Biomaterials Translational ›› 2020, Vol. 1 ›› Issue (1): 82-88.doi: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.2096-112X.2020.01.008
• RESEARCH ARTICLE • Previous Articles Next Articles
Fujian Zhao1, Zhen Yang2,3, Lu Liu2,3, Dafu Chen4, Longquan Shao1,*(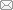 ), Xiaofeng Chen2,3,*(
), Xiaofeng Chen2,3,*( )
)
Received:2020-08-21
Revised:2020-10-26
Accepted:2020-10-30
Online:2020-12-28
Published:2020-12-28
Contact:
Longquan Shao,Xiaofeng Chen
E-mail:shaolongquan@smu.edu.cn;chenxf@scut.edu.cn
Zhao, F.; Yang, Z.; Liu, L.; Chen, D.; Shao, L.; Chen, X. Design and evaluation of a novel sub-scaffold dental implant system based on the osteoinduction of micro-nano bioactive glass. Biomater Transl. 2020, 1(1), 82-88.
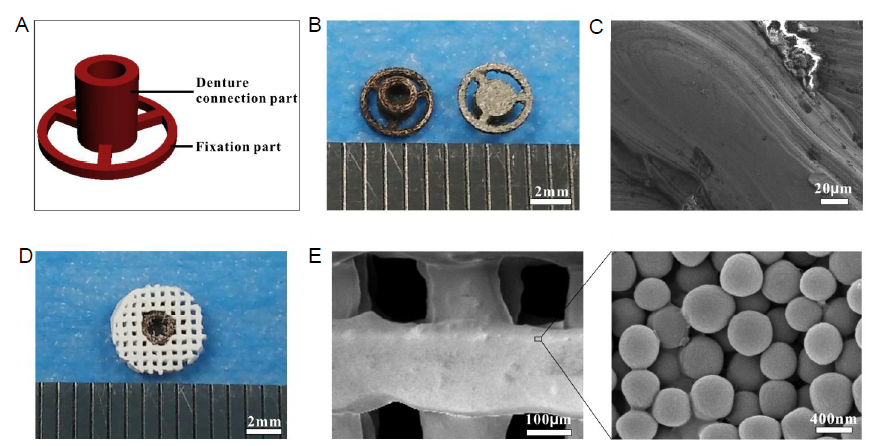
Figure 1. Composition and characterization of the SDIS. (A) A CAD model of the metal implant which consists of two parts: a denture connection part and a fixation part. (B) Digital photos of the two opposite surfaces of the metal implant, created by the SLM process. (C) SEM image of the metal implant. (D) Digital photo of the SDIS created by assembling the metal implant and MNBG scaffold together. (E) SEM image of the MNBG scaffold. Scale bars: 2 mm in B and D, 20 μm in C, 200 μm in E, 400 nm in enlarge part. CAD: computer-aided design; MNBG: micro-nano bioactive glass; SDIS: scaffold dental implant system; SEM: scanning electron microscopy; SLM: selective laser melting.
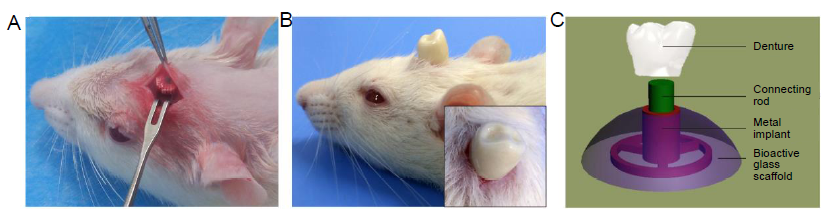
Figure 2. (A) Surgical placement of the SDIS implanted into the sub-epicranial aponeurosis; (B) Digital image of the repair effect and (insert) close-up of the top view; (C) Schematic illustration of the SDIS: the centre hole of the metal implant and the denture are joined together by a connecting rod. SDIS: scaffold dental implant system.
Figure 3. (A) Digital photo of the reparative effect. (B) Residual SDIS and surrounding bone tissue at week 6. (C) Micro-CT analysis of 3-dimensional reconstructed images of SDIS and surrounding tissue after implantation for 6 weeks. A magnified image of the join between implant and bone, showed good integration. Pink indicates residual bioactive glass scaffold, blue indicates the metal implant, and yellow indicates the skull. SDIS: scaffold dental implant system.
