Biomaterials Translational ›› 2024, Vol. 5 ›› Issue (1): 3-20.doi: 10.12336/biomatertransl.2024.01.002
• REVIEWS • Previous Articles Next Articles
Lei Qi1, Tong Zhao1, Jinge Yan1, Weiwen Ge1, Weidong Jiang1, Jing Wang1, Mazaher Gholipourmalekabadi3, Kaili Lin1,*(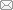 ), Xiuhui Wang2,*(
), Xiuhui Wang2,*( ), Lei Zhang1,*(
), Lei Zhang1,*( )
)
Received:2024-02-06
Revised:2024-02-21
Accepted:2024-03-23
Online:2024-03-28
Published:2024-03-28
Contact:
Kaili Lin, About author:Lei Zhang, oral66@126.com.Xiuhui Wang, blackrabbit@shu.edu.cn;Kaili Lin, lklecnu@aliyun.com;
Figure 1. Cellular biological behaviour of magnesium ions released from magnesium-containing bioceramics. Created with Adobe Illustrator 2022. BMSCs: bone marrow stem cells.
| Primary keywords | Secondary keywords |
|---|---|
| Magnesium | Bone |
| Magnesium oxide | Bone regeneration |
| MgO | Osteogenesis |
| Magnesium peroxide | Bone tissue engineering |
| Hydroxyapatite | |
| HA | |
| Beta-tricalcium phosphate | |
| TCP | |
| Magnesium phosphate | |
| Magnesium phosphate cement | |
| Akermanite | |
| AKT | |
| Magnesium silicate | |
| Forsterite | |
| Magnesium alloy | |
| Magnesium-based |
Table 1. Search terms in the review
| Primary keywords | Secondary keywords |
|---|---|
| Magnesium | Bone |
| Magnesium oxide | Bone regeneration |
| MgO | Osteogenesis |
| Magnesium peroxide | Bone tissue engineering |
| Hydroxyapatite | |
| HA | |
| Beta-tricalcium phosphate | |
| TCP | |
| Magnesium phosphate | |
| Magnesium phosphate cement | |
| Akermanite | |
| AKT | |
| Magnesium silicate | |
| Forsterite | |
| Magnesium alloy | |
| Magnesium-based |
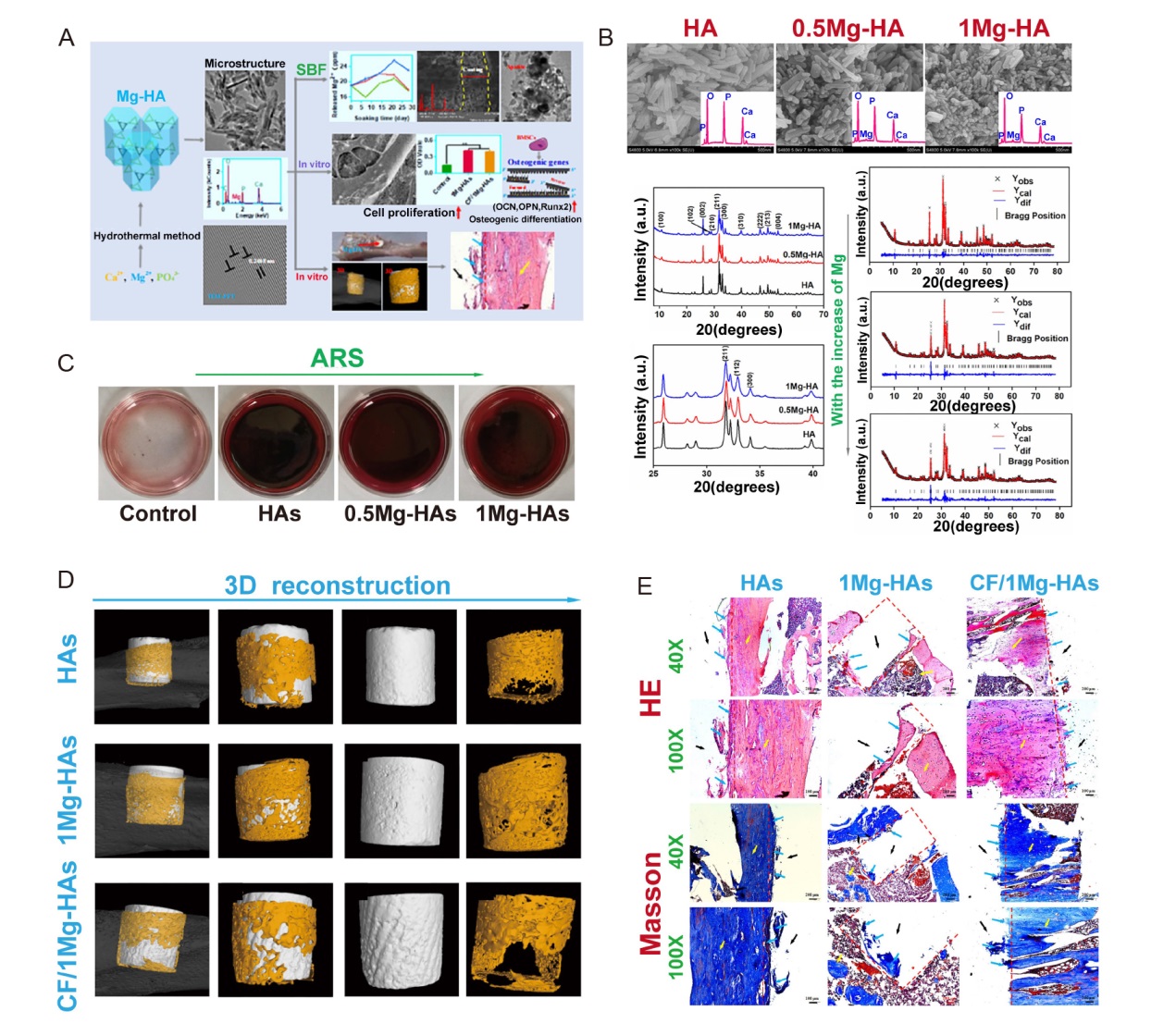
Figure 2. Carbon-fibre reinforced Mg-doped HA composites promote bone regeneration. (A) Schematic illustration of preparation of CF/Mg-HAs composites and their biological functions. Data are expreesed as mean ± SD. (B) Characterization of Mg-HA. (C) ARS of Mg-HA. (D) Micro-CT of the HAs, 1Mg-HAs and CF/1Mg-HAs 4 weeks post-surgery. (E) HE and Masson staining of the rat tibial defect 4 weeks post-surgery. The red dashed line represents the defect area. The yellow arrow represents the host bone. The blue arrow represents the new bone. Scale bars: 200 μm. Reprinted with permission from Zhao et al.40 Copyright 2022, American Chemical Society. 0.5Mg-HAs: 5% Mg-doped hydroxyapatite; 1Mg-HAs: 10% Mg-doped hydroxyapatite; 3D: three-dimensional; a.u.: absorbance unit; ARS: atomic absorption spectrometer; BMSC: bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell; CF: carbon fibre; CF/1Mg-HAs: CF-reinforced 1Mg-HAs; CT: computed tomography; HA: hydroxyapatite; HE: haematoxylin and eosin; Mg: magnesium; OCN: osteopontin; OPN: osteocalcin; Runx2: runt-related transcription factor 2; SBF: simulated body fluid.
