Application of stem cells in translational medicine
James T. Triffitt, Qian Wang
2021, 2(4): 285-286. doi:10.12336/biomatertransl.2021.04.002
VIEWPOINT
A brief history of the development of stromal stem cells (stem cells of the skeleton)
James T. Triffitt
2021, 2(4): 287-293. doi:10.12336/biomatertransl.2021.04.003
REVIEW
Human pluripotent stem cells: tools for regenerative medicine
Peter W. Andrews
2021, 2(4): 294-300. doi:10.12336/biomatertransl.2021.04.004
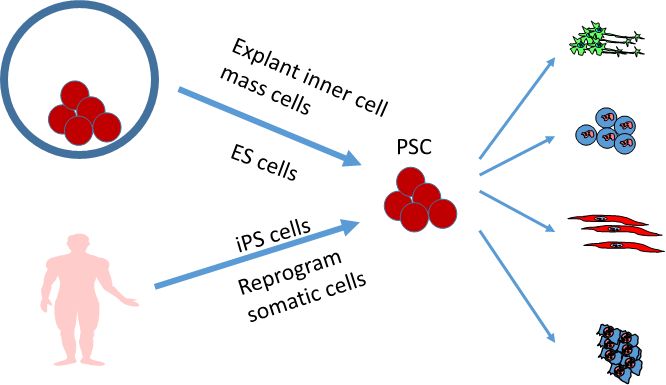 |
Human pluripotent stem cells can differentiate into a range of cell types, with applications for regenerative medicine. Several clinical trials of regenerative medicine based upon transplanting differentiated derivatives of these cells have begun, and their long term safety is critical for regenerative medicine. |
Trivia P. Frazier, Katie Hamel, Xiying Wu, Emma Rogers, Haley Lassiter, Jordan Robinson, Omair Mohiuddin, Michael Henderson, Jeffrey M. Gimble
2021, 2(4): 301-306. doi:10.12336/biomatertransl.2021.04.005
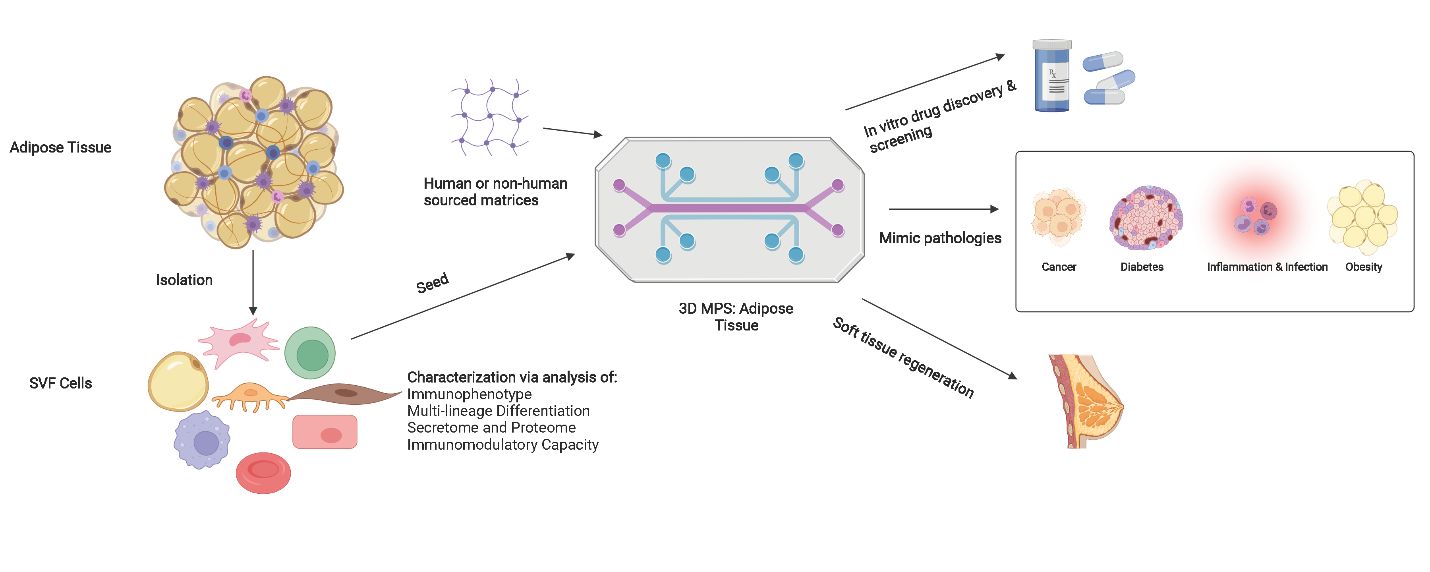 |
Adipose tissue is a rich source of primary cells that, together with biomaterial scaffolds, can be deployed to create humanized three-dimensional microphysiological systems with the potential to improve the accuracy of drug discovery and clinical translation relevant to cancer, cardiovascular disease, metabolism/obesity, and regenerative medicine. |
