Biomaterials Translational ›› 2021, Vol. 2 ›› Issue (1): 72-85.doi: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.2096-112X.2021.01.009
• REVIEW • Previous Articles
Xiangyu Deng1,2, Zengwu Shao1,*(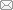 ), Yanli Zhao2,*(
), Yanli Zhao2,*( )
)
Received:2020-08-25
Revised:2020-10-20
Accepted:2020-11-04
Online:2021-03-31
Published:2021-03-28
Contact:
Zengwu Shao,Yanli Zhao
E-mail:szwpro@163.com, zhaoyanli@ntu.edu.sg
Deng, X.; Shao, Z.; Zhao, Y. Development of porphyrin and titanium dioxide sonosensitizers for sonodynamic cancer therapy. Biomater Transl. 2021, 2(1), 72-85.
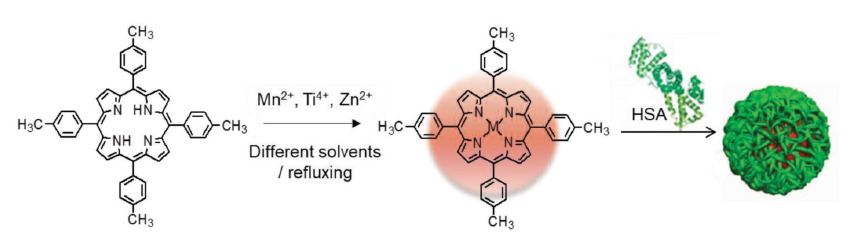
Figure 3. Schematic representation of MnTTP, ZnTTP and TiOTTP complexes synthesized using TTP as the ligand and Mn, Zn and Ti as the central metal ion, followed by HSA encapsulation to create MnTTP-HAS, ZnTTP-HAS, and TiOTTP-HAS, respectively. Reproduced with permission from Ma et al.53 Copyright WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. 2019. HSA: human serum albumin; TTP: tetratolyl porphyrin.
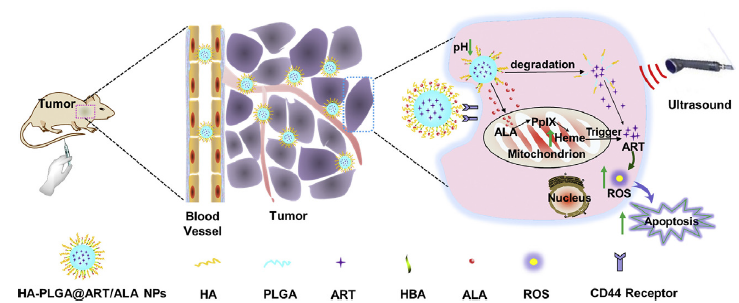
Figure 4. Tumour-targeted drug delivery system based on PLGA NPs, showing the functions of dual drug administration and SDT to maximize the synergistic effect of antitumor treatment. Reproduced with permission from Wang et al.55 Copyright (2018) Elsevier. ALA: 5-aminolevulinic acid; ART: artemisinin; HBA: 4-hydrazinobenzoic acid; NPs: nanoparticles; PLGA: poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid); PpIX: protoporphyrin IX; ROS: reactive oxygen species; SDT: sonodynamic therapy.
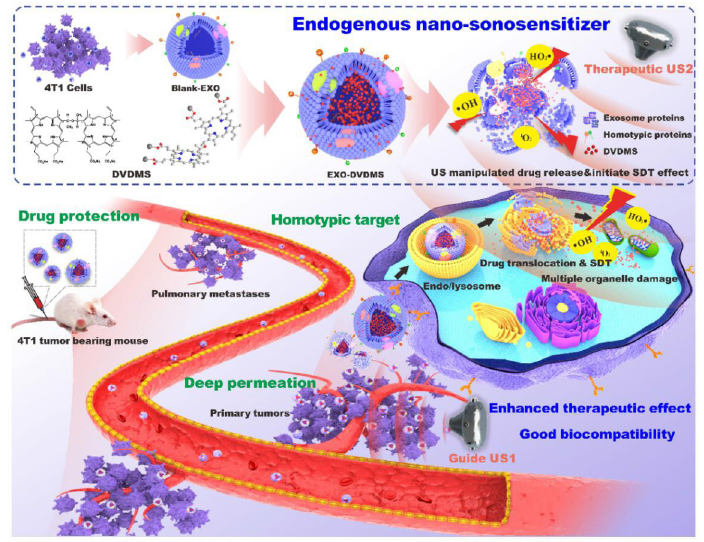
Figure 5. Preparation of an exosome-based sonosensitizer system. The sonosensitizer was loaded onto the exosomes derived from 4T1 cells. This exosome-based sonosensitizer system showed specific accumulation in the primary tumour and in metastatic lesions, achieving ultrasound-controlled drug release and effective SDT. Reproduced with permission from Liu et al.60 Copyright (2019) Ivyspring International Publisher. 1O2: singlet oxygen; DVDMS: sinoporphyrin sodium; EXO-DVDMS: a functionalized smart nanosonosensitizer created by loading sinoporphyrin sodium; SDT: sonodynamic therapy; US: ultrasound.
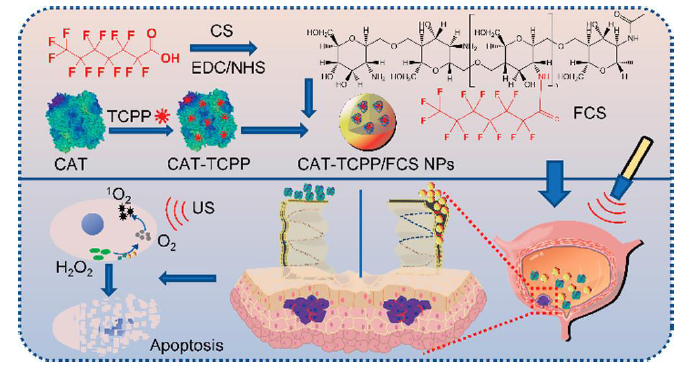
Figure 6. Formation of CAT-TCPP/FCS NPs to facilitate transmucosal delivery of sonosensitizers for enhanced SDT of bladder cancer. Reproduced with permission from Li et al.61 Copyright (2020) American Chemical Society. 1O2: singlet oxygen; CAT-TCPP: catalase-porphyrin; CS: chitosan; EDC: 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide; FCS: fluorinated chitosan; H2O2: hydrogen peroxide; NHS: N-hydroxysuccinimide; NPs: nanoparticles; SDT: sonodynamic therapy; US: ultrasound.
