Biomaterials Translational ›› 2020, Vol. 1 ›› Issue (1): 58-68.doi: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.2096-112X.2020.01.006
• REVIEW • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xing Yang1,2, Yuanyuan Li3, Xujie Liu4, Wei He5, Qianli Huang6, Qingling Feng2,*(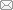 )
)
Received:2020-03-16
Revised:2020-06-30
Accepted:2020-08-21
Online:2020-12-28
Published:2020-12-28
Contact:
Qingling Feng
E-mail:biomater@mail.tsinghua.edu.cn
Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; He, W.; Huang, Q.; Feng, Q. Nanoparticles and their effects on differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Biomater Transl. 2020, 1(1), 58-68.
Figure 2. Schematic illustration of osteogenic stimulation of MSCs by HA NPs. ALP: alkaline phosphatase; HA NPs: hydroxyapatite nanoparticles; MSCs: mesenchymal stem cells; OCN: osteocalcin; OPN: osteopontin; Runx2:runt-related transcription factor 2.
| Nanoparticle | Chemical composition | Size (nm) | Shape | Surface coating | Cytotoxicity | Application and results | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydroxyapatite NPs | Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2 | Diameter: ~20; length: ~50, width: ~8; length: ~100, width: ~43; length: ~150, width: ~23; length: ~200, width: ~20 | Nanosphere, nanorod | Without | Size-, dose-dependent cytotoxicity to MSCs | Promoted proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of MSCs | |
| Silica NPs | SiO2 | 50, 90, 110, 200, 400 | nanosphere | Without | A general lack of cytotoxicity to MSCs | Transiently enhanced osteogenic protein expression in hMSCs; Released silicon ions to stimulate the osteogenic differentiation of hMSCs | |
| Calcium carbonate NPs | CaCO3 | Length: ~240, width: ~90 | Nanorod | Poly(acrylic acid) | Showed no cytotoxicity to osteoblasts at concentrations of 1-1000 μg/mL | Enhanced proliferation and expression of osteoblast-related genes | |
| Silver NPs | Ag | 10, 20, 30 | Nanosphere | Poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) | Time-, dose-dependent cytotoxicity to MSCs | Did not influence the osteogenic differentiation of MSCs or osteoblasts |
Table 1 Various nanoparticles used in osteogenic differentiation of MSCs
| Nanoparticle | Chemical composition | Size (nm) | Shape | Surface coating | Cytotoxicity | Application and results | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydroxyapatite NPs | Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2 | Diameter: ~20; length: ~50, width: ~8; length: ~100, width: ~43; length: ~150, width: ~23; length: ~200, width: ~20 | Nanosphere, nanorod | Without | Size-, dose-dependent cytotoxicity to MSCs | Promoted proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of MSCs | |
| Silica NPs | SiO2 | 50, 90, 110, 200, 400 | nanosphere | Without | A general lack of cytotoxicity to MSCs | Transiently enhanced osteogenic protein expression in hMSCs; Released silicon ions to stimulate the osteogenic differentiation of hMSCs | |
| Calcium carbonate NPs | CaCO3 | Length: ~240, width: ~90 | Nanorod | Poly(acrylic acid) | Showed no cytotoxicity to osteoblasts at concentrations of 1-1000 μg/mL | Enhanced proliferation and expression of osteoblast-related genes | |
| Silver NPs | Ag | 10, 20, 30 | Nanosphere | Poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) | Time-, dose-dependent cytotoxicity to MSCs | Did not influence the osteogenic differentiation of MSCs or osteoblasts |
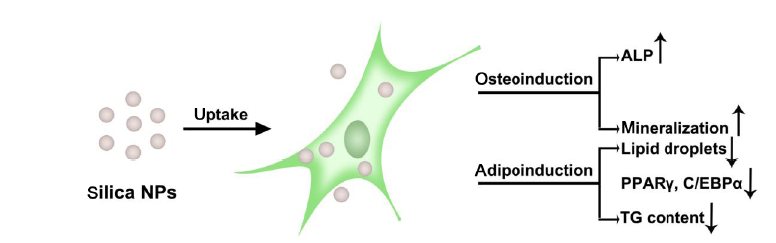
Figure 3. Schematic illustration of stimulation of osteogenesis and inhibition of adipogenesis of MSCs by silica NPs. ALP: alkaline phosphatase; C/EBPα: CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha; MSCs: mesenchymal stem cells; NPs: nanoparticles; PPARγ: peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma; TG: triglyceride.
| 1. |
Kabir, W.; Di Bella, C.; Jo, I.; Gould, D.; Choong, P. F. M. Human stem cell based tissue engineering for in vivo cartilage repair: a systematic review. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2020. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEB.2020.0155.
doi: 10.1089/ten.TEB.2020.0168 URL pmid: 33086984 |
| 2. |
Tsiapalis, D.; O’Driscoll, L. Mesenchymal stem cell derived extracellular vesicles for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine applications. Cells. 2020,9, 991.
doi: 10.3390/cells9040991 URL |
| 3. |
Macrin, D.; Joseph, J. P.; Pillai, A. A.; Devi, A. Eminent sources of adult mesenchymal stem cells and their therapeutic imminence. Stem Cell Rev ReP. 2017,13, 741-756.
doi: 10.1007/s12015-017-9759-8 URL pmid: 28812219 |
| 4. |
Maqsood, M.; Kang, M.; Wu, X.; Chen, J.; Teng, L.; Qiu, L. Adult mesenchymal stem cells and their exosomes: Sources, characteristics, and application in regenerative medicine. Life Sci. 2020,256, 118002.
doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118002 URL pmid: 32585248 |
| 5. |
Mushahary, D.; Spittler, A.; Kasper, C.; Weber, V.; Charwat, V. Isolation, cultivation, and characterization of human mesenchymal stem cells. Cytometry A. 2018,93, 19-31.
doi: 10.1002/cyto.a.23242 URL pmid: 29072818 |
| 6. |
Amjadi-Moheb, F.; Akhavan-Niaki, H. Wnt signaling pathway in osteoporosis: Epigenetic regulation, interaction with other signaling pathways, and therapeutic promises. J Cell Physiol. 2019. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28207.
doi: 10.1002/jcp.30128 URL pmid: 33305825 |
| 7. |
Pakvasa, M.; Alverdy, A.; Mostafa, S.; Wang, E.; Fu, L.; Li, A.; Oliveira, L.; Athiviraham, A.; Lee, M. J.; Wolf, J. M.; He, T. C.; Ameer, G. A.; Reid, R. R. Neural EGF-like protein 1 (NELL-1): Signaling crosstalk in mesenchymal stem cells and applications in regenerative medicine. Genes Dis. 2017,4, 127-137.
doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2017.07.006 URL pmid: 29276737 |
| 8. |
Wang, C.; Shan, S.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Hu, G.; Dai, K.; Li, Q.; Zhang, X. Mechanical stimulation promote the osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells through epigenetic regulation of Sonic Hedgehog. Exp Cell Res. 2017,352, 346-356.
doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2017.02.021 URL pmid: 28215635 |
| 9. |
Gomathi, K.; Akshaya, N.; Srinaath, N.; Moorthi, A.; Selvamurugan, N. Regulation of Runx2 by post-translational modifications in osteoblast differentiation. Life Sci. 2020,245, 117389.
URL pmid: 32007573 |
| 10. |
Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, R.; Feng, Q. Incorporation of silica nanoparticles to PLGA electrospun fibers for osteogenic differentiation of human osteoblast-like cells. Regen Biomater. 2018,5, 229-238.
doi: 10.1093/rb/rby014 URL pmid: 30094062 |
| 11. |
Zan, X.; Sitasuwan, P.; Feng, S.; Wang, Q. Effect of roughness on in situ biomineralized CaP-collagen coating on the osteogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells. Langmuir. 2016,32, 1808-1817.
URL pmid: 26795271 |
| 12. |
Carvalho, M. S.; Cabral, J. M.; da Silva, C. L.; Vashishth, D. Synergistic effect of extracellularly supplemented osteopontin and osteocalcin on stem cell proliferation, osteogenic differentiation, and angiogenic properties. J Cell Biochem. 2019,120, 6555-6569.
doi: 10.1002/jcb.27948 URL pmid: 30362184 |
| 13. |
Li, Y.; Jin, D.; Xie, W.; Wen, L.; Chen, W.; Xu, J.; Ding, J.; Ren, D. PPAR-γ and Wnt regulate the differentiation of MSCs into adipocytes and osteoblasts respectively. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018,13, 185-192.
doi: 10.2174/1574888X12666171012141908 URL pmid: 29034841 |
| 14. |
Smith, A.; Yu, X.; Yin, L. Diazinon exposure activated transcriptional factors CCAAT-enhancer-binding proteins α (C/EBPα) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) and induced adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2018,150, 48-58.
doi: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2018.07.003 URL pmid: 30195387 |
| 15. |
Ghadge, A. A.; Khaire, A. A.; Kuvalekar, A. A. Adiponectin: A potential therapeutic target for metabolic syndrome. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2018,39, 151-158.
doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2018.01.004 URL pmid: 29395659 |
| 16. |
Tautzenberger, A.; Kovtun, A.; Ignatius, A. Nanoparticles and their potential for application in bone. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012,7, 4545-4557.
doi: 10.2147/IJN.S34127 URL pmid: 22923992 |
| 17. |
Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Khan, I. Nanoparticles: Properties, applications and toxicities. Arab J Chem. 2019,12, 908-931.
doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2017.05.011 URL |
| 18. |
Li, Y.; Li, N.; Pan, W.; Yu, Z.; Yang, L.; Tang, B. Hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles with tunable structures for controlled drug delivery. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017,9, 2123-2129.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.6b13876 URL pmid: 28004570 |
| 19. |
Epple, M.; Ganesan, K.; Heumann, R.; Klesing, J.; Kovtun, A.; Neumann, S.; Sokolova, V. Application of calcium phosphate nanoparticles in biomedicine. J Mater Chem. 2010,20, 18-23.
doi: 10.1039/B910885H URL |
| 20. |
Surmeneva, M.; Lapanje, A.; Chudinova, E.; Ivanova, A.; Koptyug, A.; Loza, K.; Prymak, O.; Epple, M.; Ennen-Roth, F.; Ulbricht, M.; Rijavec, T.; Surmenev, R. Decreased bacterial colonization of additively manufactured Ti6Al4V metallic scaffolds with immobilized silver and calcium phosphate nanoparticles. Appl Surf Sci. 2019,480, 822-829.
doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.03.003 URL |
| 21. |
Chen, W.; Tian, B.; Lei, Y.; Ke, Q. F.; Zhu, Z. A.; Guo, Y. P. Hydroxyapatite coatings with oriented nanoplate and nanorod arrays: Fabrication, morphology, cytocompatibility and osteogenic differentiation. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016,67, 395-408.
doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2016.04.106 URL pmid: 27287136 |
| 22. |
Li, J.; Li, J. J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Kawazoe, N.; Chen, G. Gold nanoparticle size and shape influence on osteogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells. Nanoscale. 2016,8, 7992-8007.