Arnold I. Caplan
2021, 2(4): 307-311. doi:10.12336/biomatertransl.2021.04.006
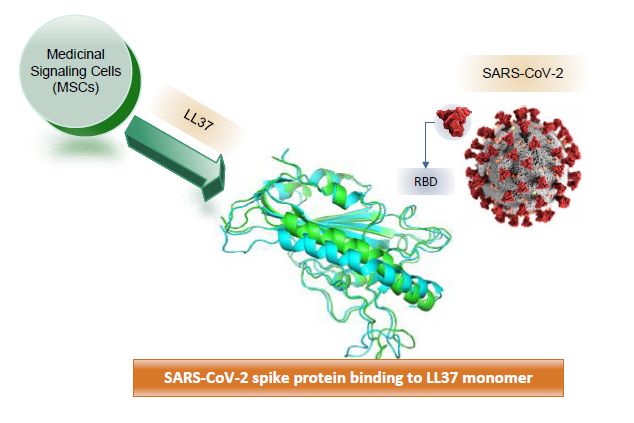 |
Medicinal Signaling Cells (MSCs) secrete antibacterial/antiviral proteins, such as human beta definsin-2 and defensin LL-37, that bind to the receptor binding domain (RBD) in the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2. |
Focal adhesion regulates osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells and osteoblasts
Yang Zhao, Qing Sun, Bo Huo
2021, 2(4): 312-322. doi:10.12336/biomatertransl.2021.04.007
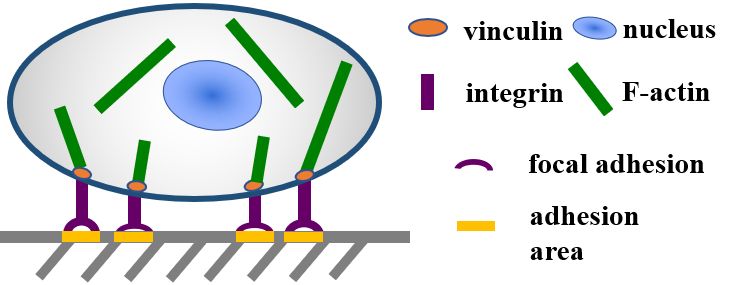 |
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and MC3T3-E1 cells were seeded onto three kinds of micropatterns [large circles with large spacing (LL), small circles with small spacing (SS), and small circles with large spacing (SL)]. At different time points, changes in the expression and distribution of the cytoskeleton protein F-actin had regulatory effects on osteogenic differentiation, and this process was strongly correlated with the yes-associated protein (YAP) pathway. |
Cellular modulation by the mechanical cues from biomaterials for tissue engineering
Qiang Wei, Shenghao Wang, Feng Han, Huan Wang, Weidong Zhang, Qifan Yu, Changjiang Liu, Luguang Ding, Jiayuan Wang, Lili Yu, Caihong Zhu, Bin Li
2021, 2(4): 323-342. doi:10.12336/biomatertransl.2021.04.001
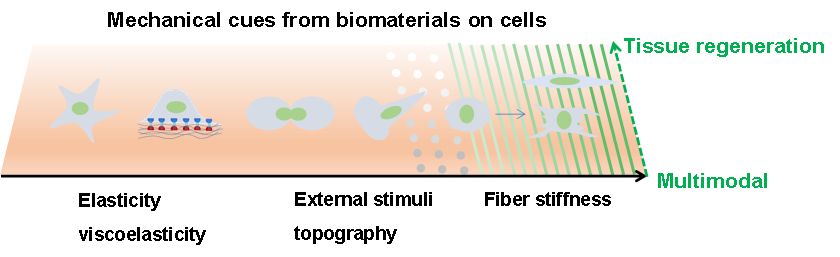 |