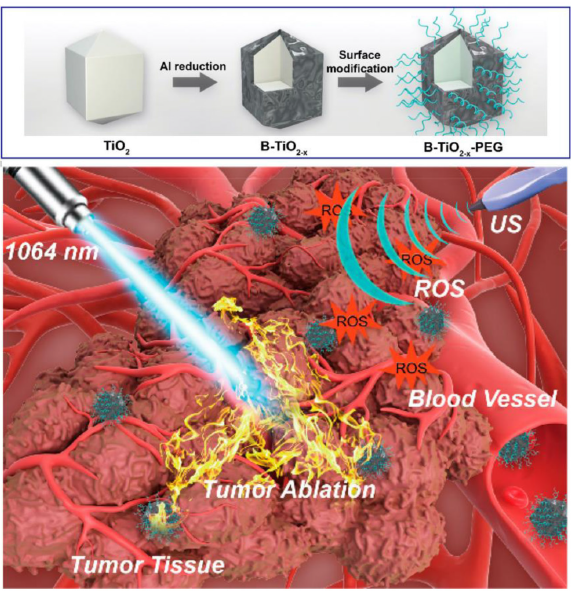
Figure 8. Preparation of TiO2@TiO2-x core/shell nanostructure for synergistic cancer therapy. Reproduced with permission from Han et al.68 Copyright (2018) American Chemical Society. B-TiO2-x: black TiO2-x; PEG: polyethylene glycol; ROS: reactive oxygen species; TiO2: titanium dioxide; US: ultrasound.
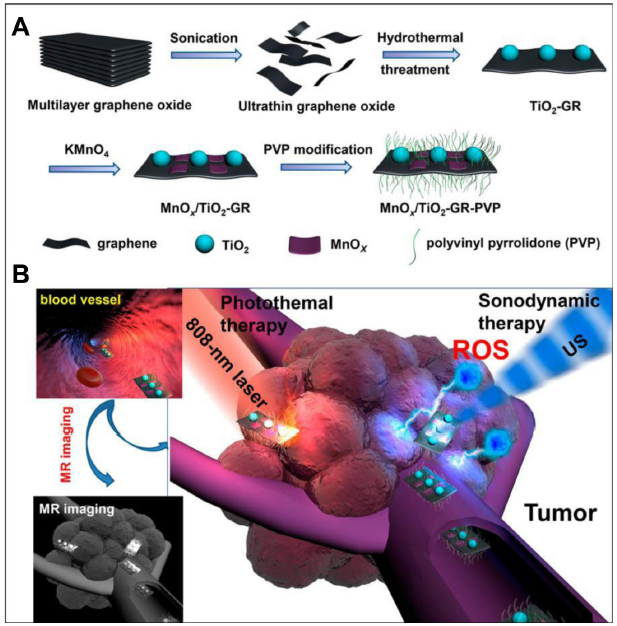
Figure 9. (A) Synthesis of nanocomposites (MnOx/TiO2-GR-PVP) containing MnOx, TiO2, reduced graphene oxide, and PVP. (B) Theranostic ability of MnOx/TiO2-GR-PVP nanocomposites for MR imaging-guided SDT/PTT against cancer. Reproduced with permission from Dai et al.70 Copyright (2017) American Chemical Society. GR: graphene; MR: magnetic resonance; PVP: polyvinylpyrrolidone; ROS: reactive oxygen species; TiO2: titanium dioxide; US: ultrasound.
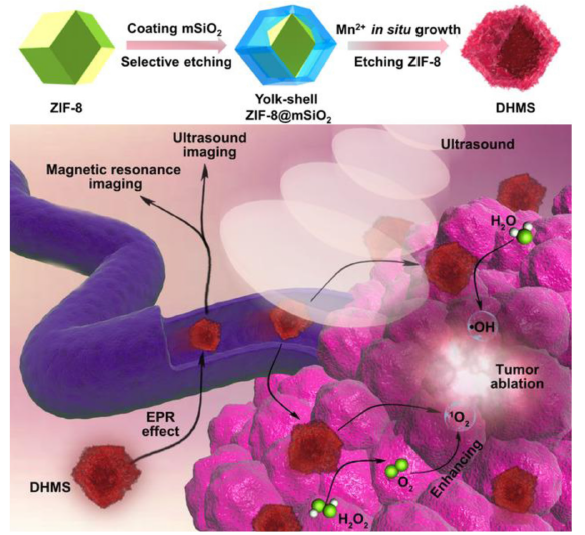
Figure 10. Preparation of DHMS capable of generating ROS under ultrasound for multimodal imaging-guided SDT. Reproduced with permission from Pan et al.71 Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. 2020. ?OH: hydroxyl radical; 1O2: singlet oxygen; DHMS: double-layer hollow manganese silicate nanoparticles; EPR: electron paramagnetic resonance; H2O2: hydrogen peroxide; mSiO2: monodispersed mesoporous silica; ROS: reactive oxygen species; SDT: sonodynamic therapy.