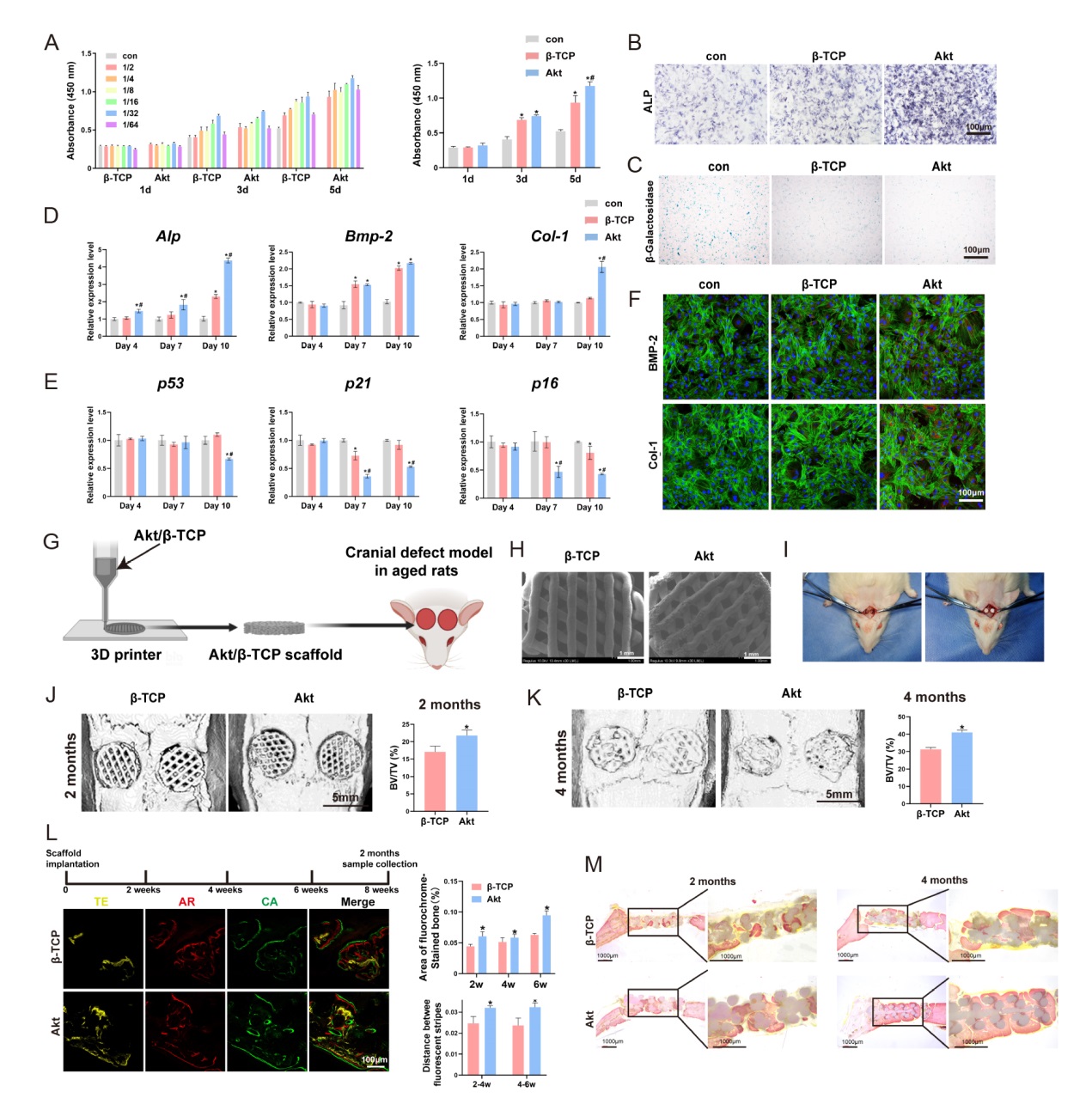
Figure 3. Akt promote senescent bone regeneration in vitro and in vivo. (A-F) The effects of Akt onproliferation (A), ALP staining (B), β-galactosidase staining (C), osteogenic-related genes (D), senescent-related genes (E) and osteogenic-related proteins (F) in O-BMSCs. (G) The schematic diagram of 3D printed Akt/β-TCP scaffold. (H) The SEM images of Akt/β-TCP scaffold. (I) Critical skull bone defects model of senescent rats. (J-M) The bone repair evaluation of 3D printed Akt/β-TCP scaffold by micro-CT, sequential fluorescence and VG staining. Data are expreesed as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, vs. β-TCP; #P < 0.05, vs. α-MEM without extracts. Scale bars: 100 μm (B, C, F, L), 1 mm (H), 5 mm (J, K). Reprinted from Qi et al.61 3D: three-dimensional; Akt: akermanite; Alp: alkaline phosphatase; AR: alizarin red; Bmp-2: bone morphogenetic protein 2; BV/TV: bone volume fraction; CA: calcein; Col-1: type I collagen; CT: computed tomography; O-BMSCs: aged bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells; SEM: scanning electron microscopy; TE: tetracycline; VG: Van Gieson; α-MEM: α-minimal essential medium; β-TCP: β-tricalcium phosphate.