URL pmid: 27010117 |
| 23. |
Li, J.; Mao, H.; Kawazoe, N.; Chen, G. Insight into the interactions between nanoparticles and cells. Biomater Sci. 2017,5, 173-189.
doi: 10.1039/c6bm00714g URL pmid: 27935611 |
| 24. |
Li, J. J.; Kawazoe, N.; Chen, G. Gold nanoparticles with different charge and moiety induce differential cell response on mesenchymal stem cell osteogenesis. Biomaterials. 2015,54, 226-236.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.03.001 URL pmid: 25858865 |
| 25. |
Huang, Y.; Zhou, G.; Zheng, L.; Liu, H.; Niu, X.; Fan, Y. Micro-/nano- sized hydroxyapatite directs differentiation of rat bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells towards an osteoblast lineage. Nanoscale. 2012,4, 2484-2490.
doi: 10.1039/c2nr12072k URL pmid: 22371072 |
| 26. |
Chen, L.; McCrate, J. M.; Lee, J. C.; Li, H. The role of surface charge on the uptake and biocompatibility of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles with osteoblast cells. Nanotechnology. 2011,22, 105708.
URL pmid: 21289408 |
| 27. |
Zhang, M.; Chen, X.; Li, C.; Shen, X. Charge-reversal nanocarriers: An emerging paradigm for smart cancer nanomedicine. J Control Release. 2020,319, 46-62.
doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.12.024 URL pmid: 31846619 |
| 28. |
Cheng, H.; Chawla, A.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jang, H. L.; Khademhosseini, A. Development of nanomaterials for bone-targeted drug delivery. Drug Discov Today. 2017,22, 1336-1350.
doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2017.04.021 URL pmid: 28487069 |
| 29. | Machado, T. R.; Leite, I. S.; Inada, N. M.; Li, M. S.; da Silva, J. S.; Andrés, J.; Beltrán-Mir, H.; Cordoncillo, E.; Longo, E. Designing biocompatible and multicolor fluorescent hydroxyapatite nanoparticles for cell-imaging applications. Mater Today Chem. 2019,14, 100211. |
| 30. |
Wang, C.; Jeong, K. J.; Kim, J.; Kang, S. W.; Kang, J.; Han, I. H.; Lee, I. W.; Oh, S. J.; Lee, J. Emission-tunable probes using terbium(III)-doped self-activated luminescent hydroxyapatite for in vitro bioimaging. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2021,581, 21-30.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.07.083 URL pmid: 32768732 |
| 31. |
Ghorbani, F.; Nojehdehian, H.; Zamanian, A. Physicochemical and mechanical properties of freeze cast hydroxyapatite-gelatin scaffolds with dexamethasone loaded PLGA microspheres for hard tissue engineering applications. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016,69, 208-220.
doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2016.06.079 URL pmid: 27612706 |
| 32. |
Cheng, A.; Schwartz, Z.; Kahn, A.; Li, X.; Shao, Z.; Sun, M.; Ao, Y.; Boyan, B. D.; Chen, H. Advances in porous scaffold design for bone and cartilage tissue engineering and regeneration. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2019,25, 14-29.
doi: 10.1089/ten.TEB.2018.0119 URL pmid: 30079807 |
| 33. |
Müller, K. H.; Motskin, M.; Philpott, A. J.; Routh, A. F.; Shanahan, C. M.; Duer, M. J.; Skepper, J. N. The effect of particle agglomeration on the formation of a surface-connected compartment induced by hydroxyapatite nanoparticles in human monocyte-derived macrophages. Biomaterials. 2014,35, 1074-1088.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.10.041 URL pmid: 24183166 |
| 34. |
Motskin, M.; Wright, D. M.; Muller, K.; Kyle, N.; Gard, T. G.; Porter, A. E.; Skepper, J. N. Hydroxyapatite nano and microparticles: correlation of particle properties with cytotoxicity and biostability. Biomaterials. 2009,30, 3307-3317.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2009.02.044 URL pmid: 19304317 |
| 35. |
Meena, R.; Kesari, K. K.; Rani, M.; Paulraj, R. Effects of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles on proliferation and apoptosis of human breast cancer cells (MCF-7). J Nanopart Res. 2012,14, 712.
doi: 10.1007/s11051-011-0712-5 URL |
| 36. |
Zhao, X.; Ng, S.; Heng, B. C.; Guo, J.; Ma, L.; Tan, T. T.; Ng, K. W.; Loo, S. C. Cytotoxicity of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles is shape and cell dependent. Arch Toxicol. 2013,87, 1037-1052.
doi: 10.1007/s00204-012-0827-1 URL pmid: 22415765 |
| 37. |
Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, R.; Feng, Q. In vitro uptake of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles and their effect on osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Int. 2018,2018, 2036176.
doi: 10.1155/2018/2036176 URL pmid: 30018644 |
| 38. |
Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Huang, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhang, R.; Feng, Q. The effect of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles on adipogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2018,106, 1822-1831.
doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.36378 URL pmid: 29468853 |
| 39. |
Remya, N. S.; Syama, S.; Gayathri, V.; Varma, H. K.; Mohanan, P. V. An in vitro study on the interaction of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells for assessing the toxicological behaviour. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2014,117, 389-397.
doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2014.02.004 URL pmid: 24675277 |
| 40. |
Liu, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, G.; Xu, X.; Tang, R. Calcium phosphate nanoparticles primarily induce cell necrosis through lysosomal rupture: the origination of material cytotoxicity. J Mater Chem B. 2014,2, 3480-3489.
doi: 10.1039/c4tb00056k URL pmid: 32261468 |
| 41. |
Liu, Y.; Wang, G.; Cai, Y.; Ji, H.; Zhou, G.; Zhao, X.; Tang, R.; Zhang, M. In vitro effects of nanophase hydroxyapatite particles on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2009,90, 1083-1091.
doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.32192 URL pmid: 18671263 |
| 42. |
Wang, J.; Yang, G.; Wang, Y.; Du, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Mao, C.; Zhang, S. Chimeric protein template-induced shape control of bone mineral nanoparticles and its impact on mesenchymal stem cell fate. Biomacromolecules. 2015,16, 1987-1996.
doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.5b00419 URL pmid: 26079683 |
| 43. |
Zakaria, S. M.; Sharif Zein, S. H.; Othman, M. R.; Yang, F.; Jansen, J. A. Nanophase hydroxyapatite as a biomaterial in advanced hard tissue engineering: a review. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2013,19, 431-441.
doi: 10.1089/ten.TEB.2012.0624 URL pmid: 23557483 |
| 44. |
Lock, J.; Liu, H. Nanomaterials enhance osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells similar to a short peptide of BMP-7. Int J Nanomedicine. 2011,6, 2769-2777.
doi: 10.2147/IJN.S24493 URL pmid: 22114505 |
| 45. | Yao, X.; Ji, H. J.; Liu, Y. K.; Cai, Y.; Zhao, X.; Tang, R.; Zhang, M. Hydroxyapatite conditioned medium enhance the osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Minerva Biotecnologica. 2010,22, 9-15. |
| 46. |
Habibovic, P.; Barralet, J. E. Bioinorganics and biomaterials: bone repair. Acta Biomater. 2011,7, 3013-3026.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2011.03.027 URL pmid: 21453799 |
| 47. |
Agell, N.; Bachs, O.; Rocamora, N.; Villalonga, P. Modulation of the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway by Ca(2+), and calmodulin. Cell Signal. 2002,14, 649-654.
doi: 10.1016/s0898-6568(02)00007-4 URL pmid: 12020764 |
| 48. |
Liu, Y. K.; Lu, Q. Z.; Pei, R.; Ji, H. J.; Zhou, G. S.; Zhao, X. L.; Tang, R. K.; Zhang, M. The effect of extracellular calcium and inorganic phosphate on the growth and osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in vitro: implication for bone tissue engineering. Biomed Mater. 2009,4, 025004.
doi: 10.1088/1748-6041/4/2/025004 URL pmid: 19208939 |
| 49. |
Kohn, D. H.; Sarmadi, M.; Helman, J. I.; Krebsbach, P. H. Effects of pH on human bone marrow stromal cells in vitro: implications for tissue engineering of bone. J Biomed Mater Res. 2002,60, 292-299.
doi: 10.1002/jbm.10050 URL pmid: 11857436 |
| 50. |
Iijima, K.; Suzuki, R.; Iizuka, A.; Ueno-Yokohata, H.; Kiyokawa, N.; Hashizume, M. Surface functionalization of tissue culture polystyrene plates with hydroxyapatite under body fluid conditions and its effect on differentiation behaviors of mesenchymal stem cells. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2016,147, 351-359.
doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2016.08.020 URL pmid: 27559995 |
| 51. |
Lee, J. S.; Kim, T. W.; Park, S.; Kim, B. S.; Im, G. I.; Cho, K. S.; Kim, C. S. Reduction of adipose tissue formation by the controlled release of BMP-2 using a hydroxyapatite-coated collagen carrier system for sinus-augmentation/extraction-socket grafting. Materials (Basel). 2015,8, 7634-7649.
doi: 10.3390/ma8115411 URL |
| 52. |
Liu, H.; Xu, G. W.; Wang, Y. F.; Zhao, H. S.; Xiong, S.; Wu, Y.; Heng, B. C.; An, C. R.; Zhu, G. H.; Xie, D. H. Composite scaffolds of nano-hydroxyapatite and silk fibroin enhance mesenchymal stem cell-based bone regeneration via the interleukin 1 alpha autocrine/paracrine signaling looP. Biomaterials. 2015,49, 103-112.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.01.017 URL pmid: 25725559 |
| 53. |
Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Lü, X. An integrated study of natural hydroxyapatite-induced osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells using transcriptomics, proteomics and microRNA analyses. Biomed Mater. 2014,9, 045005.
doi: 10.1088/1748-6041/9/4/045005 URL pmid: 24946014 |
| 54. |
Kozielski, K. L.; Rui, Y.; Green, J. J. Non-viral nucleic acid containing nanoparticles as cancer therapeutics. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2016,13, 1475-1487.
doi: 10.1080/17425247.2016.1190707 URL pmid: 27248202 |
| 55. |
Li, Y.; Hei, M.; Xu, Y.; Qian, X.; Zhu, W. Ammonium salt modified mesoporous silica nanoparticles for dual intracellular-responsive gene delivery. Int J Pharm. 2016,511, 689-702.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2016.07.029 URL pmid: 27426108 |
| 56. |
Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fu, A.; Shi, W.; Yeo, D.; Luo, K. Q.; Ow, H.; Xu, C. Tracking mesenchymal stem cell tumor-homing using fluorescent silica nanoparticles. J Mater Chem B. 2015,3, 1245-1253.
doi: 10.1039/c4tb01452a URL pmid: 32264475 |
| 57. |
Tang, L.; Cheng, J. Nonporous Silica Nanoparticles for Nanomedicine Application. Nano Today. 2013,8, 290-312.
doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2013.04.007 URL pmid: 23997809 |
| 58. |
Fruijtier-Pölloth, C. The toxicological mode of action and the safety of synthetic amorphous silica-a nanostructured material. Toxicology. 2012,294, 61-79.
doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2012.02.001 URL pmid: 22349641 |
| 59. |
Napierska, D.; Thomassen, L. C.; Lison, D.; Martens, J. A.; Hoet, P. H. The nanosilica hazard: another variable entity. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2010,7, 39.
