The long and winding road: homeostatic and disordered haematopoietic microenvironmental niches: a narrative review
|
The long and winding road: homeostatic and disordered haematopoietic microenvironmental niches: a narrative review |
| Suzanne M. Watt |
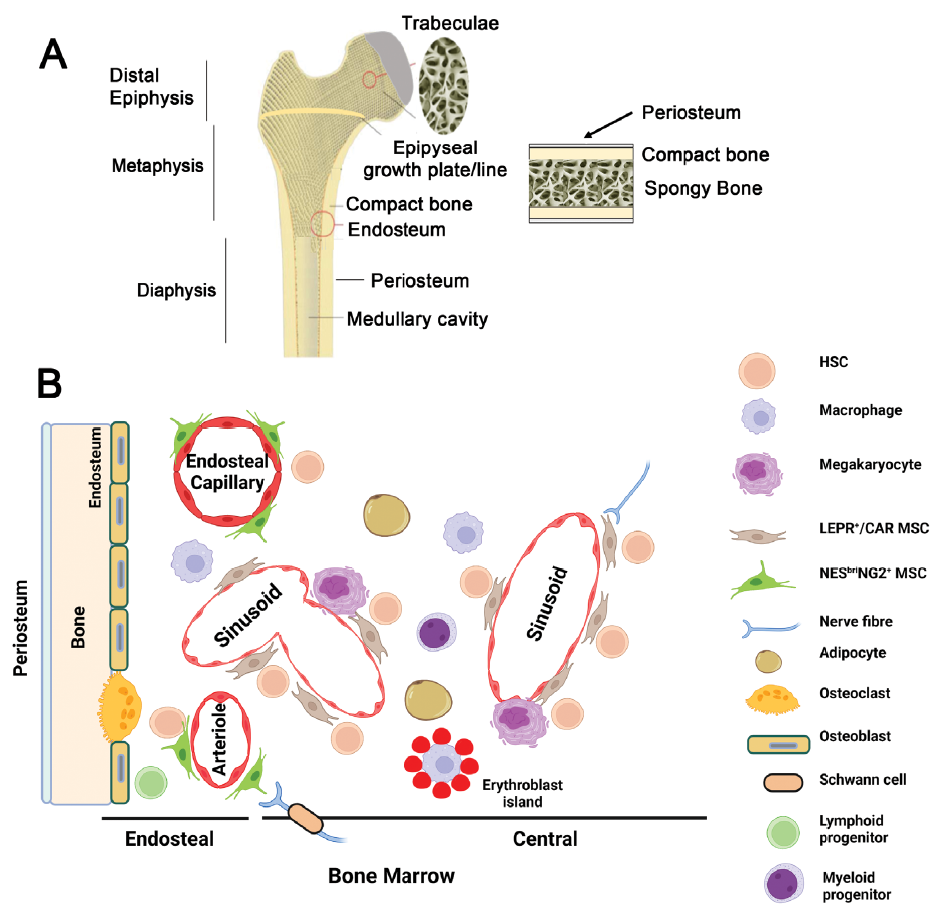
| Figure 2. Architecture of long and flat bones. (A) Diagrammatic representations of an adult long bone showing the epiphyseal, metaphyseal and diaphyseal regions (left) and an adult flat bone (right). Trabeculae and the vasculature (not shown) play key roles in steady state haematopoiesis. In human adults, the epiphyseal or growth plate is replaced by an epiphyseal line. In the adult mouse, the epiphysis and metaphysis remain separated by the growth plate that forms in the foetal bone marrow. (B) A commonly accepted diagrammatic representation of cells that are proposed to have a key role in the haematopoietic stem cells (HSC) niche. Endothelia of the endosteal capillaries, arterioles and sinusoids are associated with mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) to varying degrees and form perivascular niches for endosteal and central bone marrow HSC subsets as described. NesbriNG2+ MSCs are associated with endosteal capillaries and arterioles. The endosteum is also lined with osteoblasts and osteoclasts which are derived from MSCs and HSCs respectively and is reported to play a role in maintaining lymphoid biased HSCs and a reserve of multi-potent long term repopulating HSCs. LEPR+/CAR MSCs are associated with sinusoids in the bone marrow, where erythropoiesis and myelopoiesis are regulated. Some recent studies suggest that the sinusoids may lie closer to the endosteum than previously indicated. MSC production of the key HSC-regulator CXCL12 is altered by the action of sympathetic nerve fibres. Adipocytes, which are also derived from MSCs, and megakaryocytes regulate HSCs in these bone marrow niches. Platelet/myeloid biased HSCs are thought to associate with the megakaryocyte-sinusoidal niche. The roles and spatial distribution of these various cells in regulating HSC fate decisions remains a matter of some debate. CXCL12: C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 12; LEPR+/CAR: C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 12-abundant reticular; NESBri: Nestinbright; NG2: neural-glial antigen 2. Created with Biorender.com. |

|