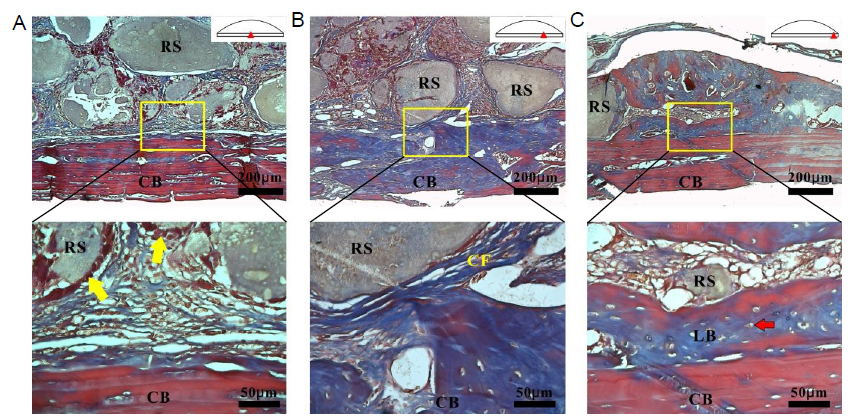
Figure 4. Histological analysis of the MNBG scaffolds and cortical bone after Masson’s trichrome staining. (A, C) Centre and edge areas. (B) Area between edge and centre, as shown in the schematic diagram. The yellow boxes show the areas which are enlarged below. The yellow arrows indicate osteoblasts and the red arrow indicates an osteocyte. Scale bars: 200 μm (upper panel), 50 μm (lower panel). CB: cortical bone; CF: collagen fibres; LB: pre-lamellar bone; MNBG: micro-nano bioactive glass; RS: residual scaffolds.
| 1. |
von Stein-Lausnitz, M.; Nickenig, H. J.; Wolfart, S.; Neumann, K.; von Stein-Lausnitz, A.; Spies, B. C.; Beuer, F. Survival rates and complication behaviour of tooth implant-supported, fixed dental prostheses: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Dent. 2019,88, 103167.
doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2019.07.005 URL pmid: 31306691 |
| 2. |
Bohner, L.; Hanisch, M.; Kleinheinz, J.; Jung, S. Dental implants in growing patients: a systematic review. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2019,57, 397-406.
doi: 10.1016/j.bjoms.2019.04.011 URL pmid: 31076220 |
| 3. |
Liaw, K.; Delfini, R. H.; Abrahams, J. J. Dental implant complications. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 2015,36, 427-433.
doi: 10.1053/j.sult.2015.09.007 URL pmid: 26589696 |
| 4. |
Hansson, S.; Halldin, A. Alveolar ridge resorption after tooth extraction: A consequence of a fundamental principle of bone physiology. J Dent Biomech. 2012,3, 1758736012456543.
doi: 10.1177/1758736012456543 URL pmid: 22924065 |
| 5. |
Li, J.; Jansen, J. A.; Walboomers, X. F.; van den Beucken, J. J. Mechanical aspects of dental implants and osseointegration: A narrative review. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2020,103, 103574.
URL pmid: 32090904 |
| 6. |
Chavda, S.; Levin, L. Human studies of vertical and horizontal alveolar ridge augmentation comparing different types of bone graft materials: a systematic review. J Oral Implantol. 2018,44, 74-84.
doi: 10.1563/aaid-joi-D-17-00053 URL pmid: 29135351 |
| 7. |
Chiapasco, M.; Casentini, P.; Zaniboni, M. Bone augmentation procedures in implant dentistry. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009, 24 Suppl, 237-259.
URL pmid: 19885448 |
| 8. |
McAllister, B. S.; Haghighat, K. Bone augmentation techniques. J Periodontol. 2007,78, 377-396.
doi: 10.1902/jop.2007.060048 URL pmid: 17335361 |
| 9. |
Ribeiro, M.; Fraguas, E. H.; Brito, K. I. C.; Kim, Y. J.; Pallos, D.; Sendyk, W. R. Bone autografts & allografts placed simultaneously with dental implants in rabbits. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2018,46, 142-147.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2017.11.006 URL pmid: 29198577 |
| 10. |
Maiorana, C.; Poli, P. P.; Mascellaro, A.; Ferrario, S.; Beretta, M. Dental implants placed in resorbed alveolar ridges reconstructed with iliac crest autogenous onlay grafts: a 26-year median follow-up retrospective study. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2019,47, 805-814.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2019.02.002 URL pmid: 30797661 |
| 11. |
Asa’ad, F.; Pagni, G.; Pilipchuk, S. P.; Giannì, A. B.; Giannobile, W. V.; Rasperini, G. 3D-printed scaffolds and biomaterials: review of alveolar bone augmentation and periodontal regeneration applications. Int J Dent. 2016,2016, 1239842.
doi: 10.1155/2016/1239842 URL pmid: 27366149 |
| 12. |
Sheikh, Z.; Sima, C.; Glogauer, M. Bone replacement materials and techniques used for achieving vertical alveolar bone augmentation. Materials. 2015,8, 2953-2993.