doi: 10.1186/1743-8977-7-39 URL pmid: 21126379 |
| 60. |
Yu, T.; Malugin, A.; Ghandehari, H. Impact of silica nanoparticle design on cellular toxicity and hemolytic activity. ACS Nano. 2011,5, 5717-5728.
doi: 10.1021/nn2013904 URL pmid: 21630682 |
| 61. |
Yu, T.; Greish, K.; McGill, L. D.; Ray, A.; Ghandehari, H. Influence of geometry, porosity, and surface characteristics of silica nanoparticles on acute toxicity: their vasculature effect and tolerance threshold. ACS Nano. 2012,6, 2289-2301.
doi: 10.1021/nn2043803 URL pmid: 22364198 |
| 62. |
Chang, J. S.; Chang, K. L.; Hwang, D. F.; Kong, Z. L. In vitro cytotoxicitiy of silica nanoparticles at high concentrations strongly depends on the metabolic activity type of the cell line. Environ Sci Technol. 2007,41, 2064-2068.
doi: 10.1021/es062347t URL pmid: 17410806 |
| 63. |
Kim, I. Y.; Joachim, E.; Choi, H.; Kim, K. Toxicity of silica nanoparticles depends on size, dose, and cell type. Nanomedicine. 2015,11, 1407-1416.
doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2015.03.004 URL pmid: 25819884 |
| 64. |
Ema, M.; Kobayashi, N.; Naya, M.; Hanai, S.; Nakanishi, J. Reproductive and developmental toxicity studies of manufactured nanomaterials. Reprod Toxicol. 2010,30, 343-352.
doi: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2010.06.002 URL pmid: 20600821 |
| 65. |
Eom, H. J.; Choi, J. Oxidative stress of silica nanoparticles in human bronchial epithelial cell, Beas-2B. Toxicol In Vitro. 2009,23, 1326-1332.
doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2009.07.010 URL pmid: 19602432 |
| 66. |
Marquis, B. J.; Love, S. A.; Braun, K. L.; Haynes, C. L. Analytical methods to assess nanoparticle toxicity. Analyst. 2009,134, 425-439.
doi: 10.1039/b818082b URL pmid: 19238274 |
| 67. |
Ha, S. W.; Sikorski, J. A.; Weitzmann, M. N.; Beck, G. R. Jr. Bio-active engineered 50 nm silica nanoparticles with bone anabolic activity: therapeutic index, effective concentration, and cytotoxicity profile in vitro. Toxicol In Vitro. 2014,28, 354-364.
doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2013.12.001 URL pmid: 24333519 |
| 68. |
Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Huang, Q.; He, W.; Zhang, R.; Feng, Q.; Benayahu, D. The stimulatory effect of silica nanoparticles on osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Biomed Mater. 2016,12, 015001.
doi: 10.1088/1748-605X/12/1/015001 URL pmid: 27910816 |
| 69. |
Shi, M.; Zhou, Y.; Shao, J.; Chen, Z.; Song, B.; Chang, J.; Wu, C.; Xiao, Y. Stimulation of osteogenesis and angiogenesis of hBMSCs by delivering Si ions and functional drug from mesoporous silica nanospheres. Acta Biomater. 2015,21, 178-189.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2015.04.019 URL pmid: 25910640 |
| 70. |
Kim, K. J.; Joe, Y. A.; Kim, M. K.; Lee, S. J.; Ryu, Y. H.; Cho, D. W.; Rhie, J. W. Silica nanoparticles increase human adipose tissue-derived stem cell proliferation through ERK1/2 activation. Int J Nanomedicine. 2015,10, 2261-2272.
doi: 10.2147/IJN.S71925 URL pmid: 25848249 |
| 71. |
Huang, D. M.; Chung, T. H.; Hung, Y.; Lu, F.; Wu, S. H.; Mou, C. Y.; Yao, M.; Chen, Y. C. Internalization of mesoporous silica nanoparticles induces transient but not sufficient osteogenic signals in human mesenchymal stem cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2008,231, 208-215.
doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2008.04.009 URL pmid: 18519141 |
| 72. |
Riggs, B. L.; Khosla, S.; Melton, L. J. 3rd. Sex steroids and the construction and conservation of the adult skeleton. Endocr Rev. 2002,23, 279-302.
doi: 10.1210/edrv.23.3.0465 URL pmid: 12050121 |
| 73. |
Beck, G. R. Jr.; Ha, S. W.; Camalier, C. E.; Yamaguchi, M.; Li, Y.; Lee, J. K.; Weitzmann, M. N. Bioactive silica-based nanoparticles stimulate bone-forming osteoblasts, suppress bone-resorbing osteoclasts, and enhance bone mineral density in vivo. Nanomedicine. 2012,8, 793-803.
doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2011.11.003 URL pmid: 22100753 |
| 74. |
Yang, W.; Yao, C.; Cui, Z.; Luo, D.; Lee, I. S.; Yao, J.; Chen, C.; Kong, X. Poly(acrylic acid)-regulated Synthesis of Rod-Like Calcium Carbonate Nanoparticles for Inducing the Osteogenic Differentiation of MC3T3-E1 Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2016,17, 639.
doi: 10.3390/ijms17050639 URL |
| 75. |
Pauksch, L.; Hartmann, S.; Rohnke, M.; Szalay, G.; Alt, V.; Schnettler, R.; Lips, K. S. Biocompatibility of silver nanoparticles and silver ions in primary human mesenchymal stem cells and osteoblasts. Acta Biomater. 2014,10, 439-449.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2013.09.037 URL pmid: 24095782 |
| 76. |
Samberg, M. E.; Loboa, E. G.; Oldenburg, S. J.; Monteiro-Riviere, N. A. Silver nanoparticles do not influence stem cell differentiation but cause minimal toxicity. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2012,7, 1197-1209.