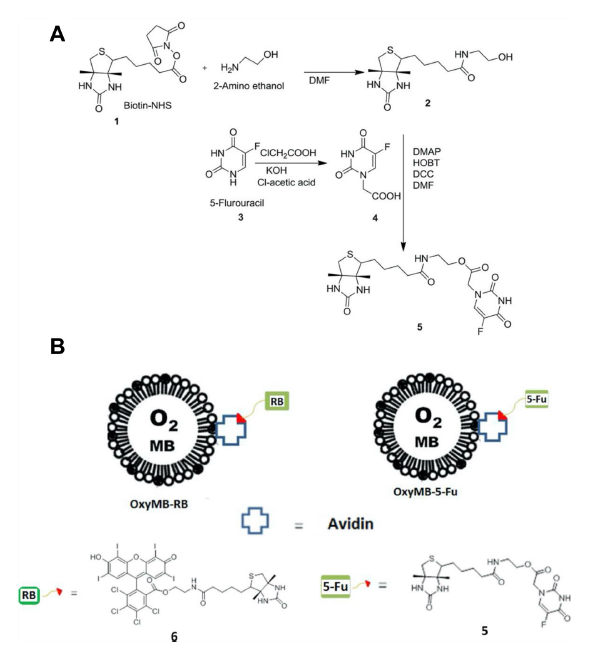
Figure 11. (A) Synthetic scheme of modified 5-fluorouracil antimetabolite (5-Fu). (B) Schematic structures of OxyMB-RB and OxyMB-5-FU conjugates. Reproduced with permission from McEwan et al.80 Copyright (2016) Elsevier. DCC: N,N′-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide; DMAP: 4-dimethylaminopyridine; DMF: N,N-dimethylformamide; HOBT: hydroxybenzotriazole; OxyMB (O2 MB): oxygen-carrying microbubbles; RB: rose bengal.
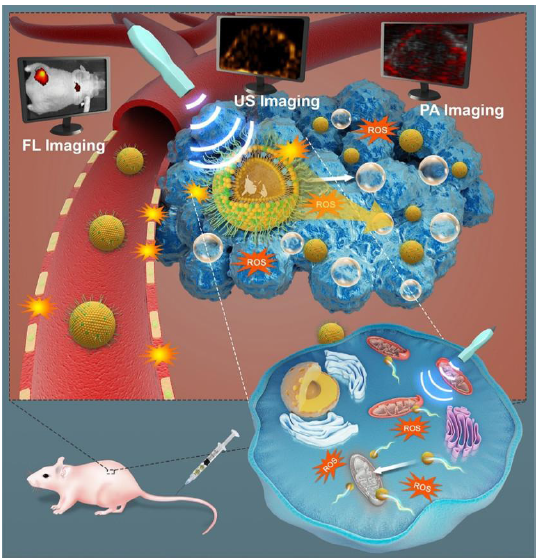
Figure 12. Schematic diagram of mitochondria-targeted SDT using US-responsive IR780-based nanodroplets. Reproduced with permission from Zhang et al.83 Copyright (2019) American Chemical Society. FL: fluorescence imaging; IR780: an ultrasound-activated sonosensitizer; PA: photoacoustic; ROS: reactive oxygen species; SDT: sonodynamic therapy; US: ultrasound.
| 1. | Ferrara, P.; Agüero, F.; Masuet-Aumatell, C.; Ramon-Torrell, J. M. Burden of cancer mortality attributable to carcinogenic infections in Spain. Med Clin (Barc). 2020, 154, 394-397. |
| 2. |
Hu, K.; Ding, P.; Wu, Y.; Tian, W.; Pan, T.; Zhang, S. Global patterns and trends in the breast cancer incidence and mortality according to sociodemographic indices: an observational study based on the global burden of diseases. BMJ Open. 2019, 9, e028461.
doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-028461 URL pmid: 31594871 |
| 3. |
Mahumud, R. A.; Alam, K.; Dunn, J.; Gow, J. Emerging cancer incidence, mortality, hospitalisation and associated burden among Australian cancer patients, 1982 - 2014: an incidence-based approach in terms of trends, determinants and inequality. BMJ Open. 2019, 9, e031874.
doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-031874 URL pmid: 31843834 |
| 4. |
Mattiuzzi, C.; Lippi, G. Epidemiologic burden of red and processed meat intake on colorectal cancer mortality. Nutr Cancer. 2020. doi: 10.1080/01635581.2020.1765259.
doi: 10.1080/01635581.2021.1884730 URL pmid: 33596716 |
| 5. | Zheng, W.; Zhang, H.; Shen, C.; Zhang, S.; Wang, D.; Li, W.; Jiang, G. Trend analysis of lung cancer mortality and years of life lost (YLL) rate from 1999 to 2016 in Tianjin, China: Does the lung cancer burden in rural areas exceed that of urban areas? Thorac Cance. 2020, 11, 867-874. |
| 6. |
Bakalova, R.; Zhelev, Z.; Miller, T.; Aoki, I.; Higashi, T. New potential biomarker for stratification of patients for pharmacological vitamin C in adjuvant settings of cancer therapy. Redox Biol. 2020, 28, 101357.
doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2019.101357 URL pmid: 31678721 |
| 7. | König, A.; Ellenrieder, V.; Nitschmann, S. New milestone in adjuvant therapy for pancreatic cancer. Internist (Berl). 2019, 60, 881-884. |
| 8. |
Park, Y. M.; Jung, C. M.; Cha, D.; Kim, D. H.; Kim, H. R.; Keum, K. C.; Cho, N. H.; Kim, S. H. A new clinical trial of neoadjuvant chemotherapy combined with transoral robotic surgery and customized adjuvant therapy for patients with T3 or T4 oropharyngeal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2017, 24, 3424-3429.
doi: 10.1245/s10434-017-6001-5 URL pmid: 28718033 |
| 9. |
Taieb, J.; André, T.; Auclin, E. Refining adjuvant therapy for non-metastatic colon cancer, new standards and perspectives. Cancer Treat Rev. 2019, 75, 1-11.
doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2019.02.002 URL pmid: 30849607 |
| 10. |
Chang, M.; Wang, M.; Wang, M.; Shu, M.; Ding, B.; Li, C.; Pang, M.; Cui, S.; Hou, Z.; Lin, J. A multifunctional cascade bioreactor based on hollow-structured Cu2MoS4 for synergetic cancer chemo-dynamic therapy/starvation therapy/phototherapy/immunotherapy with remarkably enhanced efficacy. Adv Mater. 2019, 31, e1905271.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201905271 URL pmid: 31680346 |
| 11. |
Costa, M. M.; Silva, S. B.; Quinto, A. L.; Pasquinelli, P. F.; de Queiroz dos Santos, V.; de Cássia Santos, G.; Veiga, D. F. Phototherapy 660 nm for the prevention of radiodermatitis in breast cancer patients receiving radiation therapy: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2014, 15, 330.
URL pmid: 25141962 |
| 12. |
Wei, Z.; Liang, P.; Xie, J.; Song, C.; Tang, C.; Wang, Y.; Yin, X.; Cai, Y.; Han, W.; Dong, X. Carrier-free nano-integrated strategy for synergetic cancer anti-angiogenic therapy and phototherapy. Chem Sci. 2019, 10, 2778-2784.
doi: 10.1039/c8sc04123g URL pmid: 30996997 |
| 13. |
Dougherty, T. J.; Kaufman, J. E.; Goldfarb, A.; Weishaupt, K. R.; Boyle, D.; Mittleman, A. Photoradiation therapy for the treatment of malignant tumors. Cancer Res. 1978, 38, 2628-2635.
URL pmid: 667856 |
| 14. |
Piette, J. Signalling pathway activation by photodynamic therapy: NF-κB at the crossroad between oncology and immunology. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2015, 14, 1510-1517.
doi: 10.1039/c4pp00465e URL pmid: 25656235 |
| 15. | Beltrán Hernández, I.; Angelier, M. L.; Del Buono D’Ondes, T.; Di Maggio, A.; Yu, Y.; Oliveira, S. The potential of nanobody-targeted photodynamic therapy to trigger immune responses. Cancers (Basel). 2020, 12, 978. |
| 16. |
Chiarante, N.; Duhalde Vega, M.; Valli, F.; Zotta, E.; Daghero, H.; Basika, T.; Bollati-Fogolin, M.; García Vior, M. C.; Marino, J.; Roguin, L. P. In vivo photodynamic therapy with a lipophilic zinc(II) phthalocyanine inhibits colorectal cancer and induces a Th1/CD8 antitumor immune response. Lasers Surg Med. 2020. doi: 10.1002/lsm.23284.
URL pmid: 33538345 |
| 17. |
Hamblin, M.; Abrahamse, H. Factors affecting photodynamic therapy and anti-tumor immune response. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2020. doi: 10.2174/1871520620666200318101037.
doi: 10.2174/1871520621666210126093630 URL pmid: 33573580 |
| 18. | Lobo, A. C. S.; Gomes-da-Silva, L. C.; Rodrigues-Santos, P.; Cabrita, A.; Santos-Rosa, M.; Arnaut, L. G. Immune responses after vascular photodynamic therapy with redaporfin. J Clin Med. 2019, 9, 104. |
| 19. |
Zhang, R.; Zhu, Z.; Lv, H.; Li, F.; Sun, S.; Li, J.; Lee, C. S. Immune checkpoint blockade mediated by a small-molecule nanoinhibitor targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway synergizes with photodynamic therapy to elicit antitumor immunity and antimetastatic effects on breast cancer. Small. 2019, 15, e1903881.
doi: 10.1002/smll.201903881 URL pmid: 31702880 |
| 20. |
Champeau, M.; Vignoud, S.; Mortier, L.; Mordon, S. Photodynamic therapy for skin cancer: How to enhance drug penetration?. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2019, 197, 111544.
doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2019.111544 URL pmid: 31295716 |
| 21. | Kim, J. K.; Byun, M. R.; Maeng, C. H.; Kim, Y. R.; Choi, J. W. Selective targeting of cancer stem cells (CSCs) based on photodynamic therapy (PDT) penetration depth inhibits colon polyp formation in mice. Cancers (Basel). 2020, 12, 203. |
| 22. |
Zhu, D.; Duo, Y.; Suo, M.; Zhao, Y.; Xia, L.; Zheng, Z.; Li, Y.; Tang, B. Z. Tumor-exocytosed exosome/aggregation-induced emission luminogen hybrid nanovesicles facilitate efficient tumor penetration and photodynamic therapy. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2020, 59, 13836-13843.
doi: 10.1002/anie.202003672 URL pmid: 32367646 |
| 23. |
Luo, C.; Hu, X.; Peng, R.; Huang, H.; Liu, Q.; Tan, W. Biomimetic carriers based on giant membrane vesicles for targeted drug delivery and photodynamic/photothermal synergistic therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019, 11, 43811-43819.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b11223 URL pmid: 31670932 |
| 24. |
Wu, H.; You, C.; Chen, F.; Jiao, J.; Gao, Z.; An, P.; Sun, B.; Chen, R. Enhanced cellular uptake of near-infrared triggered targeted nanoparticles by cell-penetrating peptide TAT for combined chemo/photothermal/photodynamic therapy. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019, 103, 109738.
doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2019.109738 URL pmid: 31349475 |
| 25. |
Xie, M.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, S.; Xu, G.; Xiong, R.; Sun, X.; Liu, C. A nanoplatform with tumor-targeted aggregation and drug-specific release characteristics for photodynamic/photothermal combined antitumor therapy under near-infrared laser irradiation. Nanoscale. 2020, 12, 11497-11509.