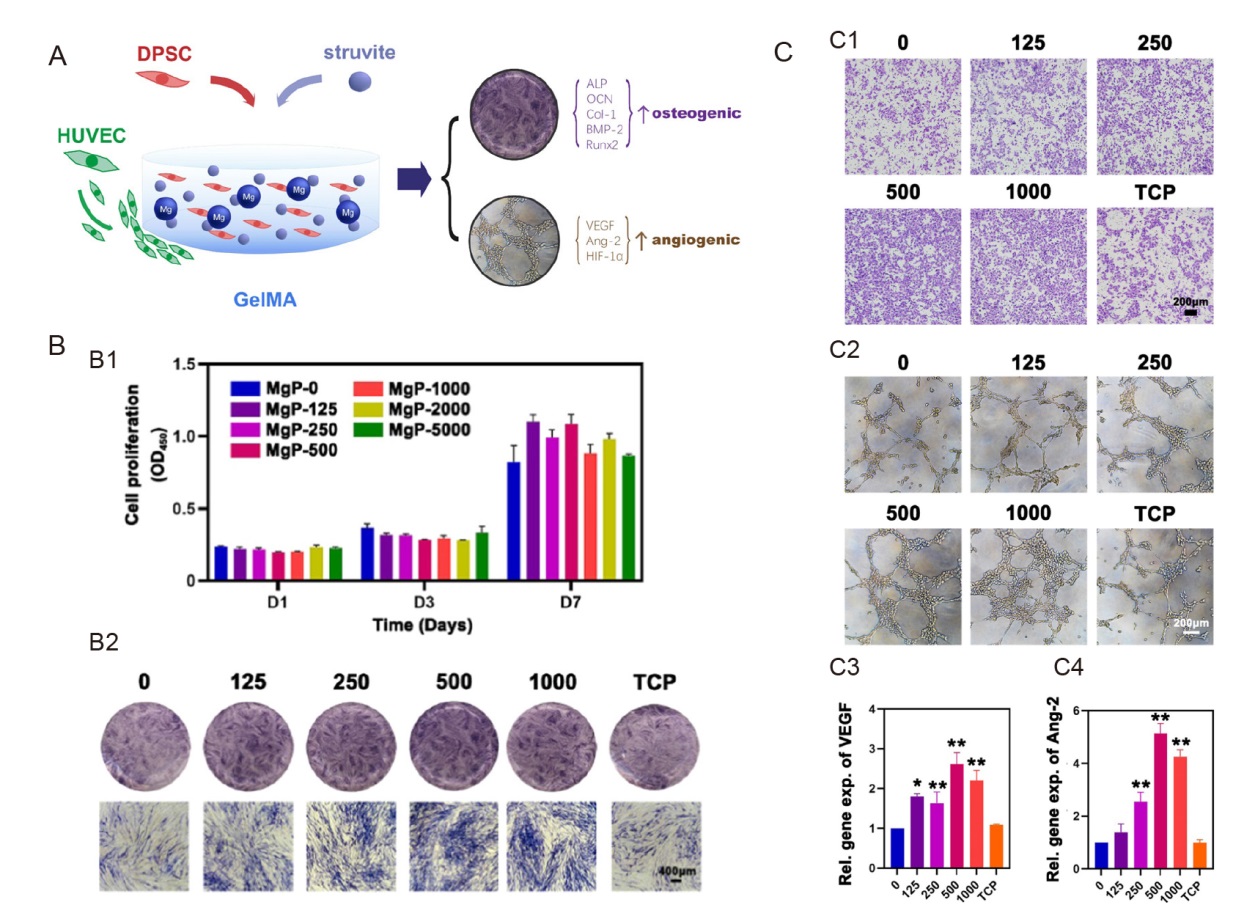
Figure 4. Cell-laden hydrogel with magnesium ammonium phosphate composite promotes angiogenesis and osteogenesis. (A) Magnesium ammonium phosphate composite cell-laden hydrogel promotes osteogenesis and angiogenesis is shown schematically. (B) The struvite extracts’ cell proliferation and osteogenic action. (B1) The proliferation of human DPSCs cultured with varying struvite extract concentrations at various time intervals as assessed using the cell counting kit-8 test (n = 3). (B2) After incubating with struvite and TCP extracts for 7 days, ALP staining was carried out to assess the osteogenic induction capacity of struvite in human DPSCs. Scale bar: 400 μm. (C) Angiogenic effect of the struvite extracts. (C1) Migration assay of HUVECs in response to serial concentrations of struvite and TCP extracts after 12 hours. Scale bar: 200 μm. (C2) Tube formation assay of HUVECs seeded on the gel basement and cultured with the struvite and TCP extracts after 6 hours. Scale bar: 200 μm. (C3) Statistical results for the percentage of HUVECs penetrating the Transwell membranes compared to the control group (n = 5). (C4) Statistical results for the percentage of HUVEC branch points compared to that in the control group (n = 5). Gradient concentration of struvite powder (0–1000 μg/mL) mixed with GelMA solution was designed as the MgP group. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, vs. GelMA solution without magnesium ammonium phosphate (0 group). Reprinted from Liu et al.142 ALP: alkaline phosphatase; Ang-2: angiotensin-2; BMP-2: bone morphogenetic protein 2; COL-1: type I collagen; DPSC: dental pulp stem cell; GelMA: gelatin methacrylate; HIF-1α: hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; HUVEC: human umbilical vein endothelial cell; MgP: magnesium ammonium phosphate powder mixed with GelMA solution; OCN: osteocalcin; Runx2: runt-related transcription factor 2; TCP: tricalcium phosphate; VEGF: vascular endothelial growth factor.