doi: 10.2217/nnm.12.18 URL |
| 77. |
Liu, X.; He, W.; Fang, Z.; Kienzle, A.; Feng, Q. Influence of silver nanoparticles on osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2014,10, 1277-1285.
doi: 10.1166/jbn.2014.1824 URL pmid: 24804548 |
| 78. |
Schwarz, K.; Milne, D. B. Growth-promoting effects of silicon in rats. Nature. 1972,239, 333-334.
doi: 10.1038/239333a0 URL pmid: 12635226 |
| 79. |
Carlisle, E. M. Silicon: a possible factor in bone calcification. Science. 1970,167, 279-280.
doi: 10.1126/science.167.3916.279 URL pmid: 5410261 |
| 80. |
Reffitt, D. M.; Ogston, N.; Jugdaohsingh, R.; Cheung, H. F.; Evans, B. A.; Thompson, R. P.; Powell, J. J.; Hampson, G. N. Orthosilicic acid stimulates collagen type 1 synthesis and osteoblastic differentiation in human osteoblast-like cells in vitro. Bone. 2003,32, 127-135.
doi: 10.1016/s8756-3282(02)00950-x URL pmid: 12633784 |
| 81. |
Zhou, Y.; Wu, C.; Xiao, Y. The stimulation of proliferation and differentiation of periodontal ligament cells by the ionic products from Ca7Si2P2O16 bioceramics. Acta Biomater. 2012,8, 2307-2316.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2012.03.012 URL pmid: 22409874 |
| 82. |
Han, P.; Wu, C.; Xiao, Y. The effect of silicate ions on proliferation, osteogenic differentiation and cell signalling pathways (WNT and SHH) of bone marrow stromal cells. Biomater Sci. 2013,1, 379-392.
doi: 10.1039/c2bm00108j URL pmid: 32481903 |
| 83. |
Gu, H.; Guo, F.; Zhou, X.; Gong, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhai, W.; Chen, L.; Cen, L.; Yin, S.; Chang, J.; Cui, L. The stimulation of osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells by ionic products from akermanite dissolution via activation of the ERK pathway. Biomaterials. 2011,32, 7023-7033.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.06.003 URL pmid: 21705076 |
| 84. |
Li, J.; Wei, L.; Sun, J.; Guan, G. Effect of ionic products of dicalcium silicate coating on osteoblast differentiation and collagen production via TGF-β1 pathway. J Biomater Appl. 2013,27, 595-604.
doi: 10.1177/0885328211416393 URL pmid: 22071351 |
| 85. |
Titushkin, I.; Cho, M. Modulation of cellular mechanics during osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Biophys J. 2007,93, 3693-3702.
doi: 10.1529/biophysj.107.107797 URL pmid: 17675345 |
| 86. |
Son, M. J.; Kim, W. K.; Kwak, M.; Oh, K. J.; Chang, W. S.; Min, J. K.; Lee, S. C.; Song, N. W.; Bae, K. H. Silica nanoparticles inhibit brown adipocyte differentiation via regulation of p38 phosphorylation. Nanotechnology. 2015,26, 435101.
doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/26/43/435101 URL pmid: 26437254 |
| 87. |
Yang, X.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Huang, Q.; He, W.; Zhang, R.; Feng, Q.; Benayahu, D. The negative effect of silica nanoparticles on adipogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017,81, 341-348.
doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2017.07.042 URL pmid: 28887982 |
| 88. |
Rai, M.; Yadav, A.; Gade, A. Silver nanoparticles as a new generation of antimicrobials. Biotechnol Adv. 2009,27, 76-83.
doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2008.09.002 URL pmid: 18854209 |
| 89. |
Singh, R.; Shedbalkar, U. U.; Wadhwani, S. A.; Chopade, B. A. Bacteriagenic silver nanoparticles: synthesis, mechanism, and applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015,99, 4579-4593.
doi: 10.1007/s00253-015-6622-1 URL pmid: 25952110 |
| 90. | Prashob, P. K. J. Multi-functional silver nanoparticles for drug delivery: A review. Int J Curr Res Rev. 2017,9, 1-5. |
| 91. |
Hasan, A.; Waibhaw, G.; Saxena, V.; Pandey, L. M. Nano-biocomposite scaffolds of chitosan, carboxymethyl cellulose and silver nanoparticle modified cellulose nanowhiskers for bone tissue engineering applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018,111, 923-934.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.01.089 URL pmid: 29415416 |
| 92. |
Wiley, B.; Sun, Y.; Mayers, B.; Xia, Y. Shape-controlled synthesis of metal nanostructures: the case of silver. Chemistry. 2005,11, 454-463.
doi: 10.1002/chem.200400927 URL pmid: 15565727 |
| 93. |
Roh, J.; Umh, H. N.; Sim, J.; Park, S.; Yi, J.; Kim, Y. Dispersion stability of citrate- and PVP-AgNPs in biological media for cytotoxicity test. Korean J Chem Eng. 2013,30, 671-674.
doi: 10.1007/s11814-012-0172-3 URL |
| 94. |
Kalbáčová, M.; Verdánová, M.; Mravec, F.; Halasová, T.; Pekař, M. Effect of CTAB and CTAB in the presence of hyaluronan on selected human cell types. Colloids Surf Physicochem Eng Aspects. 2014,460, 204-208.
doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2013.12.048 URL |
| 95. |
Yasun, E.; Li, C.; Barut, I.; Janvier, D.; Qiu, L.; Cui, C.; Tan, W. BSA modification to reduce CTAB induced nonspecificity and cytotoxicity of aptamer-conjugated gold nanorods. Nanoscale. 2015,7, 10240-10248.
