L.; Caimano, M. J.; Francone, V. P.; Mina, M. Characterization of stem and progenitor cells in the dental pulp of erupted and unerupted murine molars. Bone. 2010, 46, 1639-1651.
doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2010.02.019 URL |
| 7. |
Volponi, A. A.; Pang, Y.; Sharpe, P. T. Stem cell-based biological tooth repair and regeneration. Trends Cell Biol. 2010, 20, 715-722.
doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2010.09.012 URL |
| 8. |
Volponi, A. A.; Sharpe, P. T. The tooth -- a treasure chest of stem cells. Br Dent J. 2013, 215, 353-358.
doi: 10.1038/sj.bdj.2013.959 URL |
| 9. |
Angelova Volponi, A.; Zaugg, L. K.; Neves, V.; Liu, Y.; Sharpe, P. T. Tooth repair and regeneration. Curr Oral Health Rep. 2018, 5, 295-303.
doi: 10.1007/s40496-018-0196-9 URL |
| 10. |
Yelick, P. C.; Sharpe, P. T. Tooth bioengineering and regenerative dentistry. J Dent Res. 2019, 98, 1173-1182.
doi: 10.1177/0022034519861903 URL |
| 11. |
Smith, A. J.; Lesot, H. Induction and regulation of crown dentinogenesis: embryonic events as a template for dental tissue repair? Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 2001, 12, 425-437.
doi: 10.1177/10454411010120050501 URL |
| 12. |
Smith, J. G.; Smith, A. J.; Shelton, R. M.; Cooper, P. R. Recruitment of dental pulp cells by dentine and pulp extracellular matrix components. Exp Cell Res. 2012, 318, 2397-2406.
doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2012.07.008 URL |
| 13. | Smith, A. J.; Cassidy, N.; Perry, H.; Bègue-Kirn, C.; Ruch, J. V.; Lesot, H. Reactionary dentinogenesis. Int J Dev Biol. 1995, 39, 273-280. |
| 14. |
Couve, E.; Osorio, R.; Schmachtenberg, O. Reactionary dentinogenesis and neuroimmune response in dental caries. J Dent Res. 2014, 93, 788-793.
doi: 10.1177/0022034514539507 URL |
| 15. | Teaford, M. F.; Smith, M. M.; Ferguson, M. W. J. Development, function and evolution of teeth. University Press: Cambridge, 2000. |
| 16. |
Feng, J.; Mantesso, A.; De Bari, C.; Nishiyama, A.; Sharpe, P. T. Dual origin of mesenchymal stem cells contributing to organ growth and repair. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011, 108, 6503-6508.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1015449108 URL |
| 17. |
Vidovic, I.; Banerjee, A.; Fatahi, R.; Matthews, B. G.; Dyment, N. A.; Kalajzic, I.; Mina, M. αSMA-expressing perivascular cells represent dental pulp progenitors in vivo. J Dent Res. 2017, 96, 323-330.
doi: 10.1177/0022034516678208 URL |
| 18. |
Kaukua, N.; Shahidi, M. K.; Konstantinidou, C.; Dyachuk, V.; Kaucka, M.; Furlan, A.; An, Z.; Wang, L.; Hultman, I.; Ahrlund-Richter, L.; Blom, H.; Brismar, H.; Lopes, N. A.; Pachnis, V.; Suter, U.; Clevers, H.; Thesleff, I.; Sharpe, P.; Ernfors, P.; Fried, K.; Adameyko, I. Glial origin of mesenchymal stem cells in a tooth model system. Nature. 2014, 513, 551-554.
doi: 10.1038/nature13536 URL |
| 19. |
Miura, M.; Gronthos, S.; Zhao, M.; Lu, B.; Fisher, L. W.; Robey, P. G.; Shi, S. SHED: stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003, 100, 5807-5812.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0937635100 URL |
| 20. |
Shi, S.; Bartold, P. M.; Miura, M.; Seo, B. M.; Robey, P. G.; Gronthos, S. The efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells to regenerate and repair dental structures. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2005, 8, 191-199.
