Recent updates on the biological basis of heterogeneity in bone marrow stromal cells/skeletal stem cells
|
Recent updates on the biological basis of heterogeneity in bone marrow stromal cells/skeletal stem cells |
| Deepika Arora, Pamela Gehron Robey |
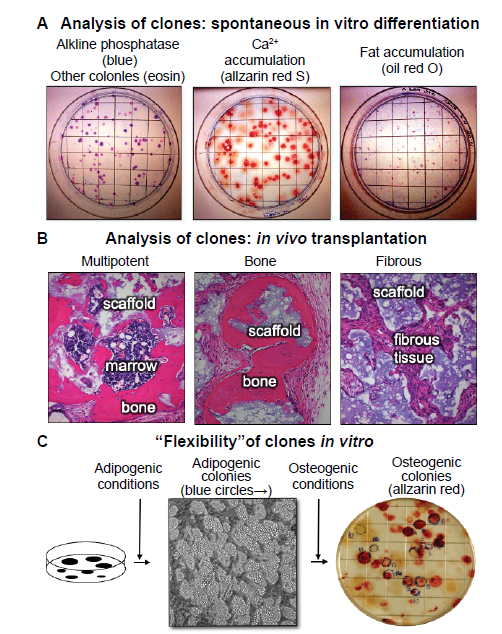
| Figure 4. Clonal analysis - an essential step in the determination of stem cell potency. (A) When colonies are allowed to grow beyond the 10–14 days usually used for colony forming efficiency, the individual colonies begin to spontaneously differentiate. The vast majority of the colonies are alkaline phosphatase positive (right panel), indicative of osteogenic and pre-adipogenic cells. Approximately 50% of the colonies were Alizarin Red positive (centre panel) and approximately 10% stained with oil red O (right panel, unpublished data). (B) When individual colonies were isolated, expanded ex vivo, and transplanted subcutaneously into immunocompromised mice with an hydroxyapatite/tricalcium phosphate scaffold, ~10% of the single colony-derived strains made a complete bone/marrow organ (multipotent), whereas ~50% formed only bone (unipotent), and the remainder formed only fibrous tissue. Adapted from Sworder et al. |

|