doi: 10.1039/c5nr01704a URL pmid: 25990591 |
| 96. |
Connor, E. E.; Mwamuka, J.; Gole, A.; Murphy, C. J.; Wyatt, M. D. Gold nanoparticles are taken up by human cells but do not cause acute cytotoxicity. Small. 2005,1, 325-327.
doi: 10.1002/smll.200400093 URL pmid: 17193451 |
| 97. |
Egorova, E. M.; Kaba, S. I. The effect of surfactant micellization on the cytotoxicity of silver nanoparticles stabilized with aerosol-OT. Toxicol In Vitro. 2019,57, 244-254.
doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2019.03.006 URL pmid: 30851410 |
| 98. |
He, W.; Liu, X.; Kienzle, A.; Müller, W. E.; Feng, Q. In vitro uptake of silver nanoparticles and their toxicity in human mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2016,16, 219-228.
doi: 10.1166/jnn.2016.10728 URL pmid: 27398448 |
| 99. |
Park, M. V.; Neigh, A. M.; Vermeulen, J. P.; de la Fonteyne, L. J.; Verharen, H. W.; Briedé, J. J.; van Loveren, H.; de Jong, W. H. The effect of particle size on the cytotoxicity, inflammation, developmental toxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles. Biomaterials. 2011,32, 9810-9817.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.08.085 URL pmid: 21944826 |
| 100. |
Hussain, S. M.; Hess, K. L.; Gearhart, J. M.; Geiss, K. T.; Schlager, J. J. In vitro toxicity of nanoparticles in BRL 3A rat liver cells. Toxicol In Vitro. 2005,19, 975-983.
doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2005.06.034 URL pmid: 16125895 |
| 101. |
Braydich-Stolle, L.; Hussain, S.; Schlager, J. J.; Hofmann, M. C. In vitro cytotoxicity of nanoparticles in mammalian germline stem cells. Toxicol Sci. 2005,88, 412-419.
doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfi256 URL pmid: 16014736 |
| 102. |
Greulich, C.; Diendorf, J.; Gessmann, J.; Simon, T.; Habijan, T.; Eggeler, G.; Schildhauer, T. A.; Epple, M.; Köller, M. Cell type-specific responses of peripheral blood mononuclear cells to silver nanoparticles. Acta Biomater. 2011,7, 3505-3514.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2011.05.030 URL pmid: 21651999 |
| 103. |
Sengstock, C.; Diendorf, J.; Epple, M.; Schildhauer, T. A.; Köller, M. Effect of silver nanoparticles on human mesenchymal stem cell differentiation. Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2014,5, 2058-2069.
doi: 10.3762/bjnano.5.214 URL pmid: 25551033 |
| 104. |
Qin, H.; Zhu, C.; An, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Hui, B.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. Silver nanoparticles promote osteogenic differentiation of human urine-derived stem cells at noncytotoxic concentrations. Int J Nanomedicine. 2014,9, 2469-2478.
doi: 10.2147/IJN.S59753 URL pmid: 24899804 |
| 105. |
Mahmood, M.; Li, Z.; Casciano, D.; Khodakovskaya, M. V.; Chen, T.; Karmakar, A.; Dervishi, E.; Xu, Y.; Mustafa, T.; Watanabe, F.; Fejleh, A.; Whitlow, M.; Al-Adami, M.; Ghosh, A.; Biris, A. S. Nanostructural materials increase mineralization in bone cells and affect gene expression through miRNA regulation. J Cell Mol Med. 2011,15, 2297-2306.
doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2010.01234.x URL pmid: 21143388 |
| 106. |
He, W.; Kienzle, A.; Liu, X.; Müller, W. E.; Elkhooly, T. A.; Feng, Q. In vitro effect of 30 nm silver nanoparticles on adipogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2016,12, 525-535.
doi: 10.1166/jbn.2016.2182 URL pmid: 27280250 |
| 107. |
He, W.; Kienzle, A.; Liu, X.; Müller, W. E. G.; Feng, Q. In vitro 30 nm silver nanoparticles promote chondrogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells. RSC Adv. 2015,5, 49809-49818.
doi: 10.1039/C5RA06386H URL |
| 108. |
Zhang, X. F.; Shen, W.; Gurunathan, S. Silver nanoparticle-mediated cellular responses in various cell lines: An in vitro model. Int J Mol Sci. 2016,17, 1603.
doi: 10.3390/ijms17101603 URL |
| 109. |
Riaz Ahmed, K. B.; Nagy, A. M.; Brown, R. P.; Zhang, Q.; Malghan, S. G.; Goering, P. L. Silver nanoparticles: Significance of physicochemical properties and assay interference on the interpretation of in vitro cytotoxicity studies. Toxicol In Vitro. 2017,38, 179-192.
doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2016.10.012 URL pmid: 27816503 |
| 110. | Dizaj, S. M.; Barzegar-Jalali, M.; Zarrintan, M. H.; Adibkia, K.; Lotfipour, F. Calcium carbonate nanoparticles; potential in bone and tooth disorders. Pharm Sci. 2015,20, 175-182. |
| 111. |
He, F.; Zhang, J.; Yang, F.; Zhu, J.; Tian, X.; Chen, X. In vitro degradation and cell response of calcium carbonate composite ceramic in comparison with other synthetic bone substitute materials. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2015,50, 257-265.
doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2015.02.019 URL pmid: 25746269 |
| 112. |
Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Liang, T.; Deng, Y.; Qi, X.; Jiang, H.; Wu, Y.; Gao, H. Hierarchical porous calcium carbonate microspheres as drug delivery vector. Prog Nat Sci Mater Int. 2017,27, 674-677.