Biomaterials that mimic the mechanical properties of native extracellular matrix greatly help guide cell functions. In this review, various mechanical cues from biomaterials and their interplay effects on cell behaviours were introduced. In addition, the underlying principles for development of suitable mechanical biomaterials are discussed. This will provide guidance for researchers to explore how multimodal mechanics of biomaterials may promotetissue regeneration. |
Yizhong Peng, Jinye Li, Hui Lin, Shuo Tian, Sheng Liu, Feifei Pu, Lei Zhao, Kaige Ma, Xiangcheng Qing, Zengwu Shao
2021, 2(4): 343-360. doi:10.12336/biomatertransl.2021.04.008
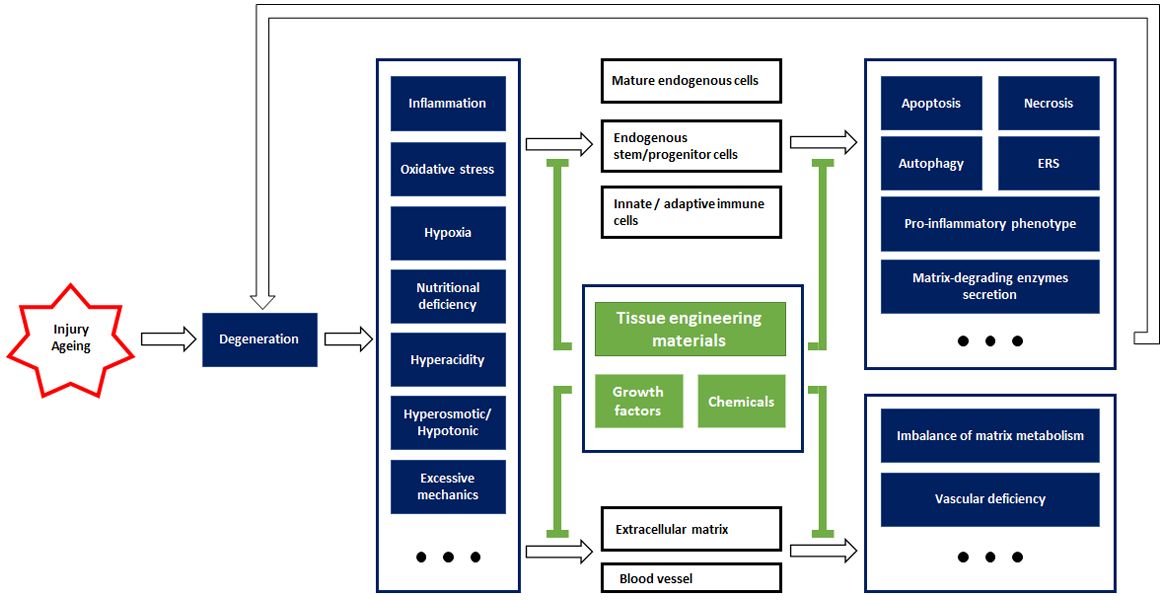 |
After tissue damage or degeneration, the resulting unfavourable microenvironment, including inflammation, etc., imposes a great burden on the endogenous cells and non-cellular components. Tissue engineering materials are efficient in relieving the pathological changes and their damaging impact on cells and extracellular components, which may help re-establish endogenous repair mechanisms and alleviate tissue damage or degeneration. |
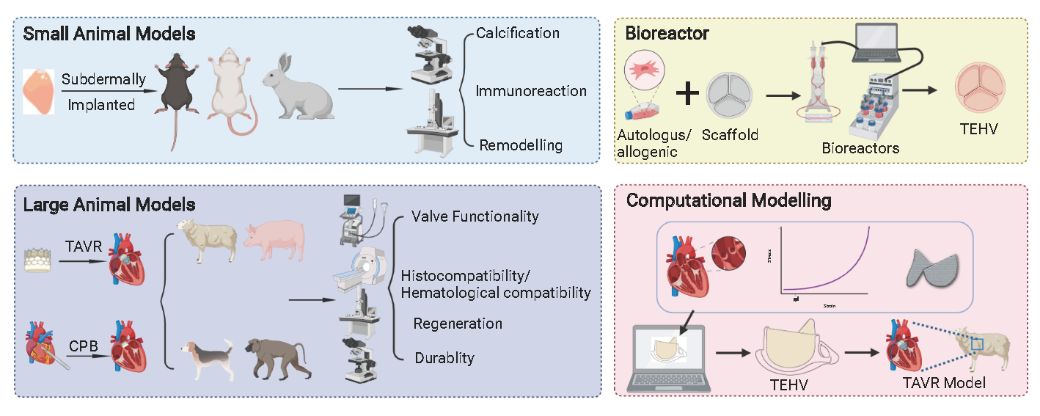 |
Experimental and computational models for testing tissue-engineered heart valves are summarised. Such animal and non-animal models, supply approaches for accessing tissue-engineered heart valves from design to assessment, and guide construction of future artificial valves. |