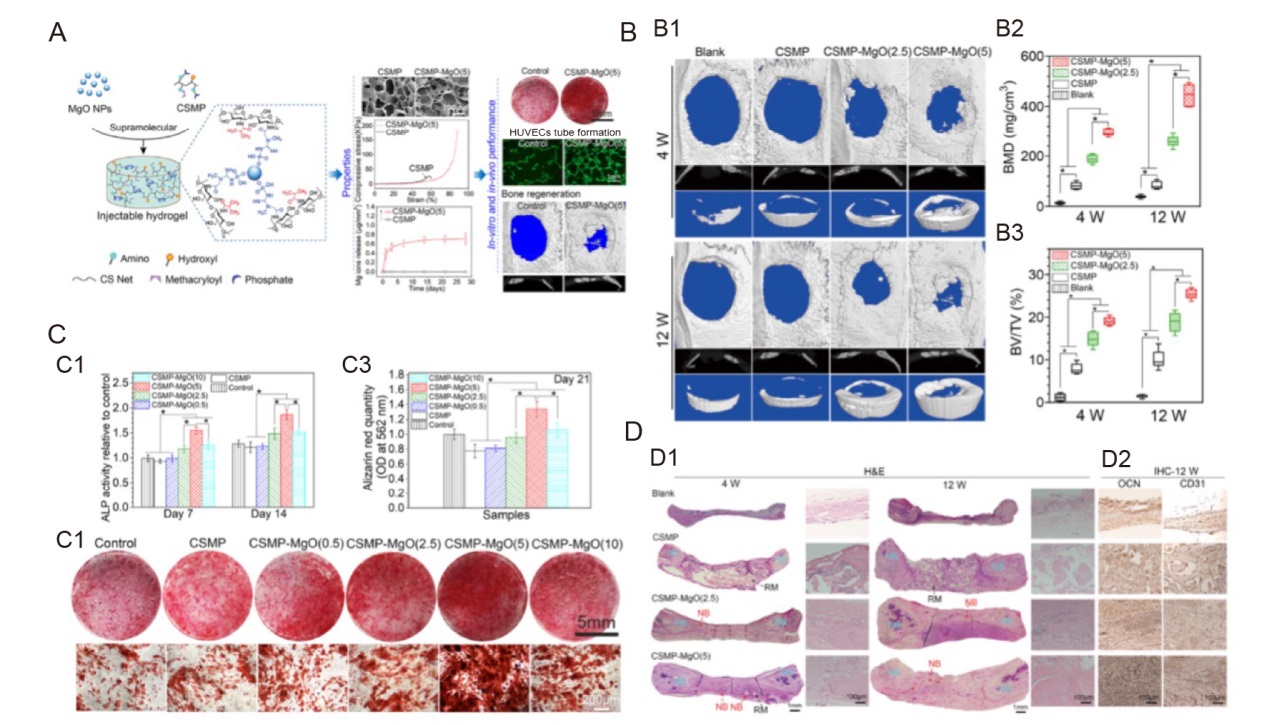
Figure 5. Magnesium oxide nanoparticle coordinated phosphate functionalised chitosan injectable hydrogel for osteogenesis and angiogenesis in bone regeneration. (A) Schematic illustration of synthesis process of novel injectable supramolecular hydrogel and its in vitro and in vivo experiments. (B) The mechanical properties and micro-CT of the newly produced bone for the hydrogels implanted in the 5 mm critical-sized calvarial defect of Sprague-Dawley rats were examined after 4 and 12 weeks. (B1) Micro-CT scans. (B2, 3) Micro-CT assessment-derived BMD and the proportion of newly regenerated bone to tissue volume in the critical-sized area. (C) The ability of hydrogels cultivated with MC3T3-E1 cells to promote osteogenesis. (C1) ALP activity for MC3T3-E1 grown for 7 and 14 days on hydrogels. (C2, 3) Alizarin red staining and amount for MC3T3-E1 grown on hydrogels for 21 days. (D) Section staining of the critical-sized calvarial defect area following 4 and 12 weeks of hydrogel implantation. (D1) Representative pictures of the defect region stained with H&E following hydrogel implantation for 4 and 12 weeks. Data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 6). *P < 0.05. HB, NB, and RM (hydrogels). (D2) OCN, an osteogenic marker, and CD31, an angiogenic marker, stained with an immunohistochemical reaction. Reprinted with permission from Chen et al.27 Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society. ALP: alkaline phosphatase; BMD: bone mineral density; BV/TV: bone volume fraction; CD31: platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1; CS: chitosan; CSMP: phosphocreatine-functionalized chitosan; CT: computed tomography; H&E: haematoxylin and eosin; HB: host bone; HUVEC: human umbilical vein endothelial cell; IHC: immunohistochemistry; MgO: magnesium oxide; NB: newly regenerated bone; NP: nanoparticle; OCN: osteocalcin; OD: optical density; RM: leftover materials.
| 1. |
Rao, S. H.; Harini, B.; Shadamarshan, R. P. K.; Balagangadharan, K.; Selvamurugan, N. Natural and synthetic polymers/bioceramics/bioactive compounds-mediated cell signalling in bone tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018, 110, 88-96.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.09.029 URL |
| 2. |
Tan, B.; Tang, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Wei, Y.; He, L.; Wu, Y.; Wu, J.; Liao, J. Biomaterial-based strategies for maxillofacial tumour therapy and bone defect regeneration. Int J Oral Sci. 2021, 13, 9.
doi: 10.1038/s41368-021-00113-9 |
| 3. |
Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yan, J.; Zhang, K.; Lin, F.; Xiang, L.; Deng, L.; Guan, Z.; Cui, W.; Zhang, H. Pharmaceutical electrospinning and 3D printing scaffold design for bone regeneration. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021, 174, 504-534.
doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2021.05.007 URL |
| 4. | Zhao, C.; Liu, W.; Zhu, M.; Wu, C.; Zhu, Y. Bioceramic-based scaffolds with antibacterial function for bone tissue engineering: a review. Bioact Mater. 2022, 18, 383-398. |
| 5. | Zhi, W.; Wang, X.; Sun, D.; Chen, T.; Yuan, B.; Li, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Xie, Z.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, X. Optimal regenerative repair of large segmental bone defect in a goat model with osteoinductive calcium phosphate bioceramic implants. Bioact Mater. 2022, 11, 240-253. |
| 6. | Bai, L.; Song, P.; Su, J. Bioactive elements manipulate bone regeneration. Biomater Transl. 2023, 4, 248-269. |
| 7. | Li, B. Early immunomodulation by magnesium ion: catalyst for superior osteogenesis. Biomater Transl. 2023, 4, 294-296. |
| 8. |
Díaz-Tocados, J. M.; Herencia, C.; Martínez-Moreno, J. M.; Montes de Oca, A.; Rodríguez-Ortiz, M. E.; Vergara, N.; Blanco, A.; Steppan, S.; Almadén, Y.; Rodríguez, M.; Muñoz-Castañeda, J. R. Magnesium Chloride promotes osteogenesis through Notch signaling activation and expansion of mesenchymal stem cells. Sci Rep. 2017, 7, 7839.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-08379-y |
| 9. |
Nourisa, J.; Zeller-Plumhoff, B.; Helmholz, H.; Luthringer-Feyerabend, B.; Ivannikov, V.; Willumeit-Römer, R. Magnesium ions regulate mesenchymal stem cells population and osteogenic differentiation: A fuzzy agent-based modeling approach. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021, 19, 4110-4122.
doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.07.005 URL |
| 10. |
Qiao, W.; Wong, K. H. M.; Shen, J.; Wang, W.; Wu, J.; Li, J.; Lin, Z.; Chen, Z.; Matinlinna, J. P.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, S.; Liu, X.; Lai, K. P.; Chen, Z.; Lam, Y. W.; Cheung, K. M. C.; Yeung, K. W. K. TRPM7 kinase-mediated immunomodulation in macrophage plays a central role in magnesium ion-induced bone regeneration. Nat Commun. 2021, 12, 2885.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23005-2 |
| 11. |
Castiglioni, S.; Cazzaniga, A.; Albisetti, W.; Maier, J. A. Magnesium and osteoporosis: current state of knowledge and future research directions. Nutrients. 2013, 5, 3022-3033.