doi: 10.3390/ma8062953 URL |
| 13. |
Zigdon-Giladi, H.; Lewinson, D.; Bick, T.; Machtei, E. E. Mesenchymal stem cells combined with barrier domes enhance vertical bone formation. J Clin Periodontol. 2013,40, 196-202.
doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12044 URL pmid: 23278529 |
| 14. |
Tamimi, F.; Torres, J.; Al-Abedalla, K.; Lopez-Cabarcos, E.; Alkhraisat, M. H.; Bassett, D. C.; Gbureck, U.; Barralet, J. E. Osseointegration of dental implants in 3D-printed synthetic onlay grafts customized according to bone metabolic activity in recipient site. Biomaterials. 2014,35, 5436-5445.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.03.050 URL pmid: 24726538 |
| 15. |
Yang, J.; Kang, Y.; Browne, C.; Jiang, T.; Yang, Y. Graded porous β-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds enhance bone regeneration in mandible augmentation. J Craniofac Surg. 2015,26, e148-153.
doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000001383 URL pmid: 25675019 |
| 16. |
Singh, A.; Daing, A.; Anand, V.; Dixit, J. Two dimensional alveolar ridge augmentation using particulate hydroxyapatite and collagen membrane: A case report. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2014,4, 151-154.
doi: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2014.01.002 URL pmid: 25737935 |
| 17. |
Kinard, L. A.; Dahlin, R. L.; Lam, J.; Lu, S.; Lee, E. J.; Kasper, F. K.; Mikos, A. G. Synthetic biodegradable hydrogel delivery of demineralized bone matrix for bone augmentation in a rat model. Acta Biomater. 2014,10, 4574-4582.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2014.07.011 URL pmid: 25046637 |
| 18. |
Kinard, L. A.; Dahlin, R. L.; Henslee, A. M.; Spicer, P. P.; Chu, C. Y.; Tabata, Y.; van den Beucken, J. J.; Jansen, J. A.; Young, S.; Wong, M. E.; Kasper, F. K.; Mikos, A. G. Tissue response to composite hydrogels for vertical bone augmentation in the rat. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014,102, 2079-2088.
doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.34878 URL pmid: 23894052 |
| 19. |
Sheikh, Z.; Hamdan, N.; Ikeda, Y.; Grynpas, M.; Ganss, B.; Glogauer, M. Natural graft tissues and synthetic biomaterials for periodontal and alveolar bone reconstructive applications: a review. Biomater Res. 2017,21, 9.
URL pmid: 28593053 |
| 20. |
Titsinides, S.; Agrogiannis, G.; Karatzas, T. Bone grafting materials in dentoalveolar reconstruction: A comprehensive review. Jpn Dent Sci Rev. 2019,55, 26-32.
doi: 10.1016/j.jdsr.2018.09.003 URL pmid: 30733842 |
| 21. |
Hu, Q.; Jiang, W.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, J.; Chen, T.; Miao, G. The effects of morphology on physicochemical properties, bioactivity and biocompatibility of micro-/nano-bioactive glasses. Adv Powder Technol. 2018,29, 1812-1819.
doi: 10.1016/j.apt.2018.04.017 URL |
| 22. |
Jones, J. R. Review of bioactive glass: from Hench to hybrids. Acta Biomater. 2013,9, 4457-4486.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2012.08.023 URL pmid: 22922331 |
| 23. |
El-Rashidy, A. A.; Roether, J. A.; Harhaus, L.; Kneser, U.; Boccaccini, A. R. Regenerating bone with bioactive glass scaffolds: A review of in vivo studies in bone defect models. Acta Biomater. 2017,62, 1-28.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2017.08.030 URL pmid: 28844964 |
| 24. |
Zhao, F.; Xie, W.; Zhang, W.; Fu, X.; Gao, W.; Lei, B.; Chen, X. 3D printing nanoscale bioactive glass scaffolds enhance osteoblast migration and extramembranous osteogenesis through stimulating immunomodulation. Adv Healthc Mater. 2018,7, e1800361.
doi: 10.1002/adhm.201800361 URL pmid: 29952135 |
| 25. |
Sheikh, Z.; Drager, J.; Zhang, Y. L.; Abdallah, M. N.; Tamimi, F.; Barralet, J. Controlling bone graft substitute microstructure to improve bone augmentation. Adv Healthc Mater. 2016,5, 1646-1655.
doi: 10.1002/adhm.201600052 URL pmid: 27214877 |
| 26. |
Armitage, J.; Natiella, J.; Greene, G. Jr.; Meenaghan, M. An evaluation of early bone changes after the insertion of mental endosseous implants into the jaws of rhesus monkeys. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1971,32, 558-568.
doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(71)90321-5 URL pmid: 4999108 |
| 27. |
Grenoble, D. E.; Voss, R. Materials and designs for implant dentistry. Biomater Med Devices Artif Organs. 1976,4, 133-169.