doi: 10.1111/ocr.2005.8.issue-3 URL |
| 21. |
Sakai, V. T.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, Z.; Neiva, K. G.; Machado, M. A.; Shi, S.; Santos, C. F.; Nör, J. E. SHED differentiate into functional odontoblasts and endothelium. J Dent Res. 2010, 89, 791-796.
doi: 10.1177/0022034510368647 URL |
| 22. |
Cordeiro, M. M.; Dong, Z.; Kaneko, T.; Zhang, Z.; Miyazawa, M.; Shi, S.; Smith, A. J.; Nör, J. E. Dental pulp tissue engineering with stem cells from exfoliated deciduous teeth. J Endod. 2008, 34, 962-969.
doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2008.04.009 URL |
| 23. |
Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Sun, Z.; Wang, X.; Yang, H.; Shi, S.; Wang, S. Stem cells from human-exfoliated deciduous teeth can differentiate into dopaminergic neuron-like cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2010, 19, 1375-1383.
doi: 10.1089/scd.2009.0258 URL |
| 24. |
Nakamura, S.; Yamada, Y.; Katagiri, W.; Sugito, T.; Ito, K.; Ueda, M. Stem cell proliferation pathways comparison between human exfoliated deciduous teeth and dental pulp stem cells by gene expression profile from promising dental pulp. J Endod. 2009, 35, 1536-1542.
doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2009.07.024 URL |
| 25. |
Laing, A. G.; Fanelli, G.; Ramirez-Valdez, A.; Lechler, R. I.; Lombardi, G.; Sharpe, P. T. Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit T-cell function through conserved induction of cellular stress. PLoS One. 2019, 14, e0213170.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0213170 URL |
| 26. |
Laing, A. G.; Riffo-Vasquez, Y.; Sharif-Paghaleh, E.; Lombardi, G.; Sharpe, P. T. Immune modulation by apoptotic dental pulp stem cells in vivo. Immunotherapy. 2018, 10, 201-211.
doi: 10.2217/imt-2017-0117 URL |
| 27. |
Gazarian, K. G.; Ramírez-García, L. R. Human deciduous teeth stem cells (SHED) display neural crest signature characters. PLoS One. 2017, 12, e0170321.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0170321 URL |
| 28. |
Huang, G. T.; Sonoyama, W.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, S.; Shi, S. The hidden treasure in apical papilla: the potential role in pulp/dentin regeneration and bioroot engineering. J Endod. 2008, 34, 645-651.
doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2008.03.001 URL |
| 29. |
Sonoyama, W.; Liu, Y.; Yamaza, T.; Tuan, R. S.; Wang, S.; Shi, S.; Huang, G. T. Characterization of the apical papilla and its residing stem cells from human immature permanent teeth: a pilot study. J Endod. 2008, 34, 166-171.
doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2007.11.021 URL |
| 30. | Hilkens, P.; Bronckaers, A.; Ratajczak, J.; Gervois, P.; Wolfs, E.; Lambrichts, I. The angiogenic potential of DPSCs and SCAPs in an in vivo model of dental pulp regeneration. Stem Cells Int. 2017, 2017, 2582080. |
| 31. |
Liu, C.; Xiong, H.; Chen, K.; Huang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Yin, X. Long-term exposure to pro-inflammatory cytokines inhibits the osteogenic/dentinogenic differentiation of stem cells from the apical papilla. Int Endod J. 2016, 49, 950-959.
doi: 10.1111/iej.2016.49.issue-10 URL |
| 32. | Chen, H.; Fu, H.; Wu, X.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, S.; Hu, H.; Liao, Y.; Wang, T.; Yang, Y.; Chen, G.; Li, Z.; Tian, W. Regeneration of pulpo-dentinal-like complex by a group of unique multipotent CD24a(+) stem cells. Sci Adv. 2020, 6, eaay1514. |
| 33. |
Nada, O. A.; El Backly, R. M. Stem cells from the apical papilla (SCAP) as a tool for endogenous tissue regeneration. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2018, 6, 103.
doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2018.00103 URL |
| 34. |
Jeon, B. G.; Kang, E. J.; Kumar, B. M.; Maeng, G. H.; Ock, S. A.; Kwack, D. O.; Park, B. W.; Rho, G. J. Comparative analysis of telomere length, telomerase and reverse transcriptase activity in human dental stem cells. Cell Transplant. 2011, 20, 1693-1705.
doi: 10.3727/096368911X565001 URL |
| 35. |
Volponi, A. A.; Gentleman, E.; Fatscher, R.; Pang, Y. W.; Gentleman, M. M.; Sharpe, P. T. Composition of mineral produced by dental mesenchymal stem cells. J Dent Res. 2015, 94, 1568-1574.
doi: 10.1177/0022034515599765 URL |
| 36. |
Bakopoulou, A.; Kritis, A.; Andreadis, D.; Papachristou, E.; Leyhausen, G.; Koidis, P.; Geurtsen, W.; Tsiftsoglou, A. Angiogenic potential and secretome of human apical papilla mesenchymal stem cells in various stress microenvironments. Stem Cells Dev. 2015, 24, 2496-2512.
doi: 10.1089/scd.2015.0197 URL |
| 37. |
Yu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, Y.; Ge, L. Profiling the secretome of human stem cells from dental apical papilla. Stem Cells Dev. 2016, 25, 499-508.
doi: 10.1089/scd.2015.0298 URL |
| 38. |
Diogenes, A.; Hargreaves, K. M. Microbial modulation of stem cells and future directions in regenerative endodontics. J Endod. 2017, 43, S95-S101.
doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2017.07.012 URL |
| 39. |
Yi, B.; Ding, T.; Jiang, S.; Gong, T.; Chopra, H.; Sha, O.; Dissanayaka, W. L.; Ge, S.; Zhang, C. Conversion of stem cells from apical papilla into endothelial cells by small molecules and growth factors. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021, 12, 266.
doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02350-5 URL |
| 40. | Pereira, D.; Sequeira, I. A scarless healing tale: comparing homeostasis and wound healing of oral mucosa with skin and oesophagus. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021, 9, 682143. |
| 41. | Lindhe, J.; Lang, N. P.; Karring, T. Clinical periodontology and implant dentistry. 5th ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: 2008. |
| 42. |
Zhang, Q.; Shi, S.; Liu, Y.; Uyanne, J.; Shi, Y.; Shi, S.; Le, A. D. Mesenchymal stem cells derived from human gingiva are capable of immunomodulatory functions and ameliorate inflammation-related tissue destruction in experimental colitis. J Immunol. 2009, 183, 7787-7798.
doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0902318 URL |
| 43. |
Yang, H.; Gao, L. N.; An, Y.; Hu, C. H.; Jin, F.; Zhou, J.; Jin, Y.; Chen, F. M. Comparison of mesenchymal stem cells derived from gingival tissue and periodontal ligament in different incubation conditions. Biomaterials. 2013, 34, 7033-7047.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.05.025 URL |
| 44. |
Nakamura, T.; Inatomi, T.; Sotozono, C.; Amemiya, T.; Kanamura, N.; Kinoshita, S. Transplantation of cultivated autologous oral mucosal epithelial cells in patients with severe ocular surface disorders. Br J Ophthalmol. 2004, 88, 1280-1284.
doi: 10.1136/bjo.2003.038497 URL |
| 45. |
Nakamura, T.; Takeda, K.; Inatomi, T.; Sotozono, C.; Kinoshita, S. Long-term results of autologous cultivated oral mucosal epithelial transplantation in the scar phase of severe ocular surface disorders. Br J Ophthalmol. 2011, 95, 942-946.