doi: 10.1016/j.pnsc.2017.11.005 URL |
| 113. |
Horie, M.; Nishio, K.; Kato, H.; Endoh, S.; Fujita, K.; Nakamura, A.; Kinugasa, S.; Hagihara, Y.; Yoshida, Y.; Iwahashi, H. Evaluation of cellular influences caused by calcium carbonate nanoparticles. Chem Biol Interact. 2014,210, 64-76.
doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2013.12.013 URL pmid: 24412303 |
| 114. |
Palmqvist, N. G. M.; Nedelec, J. M.; Seisenbaeva, G. A.; Kessler, V. G. Controlling nucleation and growth of nano-CaCO(3) via CO(2) sequestration by a calcium alkoxide solution to produce nanocomposites for drug delivery applications. Acta Biomater. 2017,57, 426-434.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2017.05.006 URL pmid: 28483694 |
| 115. |
Donatan, S.; Yashchenok, A.; Khan, N.; Parakhonskiy, B.; Cocquyt, M.; Pinchasik, B. E.; Khalenkow, D.; Möhwald, H.; Konrad, M.; Skirtach, A. Loading capacity versus enzyme activity in anisotropic and spherical calcium carbonate microparticles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016,8, 14284-14292.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.6b03492 URL pmid: 27166641 |
| 116. |
Gross-Aviv, T.; Vago, R. The role of aragonite matrix surface chemistry on the chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials. 2009,30, 770-779.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2008.10.026 URL pmid: 19036431 |
| 117. |
Kong, X.; Xu, S.; Wang, X.; Cui, F.; Yao, J. Calcium carbonate microparticles used as a gene vector for delivering p53 gene into cancer cells. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2012,100, 2312-2318.
doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.34155 URL pmid: 22529011 |
| 118. |
Huang, S.; Chen, J. C.; Hsu, C. W.; Chang, W. H. Effects of nano calcium carbonate and nano calcium citrate on toxicity in ICR mice and on bone mineral density in an ovariectomized mice model. Nanotechnology. 2009,20, 375102.
URL pmid: 19706952 |
| 119. |
Vuola, J.; Göransson, H.; Böhling, T.; Asko-Seljavaara, S. Bone marrow induced osteogenesis in hydroxyapatite and calcium carbonate implants. Biomaterials. 1996,17, 1761-1766.
doi: 10.1016/0142-9612(95)00351-7 URL pmid: 8879513 |
| 120. |
Ohgushi, H.; Okumura, M.; Yoshikawa, T.; Inoue, K.; Senpuku, N.; Tamai, S.; Shors, E. C. Bone formation process in porous calcium carbonate and hydroxyapatite. J Biomed Mater Res. 1992,26, 885-895.
doi: 10.1002/jbm.820260705 URL pmid: 1607371 |
| 121. |
Sethmann, I.; Luft, C.; Kleebe, H. J. Development of phosphatized calcium carbonate biominerals as bioactive bone graft substitute materials, Part I: Incorporation of magnesium and strontium ions. J Funct Biomater. 2018,9, 69.
doi: 10.3390/jfb9040069 URL |
| 122. |
Matta, C.; Szűcs-Somogyi, C.; Kon, E.; Robinson, D.; Neufeld, T.; Altschuler, N.; Berta, A.; Hangody, L.; Veréb, Z.; Zákány, R. Osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells is enhanced by an aragonite scaffold. Differentiation. 2019,107, 24-34.
doi: 10.1016/j.diff.2019.05.002 URL pmid: 31152959 |
| 123. |
Fujihara, K.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. Guided bone regeneration membrane made of polycaprolactone/calcium carbonate composite nano-fibers. Biomaterials. 2005,26, 4139-4147.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2004.09.014 URL pmid: 15664641 |
| 124. |
Li, X.; Yang, X.; Liu, X.; He, W.; Huang, Q.; Li, S.; Feng, Q. Calcium carbonate nanoparticles promote osteogenesis compared to adipogenesis in human bone-marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Prog Nat Sci Mater Int. 2018,28, 598-608.
doi: 10.1016/j.pnsc.2018.09.004 URL |
| 125. |
Shiwaku, Y.; Tsuchiya, K.; Xiao, L.; Suzuki, O. Effect of calcium phosphate phases affecting the crosstalk between osteoblasts and osteoclasts in vitro. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2019,107, 1001-1013.
doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.36626 URL pmid: 30684383 |
| 126. |
Park, J. W.; Hanawa, T.; Chung, J. H. The relative effects of Ca and Mg ions on MSC osteogenesis in the surface modification of microrough Ti implants. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019,14, 5697-5711.
doi: 10.2147/IJN.S214363 URL pmid: 31413570 |
| [1] | Xirui Jing, Qiuyue Ding, Qinxue Wu, Weijie Su, Keda Yu, Yanlin Su, Bing Ye, Qing Gao, Tingfang Sun, Xiaodong Guo. Magnesium-based materials in orthopaedics: material properties and animal models [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2021, 2(3): 197-213. |
| [2] | Kamolrat Metavarayuth, Esteban Villarreal, Hui Wang, Qian Wang. Surface topography and free energy regulate osteogenesis of stem cells: effects of shape-controlled gold nanoparticles [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2021, 2(2): 165-173. |
| [3] | Yiqing Wang, Xiangyu Chu, Bing Wang. Recombinant adeno-associated virus-based gene therapy combined with tissue engineering for musculoskeletal regenerative medicine [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2021, 2(1): 19-29. |
| [4] | Maryam Tamaddon, Helena Gilja, Ling Wang, J. Miguel Oliveira, Xiaodan Sun, Rongwei Tan, Chaozong Liu. Osteochondral scaffolds for early treatment of cartilage defects in osteoarthritic joints: from bench to clinic [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2020, 1(1): 3-17. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||