URL pmid: 779858 |
| 28. |
Tamimi, F.; Torres, J.; Gbureck, U.; Lopez-Cabarcos, E.; Bassett, D. C.; Alkhraisat, M. H.; Barralet, J. E. Craniofacial vertical bone augmentation: a comparison between 3D printed monolithic monetite blocks and autologous onlay grafts in the rabbit. Biomaterials. 2009,30, 6318-6326.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2009.07.049 URL pmid: 19695698 |
| 29. |
Pieri, F.; Lucarelli, E.; Corinaldesi, G.; Aldini, N. N.; Fini, M.; Parrilli, A.; Dozza, B.; Donati, D.; Marchetti, C. Dose-dependent effect of adipose-derived adult stem cells on vertical bone regeneration in rabbit calvarium. Biomaterials. 2010,31, 3527-3535.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.01.066 URL pmid: 20170950 |
| 30. |
Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, X.; Sun, X.; Xia, L.; Chang, Q.; Ye, D.; Jiang, X. Vertical alveolar ridge augmentation with beta-tricalcium phosphate and autologous osteoblasts in canine mandible. Biomaterials. 2009,30, 2489-2498.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2008.12.067 URL pmid: 19147220 |
| 31. |
Łączka, M.; Cholewa-Kowalska, K.; Osyczka, A. M. Bioactivity and osteoinductivity of glasses and glassceramics and their material determinants. Ceram Int. 2016,42, 14313-14325.
doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.06.077 URL |
| 32. |
Barradas, A. M.; Yuan, H.; van Blitterswijk, C. A.; Habibovic, P. Osteoinductive biomaterials: current knowledge of properties, experimental models and biological mechanisms. Eur Cell Mater. 2011,21, 407-429; discussion 429.
doi: 10.22203/ecm.v021a31 URL pmid: 21604242 |
| 33. |
Yuan, H.; de Bruijn, J. D.; Zhang, X.; van Blitterswijk, C. A.; de Groot, K. Bone induction by porous glass ceramic made from Bioglass (45S5). J Biomed Mater Res. 2001,58, 270-276.
URL pmid: 11319740 |
| 34. |
Miri, A. K.; Muja, N.; Kamranpour, N. O.; Lepry, W. C.; Boccaccini, A. R.; Clarke, S. A.; Nazhat, S. N. Ectopic bone formation in rapidly fabricated acellular injectable dense collagen-Bioglass hybrid scaffolds via gel aspiration-ejection. Biomaterials. 2016,85, 128-141.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2016.01.047 URL pmid: 26871889 |
| 35. |
Tang, W.; Lin, D.; Yu, Y.; Niu, H.; Guo, H.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, C. Bioinspired trimodal macro/micro/nano-porous scaffolds loading rhBMP-2 for complete regeneration of critical size bone defect. Acta Biomater. 2016,32, 309-323.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2015.12.006 URL pmid: 26689464 |
| 36. |
Meretoja, V. V.; Tirri, T.; Malin, M.; Seppälä, J. V.; Närhi, T. O. Ectopic bone formation in and soft-tissue response to P(CL/DLLA)/bioactive glass composite scaffolds. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2014,25, 159-164.
doi: 10.1111/clr.12051 URL pmid: 23106633 |
| 37. |
Urist, M. R.; Silverman, B. F.; Büring, K.; Dubuc, F. L.; Rosenberg, J. M. The bone induction principle. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1967,53, 243-283.
URL pmid: 4870495 |
| 38. |
García-Gareta, E.; Coathup, M. J.; Blunn, G. W. Osteoinduction of bone grafting materials for bone repair and regeneration. Bone. 2015,81, 112-121.
URL pmid: 26163110 |
| 39. |
Metzler, P.; von Wilmowsky, C.; Zimmermann, R.; Wiltfang, J.; Schlegel, K. A. The effect of current used bone substitution materials and platelet-rich plasma on periosteal cells by ectopic site implantation: an in-vivo pilot study. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2012,40, 409-415.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2011.07.012 URL pmid: 21872487 |
| 40. |
Zhao, F.; Lei, B.; Li, X.; Mo, Y.; Wang, R.; Chen, D.; Chen, X. Promoting in vivo early angiogenesis with sub-micrometer strontium-contained bioactive microspheres through modulating macrophage phenotypes. Biomaterials. 2018,178, 36-47.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2018.06.004 URL pmid: 29908343 |
| 41. |
Hench, L. L.; Splinter, R. J.; Allen, W. C.; Greenlee, T. K. Bonding mechanisms at the interface of ceramic prosthetic materials. J Biomed Mater Res. 1971,5, 117-141.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1097-4636 URL |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||