doi: 10.1039/d0nr00123f URL pmid: 32427255 |
| 26. |
Lamberti, M. J.; Morales Vasconsuelo, A. B.; Ferrara, M. G.; Rumie Vittar, N. B. Recapitulation of hypoxic tumor-stroma microenvironment to study photodynamic therapy implications. Photochem Photobiol. 2020, 96, 897-905.
doi: 10.1111/php.13220 URL pmid: 32012283 |
| 27. |
Li, N.; Xu, F.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, G.; Zhu, J.; Shen, X.; He, D. Perfluorocarbon nanocapsules improve hypoxic microenvironment for the tumor ultrasound diagnosis and photodynamic therapy. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2018, 14, 2162-2171.
doi: 10.1166/jbn.2018.2656 URL pmid: 30305223 |
| 28. | Butzbach, K.; Konhäuser, M.; Fach, M.; Bamberger, D. N.; Breitenbach, B.; Epe, B.; Wich, P. R. Receptor-mediated uptake of folic acid-functionalized dextran nanoparticles for applications in photodynamic therapy. Polymers. 2019, 11, 896. |
| 29. |
Chen, Y.; Liu, W.; Shang, Y.; Cao, P.; Cui, J.; Li, Z.; Yin, X.; Li, Y. Folic acid-nanoscale gadolinium-porphyrin metal-organic frameworks: fluorescence and magnetic resonance dual-modality imaging and photodynamic therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019, 14, 57-74.
doi: 10.2147/IJN.S177880 URL pmid: 30587985 |
| 30. |
Oshiro-Junior, J. A.; Sato, M. R.; Boni, F. I.; Santos, K. L. M.; de Oliveira, K. T.; de Freitas, L. M.; Fontana, C. R.; Nicholas, D.; McHale, A.; Callan, J. F.; Chorilli, M. Phthalocyanine-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers functionalized with folic acid for photodynamic therapy. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020, 108, 110462.
doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2019.110462 URL pmid: 31923986 |
| 31. |
Deng, L.; Sheng, D.; Liu, M.; Yang, L.; Ran, H.; Li, P.; Cai, X.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Z. A near-infrared laser and H2O2 activated bio-nanoreactor for enhanced photodynamic therapy of hypoxic tumors. Biomater Sci. 2020, 8, 858-870.
doi: 10.1039/c9bm01126a URL pmid: 31808470 |
| 32. |
Lu, K. Y.; Lin, P. Y.; Chuang, E. Y.; Shih, C. M.; Cheng, T. M.; Lin, T. Y.; Sung, H. W.; Mi, F. L. H2O2-depleting and O2-generating selenium nanoparticles for fluorescence imaging and photodynamic treatment of proinflammatory-activated macrophages. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017, 9, 5158-5172.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.6b15515 URL pmid: 28120612 |
| 33. | Zhang, Y.; Shen, T. T.; Kirillov, A. M.; Liu, W. S.; Tang, Y. NIR light/H2O2-triggered nanocomposites for a highly efficient and selective synergistic photodynamic and photothermal therapy against hypoxic tumor cells. Chem Commun (Camb). 2016, 52, 7939-7942. |
| 34. |
He, C.; Duan, X.; Guo, N.; Chan, C.; Poon, C.; Weichselbaum, R. R.; Lin, W. Core-shell nanoscale coordination polymers combine chemotherapy and photodynamic therapy to potentiate checkpoint blockade cancer immunotherapy. Nat Commun. 2016, 7, 12499.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms12499 URL pmid: 27530650 |
| 35. |
Solovieva, A. B.; Vanin, A. F.; Shekhter, A. B.; Glagolev, N. N.; Aksenova, N. A.; Mikoyan, V. D.; Kotova, S. L.; Rudenko, T. G.; Fayzullin, A. L.; Timashev, P. S. Is it possible to combine photodynamic therapy and application of dinitrosyl iron complexes in the wound treatment? Nitric Oxide. 2019, 83, 24-32.
doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2018.12.004 URL pmid: 30557618 |
| 36. | Wang, Z.; Zhang, F.; Shao, D.; Chang, Z.; Wang, L.; Hu, H.; Zheng, X.; Li, X.; Chen, F.; Tu, Z.; Li, M.; Sun, W.; Chen, L.; Dong, W. F. Janus nanobullets combine photodynamic therapy and magnetic hyperthermia to potentiate synergetic anti-metastatic immunotherapy. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2019, 6, 1901690. |
| 37. |
Garcia, M. R.; Requena, M. B.; Pratavieira, S.; Moriyama, L. T.; Becker, M.; Bagnato, V. S.; Kurachi, C.; Magalhães, D. V. Development of a system to treat and online monitor photodynamic therapy of skin cancer using PpIX near-infrared fluorescence. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2020, 30, 101680.
doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2020.101680 URL pmid: 32006649 |
| 38. |
Zhang, L.; Ji, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yang, S. Photodynamic therapy enhances skin cancer chemotherapy effects through autophagy regulation. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2019, 28, 159-165.
doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2019.08.023 URL pmid: 31445100 |
| 39. |
Pan, X.; Bai, L.; Wang, H.; Wu, Q.; Wang, H.; Liu, S.; Xu, B.; Shi, X.; Liu, H. Metal-organic-framework-derived carbon nanostructure augmented sonodynamic cancer therapy. Adv Mater. 2018, 30, e1800180.
doi: 10.1002/adma.201800180 URL pmid: 29672956 |
| 40. |
Pan, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Sun, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, W.; Shen, H.; Liu, H. Sonodynamic therapy (SDT): a novel strategy for cancer nanotheranostics. Sci China Life Sci. 2018, 61, 415-426.
doi: 10.1007/s11427-017-9262-x URL pmid: 29666990 |
| 41. |
Wan, G. Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, B. W.; Liu, Y. Y.; Wang, Y. S.; Zhang, N. Recent advances of sonodynamic therapy in cancer treatment. Cancer Biol Med. 2016, 13, 325-338.
doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2016.0068 URL pmid: 27807500 |
| 42. |
Zhang, Q.; Bao, C.; Cai, X.; Jin, L.; Sun, L.; Lang, Y.; Li, L. Sonodynamic therapy-assisted immunotherapy: A novel modality for cancer treatment. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 1330-1345.
doi: 10.1111/cas.13578 URL pmid: 29575297 |
| 43. | Bilmin, K.; Kujawska, T.; Grieb, P. Sonodynamic therapy for gliomas. Perspectives and prospects of selective sonosensitization of glioma cells. Cells. 2019, 8, 1428. |
| 44. |
Prada, F.; Sheybani, N.; Franzini, A.; Moore, D.; Cordeiro, D.; Sheehan, J.; Timbie, K.; Xu, Z. Fluorescein-mediated sonodynamic therapy in a rat glioma model. J Neurooncol. 2020, 148, 445-454.
doi: 10.1007/s11060-020-03536-2 URL pmid: 32500440 |
| 45. |
Xie, R.; Xu, T.; Zhu, J.; Wei, X.; Zhu, W.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Han, Y.; Zhou, J.; Bai, Y. The combination of glycolytic inhibitor 2-deoxyglucose and microbubbles increases the effect of 5-aminolevulinic acid-sonodynamic therapy in liver cancer cells. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2017, 43, 2640-2650.
doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2017.06.031 URL pmid: 28843620 |
| 46. |
Li, X.; Gao, L.; Zheng, L.; Kou, J.; Zhu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Dan, J.; Xu, H.; Yang, Y.; Li, H.; Shi, S.; Cao, W.; Zhao, Y.; Tian, Y.; Yang, L. The efficacy and mechanism of apoptosis induction by hypericin-mediated sonodynamic therapy in THP-1 macrophages. Int J Nanomedicine. 2015, 10, 821-838.
doi: 10.2147/IJN.S75398 URL pmid: 25653524 |
| 47. |
McHale, A. P.; Callan, J. F.; Nomikou, N.; Fowley, C.; Callan, B. Sonodynamic therapy: concept, mechanism and application to cancer treatment. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016, 880, 429-450.
doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-22536-4_22 URL pmid: 26486350 |
| 48. |
Song, D.; Yue, W.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, N. Study of the mechanism of sonodynamic therapy in a rat glioma model. Onco Targets Ther. 2014, 7, 1801-1810.
doi: 10.2147/OTT.S52426 URL pmid: 25336971 |
| 49. |
Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, P.; Zhang, K.; Wang, H.; Feng, X.; Liu, Q. Efficacy of chlorin e6-mediated sono-photodynamic therapy on 4T1 cells. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2014, 29, 42-52.
doi: 10.1089/cbr.2013.1526 URL pmid: 24206161 |
| 50. | Huang, P.; Qian, X.; Chen, Y.; Yu, L.; Lin, H.; Wang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Shi, J. Metalloporphyrin-encapsulated biodegradable nanosystems for highly efficient magnetic resonance imaging-guided sonodynamic cancer therapy. J Am Chem Soc. 2017, 139, 1275-1284. |
| 51. |
Li, J. H.; Chen, Z. Q.; Huang, Z.; Zhan, Q.; Ren, F. B.; Liu, J. Y.; Yue, W.; Wang, Z. In vitro study of low intensity ultrasound combined with different doses of PDT: Effects on C6 glioma cells. Oncol Lett. 2013, 5, 702-706.
doi: 10.3892/ol.2012.1060 URL pmid: 23420417 |
| 52. |
Li, C.; Zhang, K.; Wang, P.; Hu, J.; Liu, Q.; Wang, X. Sonodynamic antitumor effect of a novel sonosensitizer on S180 solid tumor. Biopharm Drug Dispos. 2014, 35, 50-59.
doi: 10.1002/bdd.1868 URL pmid: 24122725 |
| 53. |
Ma, A.; Chen, H.; Cui, Y.; Luo, Z.; Liang, R.; Wu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Yin, T.; Ni, J.; Zheng, M.; Cai, L. Metalloporphyrin complex-based nanosonosensitizers for deep-tissue tumor theranostics by noninvasive sonodynamic therapy. Small. 2019, 15, e1804028.
doi: 10.1002/smll.201804028 URL pmid: 30589210 |
| 54. |
Yue, W.; Chen, L.; Yu, L.; Zhou, B.; Yin, H.; Ren, W.; Liu, C.; Guo, L.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, L.; Zhang, K.; Xu, H.; Chen, Y. Checkpoint blockade and nanosonosensitizer-augmented noninvasive sonodynamic therapy combination reduces tumour growth and metastases in mice. Nat Commun. 2019, 10, 2025.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09760-3 URL pmid: 31048681 |
| 55. |
Wang, L.; Hu, Y.; Hao, Y.; Li, L.; Zheng, C.; Zhao, H.; Niu, M.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Tumor-targeting core-shell structured nanoparticles for drug procedural controlled release and cancer sonodynamic combined therapy. J Control Release. 2018, 286, 74-84.
doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.07.028 URL pmid: 30026078 |
| 56. |
Arrighetti, N.; Corbo, C.; Evangelopoulos, M.; Pastò, A.; Zuco, V.; Tasciotti, E. Exosome-like nanovectors for drug delivery in cancer. Curr Med Chem. 2019, 26, 6132-6148.
doi: 10.2174/0929867325666180831150259 URL pmid: 30182846 |
| 57. |
Gomari, H.;.; Forouzandeh Moghadam, M.; Soleimani, M. Targeted cancer therapy using engineered exosome as a natural drug delivery vehicle. Onco Targets Ther. 2018, 11, 5753-5762.