doi: 10.3390/nu5083022 URL |
| 12. |
Li, X.; Dai, B.; Guo, J.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, J.; Xu, S.; Yao, Z.; Chang, L.; Li, Y.; He, X.; Chow, D. H. K.; Zhang, S.; Yao, H.; Tong, W.; Ngai, T.; Qin, L. Biosynthesized bandages carrying magnesium oxide nanoparticles induce cortical bone formation by modulating endogenous periosteal cells. ACS Nano. 2022, 16, 18071-18089.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.2c04747 URL |
| 13. |
Maier, J. A.; Castiglioni, S.; Locatelli, L.; Zocchi, M.; Mazur, A. Magnesium and inflammation: Advances and perspectives. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2021, 115, 37-44.
doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2020.11.002 URL |
| 14. |
Bessa-Gonçalves, M.; Silva, A. M.; Brás, J. P.; Helmholz, H.; Luthringer-Feyerabend, B. J. C.; Willumeit-Römer, R.; Barbosa, M. A.; Santos, S. G. Fibrinogen and magnesium combination biomaterials modulate macrophage phenotype, NF-kB signaling and crosstalk with mesenchymal stem/stromal cells. Acta Biomater. 2020, 114, 471-484.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.07.028 URL |
| 15. | Zhang, J.; Tang, L.; Qi, H.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Dual function of magnesium in bone biomineralization. Adv Healthc Mater. 2019, 8, e1901030. |
| 16. |
Danks, A. E.; Hall, S. R.; Schnepp, Z. The evolution of ‘sol-gel’ chemistry as a technique for materials synthesis. Mater Horiz. 2016, 3, 91-112.
doi: 10.1039/C5MH00260E URL |
| 17. | Peng, Z. D.; Yang, J. H.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Y. X.; Li, Z. Q. Thermodynamic analysis on preparing doped zinc oxide varistor ceramic powders by coprecipitation process. Wuji Cailiao Xuebao. 1999, 14, 733-738. |
| 18. |
Sōmiya, S. Hydrothermal preparation and sintering of fine ceramic powders. MRS Online Proc Libr. 1983, 24, 255-271.
doi: 10.1557/PROC-24-255 URL |
| 19. |
Debuigne, F.; Jeunieau, L.; Wiame, M. B.; Nagy, J. Synthesis of organic nanoparticles in different W/O microemulsions. Langmuir. 2000, 16, 7605-7611.
doi: 10.1021/la991638v URL |
| 20. |
Eslamian, M.; Ahmed, M.; Ashgriz, N. Modelling of nanoparticle formation during spray pyrolysis. Nanotechnology. 2006, 17, 1674-1685.
doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/17/6/023 URL |
| 21. |
Eslamian, M.; Shekarriz, M. Recent advances in nanoparticle preparation by spray and micro-emulsion methods. Recent Pat Nanotechnol. 2009, 3, 99-115.
doi: 10.2174/187221009788490068 URL |
| 22. |
Brewster, J. H.; Kodas, T. T. Generation of unagglomerated, dense, BaTiO3 particles by flame-spray pyrolysis. AIChE J. 1997, 43, 2665-2669.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1547-5905 URL |
| 23. |
Deville, S.; Saiz, E.; Nalla, R. K.; Tomsia, A. P. Freezing as a path to build complex composites. Science. 2006, 311, 515-518.
doi: 10.1126/science.1120937 URL |
| 24. |
Putra, N. E.; Borg, K. G. N.; Diaz-Payno, P. J.; Leeflang, M. A.; Klimopoulou, M.; Taheri, P.; Mol, J. M. C.; Fratila-Apachitei, L. E.; Huan, Z.; Chang, J.; Zhou, J.; Zadpoor, A. A. Additive manufacturing of bioactive and biodegradable porous iron-akermanite composites for bone regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2022, 148, 355-373.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2022.06.009 URL |
| 25. |
Putra, N. E.; Leeflang, M. A.; Klimopoulou, M.; Dong, J.; Taheri, P.; Huan, Z.; Fratila-Apachitei, L. E.; Mol, J. M. C.; Chang, J.; Zhou, J.; Zadpoor, A. A. Extrusion-based 3D printing of biodegradable, osteogenic, paramagnetic, and porous FeMn-akermanite bone substitutes. Acta Biomater. 2023, 162, 182-198.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2023.03.033 URL |
| 26. |
Canales, D. A.; Reyes, F.; Saavedra, M.; Peponi, L.; Leonés, A.; Palza, H.; Boccaccini, A. R.; Grünewald, A.; Zapata, P. A. Electrospun fibers of poly (lactic acid) containing bioactive glass and magnesium oxide nanoparticles for bone tissue regeneration. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022, 210, 324-336.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.05.047 URL |
| 27. |
Chen, Y.; Sheng, W.; Lin, J.; Fang, C.; Deng, J.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, M.; Liu, P.; Weng, J.; Yu, F.; Wang, D.; Kang, B.; Zeng, H. Magnesium oxide nanoparticle coordinated phosphate-functionalized chitosan injectable hydrogel for osteogenesis and angiogenesis in bone regeneration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022, 14, 7592-7608.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c21260 URL |
| 28. |
Zhao, X.; Wei, S.; Yang, Z.; Yang, P.; Liu, A. High-strength and tough bioactive Mg-doped hydroxyapatite bioceramics with oriented microchannels. Ceram Int. 2022, 48, 13494-13507.
doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.01.227 URL |
| 29. |
Duda, G. N.; Geissler, S.; Checa, S.; Tsitsilonis, S.; Petersen, A.; Schmidt-Bleek, K. The decisive early phase of bone regeneration. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2023, 19, 78-95.
doi: 10.1038/s41584-022-00887-0 |
| 30. |
Jang, J. W.; Min, K. E.; Kim, C.; Shin, J.; Lee, J.; Yi, S. Review: Scaffold characteristics, fabrication methods, and biomaterials for the bone tissue engineering. Int J Precis Eng Manuf. 2023, 24, 511-529.
doi: 10.1007/s12541-022-00755-7 |
| 31. |
Beattie, J. H.; Avenell, A. Trace element nutrition and bone metabolism. Nutr Res Rev. 1992, 5, 167-188.
doi: 10.1079/NRR19920013 URL |
| 32. |
Kanasan, N.; Adzila, S.; Koh, C. T.; Rahman, H. A.; Panerselvan, G. Effects of magnesium doping on the properties of hydroxyapatite/sodium alginate biocomposite. Adv Appl Ceram. 2019, 118, 381-386.