doi: 10.1136/bjo.2010.188714 URL |
| 46. |
Nagata, M.; Chu, A. K. Y.; Ono, N.; Welch, J. D.; Ono, W. Single-cell transcriptomic analysis reveals developmental relationships and specific markers of mouse periodontium cellular subsets. Front Dent Med. 2021, 2, 679937.
doi: 10.3389/fdmed.2021.679937 URL |
| 47. |
Wada, N.; Menicanin, D.; Shi, S.; Bartold, P. M.; Gronthos, S. Immunomodulatory properties of human periodontal ligament stem cells. J Cell Physiol. 2009, 219, 667-676.
doi: 10.1002/jcp.v219:3 URL |
| 48. | Zhao, J.; Volponi, A. A.; Caetano, A.; Sharpe, P. T. Mesenchymal stem cells in teeth. In Encyclopedia of Bone Biology, Elsevier: 2020; pp 109-118. |
| 49. |
Iwasaki, K.; Komaki, M.; Yokoyama, N.; Tanaka, Y.; Taki, A.; Kimura, Y.; Takeda, M.; Oda, S.; Izumi, Y.; Morita, I. Periodontal ligament stem cells possess the characteristics of pericytes. J Periodontol. 2013, 84, 1425-1433.
doi: 10.1902/jop.2012.120547 URL |
| 50. |
Caetano, A. J.; Yianni, V.; Volponi, A.; Booth, V.; D’Agostino, E. M.; Sharpe, P. Defining human mesenchymal and epithelial heterogeneity in response to oral inflammatory disease. eLife. 2021, 10, e62810.
doi: 10.7554/eLife.62810 URL |
| 51. | Human cell atlas. https://www.humancellatlas.org/. Access March 1. 2022. |
| 52. |
An, Z.; Sabalic, M.; Bloomquist, R. F.; Fowler, T. E.; Streelman, T.; Sharpe, P. T. A quiescent cell population replenishes mesenchymal stem cells to drive accelerated growth in mouse incisors. Nat Commun. 2018, 9, 378.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02785-6 URL |
| 53. |
An, Z.; Akily, B.; Sabalic, M.; Zong, G.; Chai, Y.; Sharpe, P. T. Regulation of mesenchymal stem to transit-amplifying cell transition in the continuously growing mouse incisor. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 3102-3111.
doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.05.001 URL |
| 54. |
Seidel, K.; Marangoni, P.; Tang, C.; Houshmand, B.; Du, W.; Maas, R. L.; Murray, S.; Oldham, M. C.; Klein, O. D. Resolving stem and progenitor cells in the adult mouse incisor through gene co-expression analysis. eLife. 2017, 6, e24712.
doi: 10.7554/eLife.24712 URL |
| 55. |
Krivanek, J.; Soldatov, R. A.; Kastriti, M. E.; Chontorotzea, T.; Herdina, A. N.; Petersen, J.; Szarowska, B.; Landova, M.; Matejova, V. K.; Holla, L. I.; Kuchler, U.; Zdrilic, I. V.; Vijaykumar, A.; Balic, A.; Marangoni, P.; Klein, O. D.; Neves, V. C. M.; Yianni, V.; Sharpe, P. T.; Harkany, T.; Metscher, B. D.; Bajénoff, M.; Mina, M.; Fried, K.; Kharchenko, P. V.; Adameyko, I. Dental cell type atlas reveals stem and differentiated cell types in mouse and human teeth. Nat Commun. 2020, 11, 4816.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18512-7 URL |
| 56. | Yu, T.; Volponi, A. A.; Babb, R.; An, Z.; Sharpe, P. T. Stem cells in tooth development, growth, repair, and regeneration. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2015, 115, 187-212. |
| 57. |
Zhao, J.; Faure, L.; Adameyko, I.; Sharpe, P. T. Stem cell contributions to cementoblast differentiation in healthy periodontal ligament and periodontitis. Stem Cells. 2021, 39, 92-102.
doi: 10.1002/stem.3288 URL |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||