doi: 10.2147/OTT.S173110 URL pmid: 30254468 |
| 58. |
Saari, H.; Lázaro-Ibáñez, E.; Viitala, T.; Vuorimaa-Laukkanen, E.; Siljander, P.; Yliperttula, M. Microvesicle- and exosome-mediated drug delivery enhances the cytotoxicity of Paclitaxel in autologous prostate cancer cells. J Control Release. 2015, 220, 727-737.
doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.09.031 URL pmid: 26390807 |
| 59. |
Vázquez-Ríos, A. J.; Molina-Crespo, Á.; Bouzo, B. L.; López-López, R.; Moreno-Bueno, G.; de la Fuente, M. Exosome-mimetic nanoplatforms for targeted cancer drug delivery. J Nanobiotechnology. 2019, 17, 85.
doi: 10.1186/s12951-019-0517-8 URL pmid: 31319859 |
| 60. |
Liu, Y.; Bai, L.; Guo, K.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, K.; Liu, Q.; Wang, P.; Wang, X. Focused ultrasound-augmented targeting delivery of nanosonosensitizers from homogenous exosomes for enhanced sonodynamic cancer therapy. Theranostics. 2019, 9, 5261-5281.
doi: 10.7150/thno.33183 URL pmid: 31410214 |
| 61. |
Li, G.; Wang, S.; Deng, D.; Xiao, Z.; Dong, Z.; Wang, Z.; Lei, Q.; Gao, S.; Huang, G.; Zhang, E.; Zeng, G.; Wen, Z.; Wu, S.; Liu, Z. Fluorinated chitosan to enhance transmucosal delivery of sonosensitizer-conjugated catalase for sonodynamic bladder cancer treatment post-intravesical instillation. ACS Nano. 2020, 14, 1586-1599.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.9b06689 URL pmid: 32011860 |
| 62. |
Ninomiya, K.; Ogino, C.; Oshima, S.; Sonoke, S.; Kuroda, S.; Shimizu, N. Targeted sonodynamic therapy using protein-modified TiO2 nanoparticles. Ultrason Sonochem. 2012, 19, 607-614.
doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2011.09.009 URL pmid: 22019790 |
| 63. |
Shen, S.; Guo, X.; Wu, L.; Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Kong, F.; Shen, H.; Xie, M.; Ge, Y.; Jin, Y. Dual-core@shell-structured Fe3O4-NaYF4@TiO2 nanocomposites as a magnetic targeting drug carrier for bioimaging and combined chemo-sonodynamic therapy. J Mater Chem B. 2014, 2, 5775-5784.
doi: 10.1039/c4tb00841c URL pmid: 32262021 |
| 64. |
Shen, S.; Wu, L.; Liu, J.; Xie, M.; Shen, H.; Qi, X.; Yan, Y.; Ge, Y.; Jin, Y. Core-shell structured Fe3O4@TiO2-doxorubicin nanoparticles for targeted chemo-sonodynamic therapy of cancer. Int J Pharm. 2015, 486, 380-388.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2015.03.070 URL pmid: 25841570 |
| 65. |
Yamaguchi, S.; Kobayashi, H.; Narita, T.; Kanehira, K.; Sonezaki, S.; Kudo, N.; Kubota, Y.; Terasaka, S.; Houkin, K. Sonodynamic therapy using water-dispersed TiO2-polyethylene glycol compound on glioma cells: comparison of cytotoxic mechanism with photodynamic therapy. Ultrason Sonochem. 2011, 18, 1197-1204.
doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2010.12.017 URL pmid: 21257331 |
| 66. |
You, D. G.; Deepagan, V. G.; Um, W.; Jeon, S.; Son, S.; Chang, H.; Yoon, H. I.; Cho, Y. W.; Swierczewska, M.; Lee, S.; Pomper, M. G.; Kwon, I. C.; Kim, K.; Park, J. H. ROS-generating TiO2 nanoparticles for non-invasive sonodynamic therapy of cancer. Sci Rep. 2016, 6, 23200.
doi: 10.1038/srep23200 URL pmid: 26996446 |
| 67. |
Gao, F.; He, G.; Yin, H.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Lan, C.; Zhang, S.; Yang, B. Titania-coated 2D gold nanoplates as nanoagents for synergistic photothermal/sonodynamic therapy in the second near-infrared window. Nanoscale. 2019, 11, 2374-2384.
doi: 10.1039/c8nr07188h URL pmid: 30667014 |
| 68. |
Han, X.; Huang, J.; Jing, X.; Yang, D.; Lin, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, P.; Chen, Y. Oxygen-deficient black titania for synergistic/enhanced sonodynamic and photoinduced cancer therapy at near infrared-II biowindow. ACS Nano. 2018, 12, 4545-4555.
URL pmid: 29697960 |
| 69. |
Harada, A.; Ono, M.; Yuba, E.; Kono, K. Titanium dioxide nanoparticle-entrapped polyion complex micelles generate singlet oxygen in the cells by ultrasound irradiation for sonodynamic therapy. Biomater Sci. 2013, 1, 65-73.
doi: 10.1039/c2bm00066k URL pmid: 32481997 |
| 70. |
Dai, C.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Z.; Wu, R.; Chen, Y. Two-dimensional graphene augments nanosonosensitized sonocatalytic tumor eradication. ACS Nano. 2017, 11, 9467-9480.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.7b05215 URL pmid: 28829584 |
| 71. |
Pan, X.; Wang, W.; Huang, Z.; Liu, S.; Guo, J.; Zhang, F.; Yuan, H.; Li, X.; Liu, F.; Liu, H. MOF-derived double-layer hollow nanoparticles with oxygen generation ability for multimodal imaging-guided sonodynamic therapy. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2020, 59, 13557-13561.
URL pmid: 32374941 |
| 72. |
Sugita, N.; Iwase, Y.; Yumita, N.; Ikeda, T.; Umemura, S. Sonodynamically induced cell damage using rose bengal derivative. Anticancer Res. 2010, 30, 3361-3366.