doi: 10.1080/17436753.2019.1611983 URL |
| 33. |
Tonelli, M.; Faralli, A.; Ridi, F.; Bonini, M. 3D printable magnesium-based cements towards the preparation of bioceramics. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 598, 24-35.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2021.04.025 URL |
| 34. |
Nabiyouni, M.; Brückner, T.; Zhou, H.; Gbureck, U.; Bhaduri, S. B. Magnesium-based bioceramics in orthopedic applications. Acta Biomater. 2018, 66, 23-43.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2017.11.033 URL |
| 35. | Luo, Y.; Wang, J.; Ong, M. T. Y.; Yung, P. S.; Wang, J.; Qin, L. Update on the research and development of magnesium-based biodegradable implants and their clinical translation in orthopaedics. Biomater Transl. 2021, 2, 188-196. |
| 36. |
Trabelsi, M.; AlShahrani, I.; Algarni, H.; Ben Ayed, F.; Yousef, E. S. Mechanical and tribological properties of the tricalcium phosphate - magnesium oxide composites. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019, 96, 716-729.
doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2018.11.070 URL |
| 37. |
Sikder, P.; Ren, Y.; Bhaduri, S. B. Microwave processing of calcium phosphate and magnesium phosphate based orthopedic bioceramics: A state-of-the-art review. Acta Biomater. 2020, 111, 29-53.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.05.018 URL |
| 38. |
George, S. M.; Nayak, C.; Singh, I.; Balani, K. Multifunctional hydroxyapatite composites for orthopedic applications: a review. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2022, 8, 3162-3186.
doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.2c00140 URL |
| 39. |
Ullah, I.; Gloria, A.; Zhang, W.; Ullah, M. W.; Wu, B.; Li, W.; Domingos, M.; Zhang, X. Synthesis and characterization of sintered Sr/Fe-modified hydroxyapatite bioceramics for bone tissue engineering applications. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020, 6, 375-388.
doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.9b01666 URL |
| 40. |
Zhao, X.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Yang, P.; Wang, P.; Wei, S.; Liu, A.; Zhao, Z. Potential load-bearing bone substitution material: carbon-fiber-reinforced magnesium-doped hydroxyapatite composites with excellent mechanical performance and tailored biological properties. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2022, 8, 921-938.
doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.1c01247 URL |
| 41. |
Coelho, C. C.; Padrão, T.; Costa, L.; Pinto, M. T.; Costa, P. C.; Domingues, V. F.; Quadros, P. A.; Monteiro, F. J.; Sousa, S. R. The antibacterial and angiogenic effect of magnesium oxide in a hydroxyapatite bone substitute. Sci Rep. 2020, 10, 19098.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-76063-9 |
| 42. |
Coelho, C. C.; Araújo, R.; Quadros, P. A.; Sousa, S. R.; Monteiro, F. J. Antibacterial bone substitute of hydroxyapatite and magnesium oxide to prevent dental and orthopaedic infections. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019, 97, 529-538.
doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2018.12.059 URL |
| 43. |
Ballouze, R.; Marahat, M. H.; Mohamad, S.; Saidin, N. A.; Kasim, S. R.; Ooi, J. P. Biocompatible magnesium-doped biphasic calcium phosphate for bone regeneration. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2021, 109, 1426-1435.
doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.v109.10 URL |
| 44. |
Frasnelli, M.; Sglavo, V. M. Effect of Mg(2+) doping on beta-alpha phase transition in tricalcium phosphate (TCP) bioceramics. Acta Biomater. 2016, 33, 283-289.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.01.015 URL |
| 45. |
He, F.; Rao, J.; Zhou, J.; Fu, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zuo, F.; Shi, H. Fabrication of 3D printed Ca(3)Mg(3)(PO(4))(4)-based bioceramic scaffolds with tailorable high mechanical strength and osteostimulation effect. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2023, 229, 113472.
doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2023.113472 URL |
| 46. |
Ge, M.; Xie, D.; Yang, Y.; Tian, Z. Sintering densification mechanism and mechanical properties of the 3D-printed high-melting-point-difference magnesium oxide/calcium phosphate composite bio-ceramic scaffold. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2023, 144, 105978.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2023.105978 URL |
| 47. |
Zhang, Y.; Lin, T.; Meng, H.; Wang, X.; Peng, H.; Liu, G.; Wei, S.; Lu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, A.; Xu, W.; Shao, H.; Peng, J. 3D gel-printed porous magnesium scaffold coated with dibasic calcium phosphate dihydrate for bone repair in vivo. J Orthop Translat. 2022, 33, 13-23.
doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2021.11.005 URL |
| 48. |
Cao, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, C.; Xian, J.; Li, M.; Nath Varma, S.; Qin, Z.; Deng, Q.; Zhang, X.; Yang, W.; Liu, C. Magnesium-rich calcium phosphate derived from tilapia bone has superior osteogenic potential. J Funct Biomater. 2023, 14, 390.
doi: 10.3390/jfb14070390 URL |
| 49. |
Wu, F.; Su, J.; Wei, J.; Guo, H.; Liu, C. Injectable bioactive calcium-magnesium phosphate cement for bone regeneration. Biomed Mater. 2008, 3, 044105.
doi: 10.1088/1748-6041/3/4/044105 URL |
| 50. |
Karfarma, M.; Esnaashary, M. H.; Rezaie, H. R.; Javadpour, J.; Naimi-Jamal, M. R. Poly(propylene fumarate)/magnesium calcium phosphate injectable bone composite: effect of filler size and its weight fraction on mechanical properties. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2019, 233, 1165-1174.
doi: 10.1177/0954411919877277 URL |
| 51. |
Wu, J.; Liu, F.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Fang, C.; Leung, F.; Yeung, K. W. K.; Wong, T. M. The development of a magnesium-releasing and long-term mechanically stable calcium phosphate bone cement possessing osteogenic and immunomodulation effects for promoting bone fracture regeneration. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 803723.
doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.803723 URL |
| 52. |
Wu, X.; Dai, H.; Yu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Long, Y.; Li, W.; Tu, J. Magnesium calcium phosphate cement incorporating citrate for vascularized bone regeneration. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020, 6, 6299-6308.
doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.0c00929 URL |
| 53. |
Kanter, B.; Vikman, A.; Brückner, T.; Schamel, M.; Gbureck, U.; Ignatius, A. Bone regeneration capacity of magnesium phosphate cements in a large animal model. Acta Biomater. 2018, 69, 352-361.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2018.01.035 URL |
| 54. |
Kaiser, F.; Schröter, L.; Stein, S.; Krüger, B.; Weichhold, J.; Stahlhut, P.; Ignatius, A.; Gbureck, U. Accelerated bone regeneration through rational design of magnesium phosphate cements. Acta Biomater. 2022, 145, 358-371.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2022.04.019 URL |
| 55. |
Brückner, T.; Meininger, M.; Groll, J.; Kübler, A. C.; Gbureck, U. Magnesium phosphate cement as mineral bone adhesive. Materials (Basel). 2019, 12, 3819.