URL pmid: 20944109 |
| 73. |
Ohmura, T.; Fukushima, T.; Shibaguchi, H.; Yoshizawa, S.; Inoue, T.; Kuroki, M.; Sasaki, K.; Umemura, S. Sonodynamic therapy with 5-aminolevulinic acid and focused ultrasound for deep-seated intracranial glioma in rat. Anticancer Res. 2011, 31, 2527-2533.
URL pmid: 21873170 |
| 74. |
Wang, F.; Gao, Q.; Guo, S.; Cheng, J.; Sun, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, W.; Tian, Y. The sonodynamic effect of curcumin on THP-1 cell-derived macrophages. Biomed Res Int. 2013, 2013, 737264.
doi: 10.1155/2013/737264 URL pmid: 23509769 |
| 75. |
Wang, J.; Guo, Y.; Liu, B.; Jin, X.; Liu, L.; Xu, R.; Kong, Y.; Wang, B. Detection and analysis of reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated by nano-sized TiO2 powder under ultrasonic irradiation and application in sonocatalytic degradation of organic dyes. Ultrason Sonochem. 2011, 18, 177-183.
doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2010.05.002 URL pmid: 20684888 |
| 76. | Chen, H. J.; Huang, X. R.; Zhou, X. B.; Zheng, B. Y.; Huang, J. D. Potential sonodynamic anticancer activities of artemether and liposome-encapsulated artemether. Chem Commun (Camb). 2015, 51, 4681-4684. |
| 77. |
Kennedy, J. E. High-intensity focused ultrasound in the treatment of solid tumours. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005, 5, 321-327.
doi: 10.1038/nrc1591 URL pmid: 15776004 |
| 78. |
Wan, Q.; Zou, C.; Hu, D.; Zhou, J.; Chen, M.; Tie, C.; Qiao, Y.; Yan, F.; Cheng, C.; Sheng, Z.; Zhang, B.; Liu, X.; Liang, D.; Zheng, H. Imaging-guided focused ultrasound-induced thermal and sonodynamic effects of nanosonosensitizers for synergistic enhancement of glioblastoma therapy. Biomater Sci. 2019, 7, 3007-3015.
URL pmid: 31112151 |
| 79. |
Liang, S.; Deng, X.; Chang, Y.; Sun, C.; Shao, S.; Xie, Z.; Xiao, X.; Ma, P.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, Z.; Lin, J. Intelligent hollow Pt-CuS Janus architecture for synergistic catalysis-enhanced sonodynamic and photothermal cancer therapy. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 4134-4145.
doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b01595 URL pmid: 31084016 |
| 80. |
McEwan, C.; Kamila, S.; Owen, J.; Nesbitt, H.; Callan, B.; Borden, M.; Nomikou, N.; Hamoudi, R. A.; Taylor, M. A.; Stride, E.; McHale, A. P.; Callan, J. F. Combined sonodynamic and antimetabolite therapy for the improved treatment of pancreatic cancer using oxygen loaded microbubbles as a delivery vehicle. Biomaterials. 2016, 80, 20-32.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.11.033 URL pmid: 26702983 |
| 81. |
Prescott, M.; Mitchell, J.; Totti, S.; Lee, J.; Velliou, E.; Bussemaker, M. Sonodynamic therapy combined with novel anti-cancer agents, sanguinarine and ginger root extract: Synergistic increase in toxicity in the presence of PANC-1 cells in vitro. Ultrason Sonochem. 2018, 40, 72-80.
doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2017.05.018 URL pmid: 28533126 |
| 82. |
Ninomiya, K.; Fukuda, A.; Ogino, C.; Shimizu, N. Targeted sonocatalytic cancer cell injury using avidin-conjugated titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Ultrason Sonochem. 2014, 21, 1624-1628.
doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2014.03.010 URL pmid: 24717690 |
| 83. |
Zhang, L.; Yi, H.; Song, J.; Huang, J.; Yang, K.; Tan, B.; Wang, D.; Yang, N.; Wang, Z.; Li, X. Mitochondria-targeted and ultrasound-activated nanodroplets for enhanced deep-penetration sonodynamic cancer therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019, 11, 9355-9366.
URL pmid: 30734551 |
| 84. |
Peng, Y.; Jia, L.; Wang, S.; Cao, W.; Zheng, J. Sonodynamic therapy improves anti-tumor immune effect by increasing the infiltration of CD8+ T cells and altering tumor blood vessels in murine B16F10 melanoma xenograft. Oncol Rep. 2018, 40, 2163-2170.
doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6612 URL pmid: 30106435 |
| 85. |
Guo, T.; Liu, T.; Sun, Y.; Liu, X.; Xiong, R.; Li, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Tian, Z.; Tian, Y. Sonodynamic therapy inhibits palmitate-induced beta cell dysfunction via PINK1/Parkin-dependent mitophagy. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 457.
doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1695-x URL pmid: 31186419 |
| 86. |
Kou, J. Y.; Li, Y.; Zhong, Z. Y.; Jiang, Y. Q.; Li, X. S.; Han, X. B.; Liu, Z. N.; Tian, Y.; Yang, L. M. Berberine-sonodynamic therapy induces autophagy and lipid unloading in macrophage. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2558.
doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.354 URL pmid: 28102849 |
| 87. |
Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Sun, X.; Tian, F.; Guo, S.; Wang, W.; Tian, Z.; Jin, H.; Zhang, Z.; Tian, Y. Sonodynamic therapy-induced foam cells apoptosis activates the phagocytic PPARγ-LXRα-ABCA1/ABCG1 pathway and promotes cholesterol efflux in advanced plaque. Theranostics. 2018, 8, 4969-4984.
URL pmid: 30429880 |
| [1] | Ronghua Tan, Ying Wan, Xiangliang Yang. Hydroxyethyl starch and its derivatives as nanocarriers for delivery of diagnostic and therapeutic agents towards cancers [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2020, 1(1): 46-57. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||