doi: 10.3390/ma12233819 URL |
| 56. |
Azeena, S.; Subhapradha, N.; Selvamurugan, N.; Narayan, S.; Srinivasan, N.; Murugesan, R.; Chung, T. W.; Moorthi, A. Antibacterial activity of agricultural waste derived wollastonite doped with copper for bone tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017, 71, 1156-1165.
doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2016.11.118 URL |
| 57. |
Namdar, A.; Salahinejad, E. Advances in ion-doping of Ca-Mg silicate bioceramics for bone tissue engineering. Coord Chem Rev. 2023, 478, 215001.
doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2022.215001 URL |
| 58. |
Bavya Devi, K.; Nandi, S. K.; Roy, M. Magnesium silicate bioceramics for bone regeneration: a review. J Indian Inst Sci. 2019, 99, 261-288.
doi: 10.1007/s41745-019-00119-7 |
| 59. |
Huang, Y.; Jin, X.; Zhang, X.; Sun, H.; Tu, J.; Tang, T.; Chang, J.; Dai, K. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of akermanite bioceramics for bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2009, 30, 5041-5048.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2009.05.077 URL |
| 60. |
Xia, L.; Yin, Z.; Mao, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, K.; Chang, J.; Fang, B. Akermanite bioceramics promote osteogenesis, angiogenesis and suppress osteoclastogenesis for osteoporotic bone regeneration. Sci Rep. 2016, 6, 22005.
doi: 10.1038/srep22005 |
| 61. | Qi, L.; Fang, X.; Yan, J.; Pan, C.; Ge, W.; Wang, J.; Shen, S. G.; Lin, K.; Zhang, L. Magnesium-containing bioceramics stimulate exosomal miR-196a-5p secretion to promote senescent osteogenesis through targeting Hoxa7/MAPK signaling axis. Bioact Mater. 2024, 33, 14-29. |
| 62. |
Saran, U.; Gemini Piperni, S.; Chatterjee, S. Role of angiogenesis in bone repair. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2014, 561, 109-117.
doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2014.07.006 URL |
| 63. |
Zhai, W.; Lu, H.; Chen, L.; Lin, X.; Huang, Y.; Dai, K.; Naoki, K.; Chen, G.; Chang, J. Silicate bioceramics induce angiogenesis during bone regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 341-349.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2011.09.008 URL |
| 64. |
Mayr-Wohlfart, U.; Waltenberger, J.; Hausser, H.; Kessler, S.; Günther, K. P.; Dehio, C.; Puhl, W.; Brenner, R. E. Vascular endothelial growth factor stimulates chemotactic migration of primary human osteoblasts. Bone. 2002, 30, 472-477.
doi: 10.1016/S8756-3282(01)00690-1 URL |
| 65. |
Diba, M.; Goudouri, O. M.; Tapia, F.; Boccaccini, A. R. Magnesium-containing bioactive polycrystalline silicate-based ceramics and glass-ceramics for biomedical applications. Curr Opin Solid State Mater Sci. 2014, 18, 147-167.
doi: 10.1016/j.cossms.2014.02.004 URL |
| 66. |
Winet, H. The role of microvasculature in normal and perturbed bone healing as revealed by intravital microscopy. Bone. 1996, 19, 39S-57S.
doi: 10.1016/S8756-3282(96)00133-0 URL |
| 67. |
Yi, D.; Wu, C.; Ma, X.; Ji, H.; Zheng, X.; Chang, J. Preparation and in vitro evaluation of plasma-sprayed bioactive akermanite coatings. Biomed Mater. 2012, 7, 065004.
doi: 10.1088/1748-6041/7/6/065004 URL |
| 68. |
Kharaziha, M.; Fathi, M. H. Synthesis and characterization of bioactive forsterite nanopowder. Ceram Int. 2009, 35, 2449-2454.
doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2009.02.001 URL |
| 69. |
Ni, S.; Chang, J.; Chou, L. In vitro studies of novel CaO-SiO2-MgO system composite bioceramics. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2008, 19, 359-367.
doi: 10.1007/s10856-007-3186-3 URL |
| 70. |
Fathi, M. H.; Kharaziha, M. Two-step sintering of dense, nanostructural forsterite. Mater Lett. 2009, 63, 1455-1458.
doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2009.03.040 URL |
| 71. |
Kharaziha, M.; Fathi, M. H. Improvement of mechanical properties and biocompatibility of forsterite bioceramic addressed to bone tissue engineering materials. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2010, 3, 530-537.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2010.06.003 URL |
| 72. |
Naghiu, M. A.; Gorea, M.; Mutch, E.; Kristaly, F.; Tomoaia-Cotisel, M. Forsterite nanopowder: structural characterization and biocompatibility evaluation. J Mater Sci Technol. 2013, 29, 628-632.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmst.2013.04.007 URL |
| 73. |
Devi, K. B.; Tripathy, B.; Kumta, P. N.; Nandi, S. K.; Roy, M. In vivo biocompatibility of zinc-doped magnesium silicate bio-ceramics. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2018, 4, 2126-2133.
doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.8b00297 URL |
| 74. |
Devi, K. B.; Tripathy, B.; Roy, A.; Lee, B.; Kumta, P. N.; Nandi, S. K.; Roy, M. In vitro biodegradation and in vivo biocompatibility of forsterite bio-ceramics: effects of strontium substitution. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2019, 5, 530-543.
doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.8b00788 URL |
| 75. | Choudhary, R.; Chatterjee, A.; Venkatraman, S. K.; Koppala, S.; Abraham, J.; Swamiappan, S. Antibacterial forsterite (Mg(2)SiO(4)) scaffold: A promising bioceramic for load bearing applications. Bioact Mater. 2018, 3, 218-224. |
| 76. |
Xie, Y.; Zhai, W.; Chen, L.; Chang, J.; Zheng, X.; Ding, C. Preparation and in vitro evaluation of plasma-sprayed Mg(2)SiO(4) coating on titanium alloy. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 2331-2337.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2009.03.003 URL |
| 77. |
Rizwan, M.; Hamdi, M.; Basirun, W. J. Bioglass® 45S5-based composites for bone tissue engineering and functional applications. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2017, 105, 3197-3223.
doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.v105.11 URL |
| 78. |
Lalzawmliana, V.; Anand, A.; Roy, M.; Kundu, B.; Nandi, S. K. Mesoporous bioactive glasses for bone healing and biomolecules delivery. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020, 106, 110180.
doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2019.110180 URL |
| 79. | Thanigachalam, M.; Subramanian, A. V. M. Fabrication, microstructure and properties of advanced ceramic-reinforced composites for dental implants: a review. Biomater Transl. 2023, 4, 151-165. |
| 80. |
Sivakumar, P. M.; Yetisgin, A. A.; Demir, E.; Sahin, S. B.; Cetinel, S. Polysaccharide-bioceramic composites for bone tissue engineering: A review. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023, 250, 126237.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.126237 URL |
| 81. |
Bellucci, D.; Cannillo, V.; Anesi, A.; Salvatori, R.; Chiarini, L.; Manfredini, T.; Zaffe, D. Bone regeneration by novel bioactive glasses containing strontium and/or magnesium: a preliminary in-vivo study. Materials (Basel). 2018, 11, 2223.
doi: 10.3390/ma11112223 URL |
| 82. |
Verné, E.; Bretcanu, O.; Balagna, C.; Bianchi, C. L.; Cannas, M.; Gatti, S.; Vitale-Brovarone, C. Early stage reactivity and in vitro behavior of silica-based bioactive glasses and glass-ceramics. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2009, 20, 75-87.
doi: 10.1007/s10856-008-3537-8 URL |
| 83. |
Diba, M.; Tapia, F.; Boccaccini, A. R.; Strobel, L. A. Magnesium-containing bioactive glasses for biomedical applications. Int J Appl Glass Sci. 2012, 3, 221-253.
doi: 10.1111/ijag.2012.3.issue-3 URL |
| 84. |
Oliveira, J. M.; Correia, R. N.; Fernandes, M. H. Effects of Si speciation on the in vitro bioactivity of glasses. Biomaterials. 2002, 23, 371-379.
doi: 10.1016/S0142-9612(01)00115-6 URL |
| 85. |
Magallanes-Perdomo, M.; De Aza, A. H.; Sobrados, I.; Sanz, J.; Pena, P. Structure and properties of bioactive eutectic glasses based on the Ca3(PO4)2-CaSiO3-CaMg(SiO3)2 system. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 820-829.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2011.10.017 URL |
| 86. |
Hand, R. J.; Tadjiev, D. R. Mechanical properties of silicate glasses as a function of composition. J Non Cryst Solids 2010, 356, 2417-2423.
doi: 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2010.05.007 URL |
| 87. |
Zheng, Q.; Potuzak, M.; Mauro, J. C.; Smedskjaer, M. M.; Youngman, R. E.; Yue, Y. Composition-structure-property relationships in boroaluminosilicate glasses. J Non Cryst Solids. 2012, 358, 993-1002.
doi: 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2012.01.030 URL |
| 88. |
Chen, X.; Ou, J.; Wei, Y.; Huang, Z.; Kang, Y.; Yin, G. Effect of MgO contents on the mechanical properties and biological performances of bioceramics in the MgO-CaO-SiO2 system. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2010, 21, 1463-1471.
doi: 10.1007/s10856-010-4025-5 URL |
| 89. |
Yang, S.; Liang, L.; Liu, L.; Yin, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lei, G.; Zhou, K.; Huang, Q.; Wu, H. Using MgO nanoparticles as a potential platform to precisely load and steadily release Ag ions for enhanced osteogenesis and bacterial killing. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021, 119, 111399.
doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2020.111399 URL |
| 90. |
Alinda Shaly, A.; Hannah Priya, G.; Mahendiran, M.; Mary Linet, J. A behavioural study of hydrothermally derived novel alumina/magnesia/hydroxyapatite (Al(2)O(3)/MgO/HA) bioceramic nanocomposite. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2022, 133, 105313.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2022.105313 URL |
| 91. |
Hao, L.; Lawrence, J.; Chian, K. S. Effects of CO2 laser irradiation on the surface properties of magnesia-partially stabilised zirconia (MgO-PSZ) bioceramic and the subsequent improvements in human osteoblast cell adhesion. J Biomater Appl. 2004, 19, 81-105.
doi: 10.1177/0885328204043546 URL |
| 92. |
Lengyel, J. S.; Milne, J. L.; Subramaniam, S. Electron tomography in nanoparticle imaging and analysis. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2008, 3, 125-131.
doi: 10.2217/17435889.3.1.125 URL |
| 93. |
Nandi, S. K.; Roy, M.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Bose, S. In vivo biocompatibility of SrO and MgO doped brushite cements. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2023, 111, 599-609.
doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.v111.3 URL |
| 94. |
Li, C.; Sun, J.; Shi, K.; Long, J.; Li, L.; Lai, Y.; Qin, L. Preparation and evaluation of osteogenic nano-MgO/PMMA bone cement for bone healing in a rat critical size calvarial defect. J Mater Chem B. 2020, 8, 4575-4586.
doi: 10.1039/D0TB00074D URL |
| 95. |
Ke, D.; Tarafder, S.; Vahabzadeh, S.; Bose, S. Effects of MgO, ZnO, SrO, and SiO(2) in tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on in vitro gene expression and in vivo osteogenesis. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019, 96, 10-19.
doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2018.10.073 URL |
| 96. |
Chen, R.; Chen, H. B.; Xue, P. P.; Yang, W. G.; Luo, L. Z.; Tong, M. Q.; Zhong, B.; Xu, H. L.; Zhao, Y. Z.; Yuan, J. D. HA/MgO nanocrystal-based hybrid hydrogel with high mechanical strength and osteoinductive potential for bone reconstruction in diabetic rats. J Mater Chem B. 2021, 9, 1107-1122.
doi: 10.1039/D0TB02553D URL |
| 97. | Yuan, B.; Chen, H.; Zhao, R.; Deng, X.; Chen, G.; Yang, X.; Xiao, Z.; Aurora, A.; Iulia, B. A.; Zhang, K.; Zhu, X.; Iulian, A. V.; Hai, S.; Zhang, X. Construction of a magnesium hydroxide/graphene oxide/hydroxyapatite composite coating on Mg-Ca-Zn-Ag alloy to inhibit bacterial infection and promote bone regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2022, 18, 354-367. |
| 98. | Wang, G.; Jiang, W.; Mo, S.; Xie, L.; Liao, Q.; Hu, L.; Ruan, Q.; Tang, K.; Mehrjou, B.; Liu, M.; Tong, L.; Wang, H.; Zhuang, J.; Wu, G.; Chu, P. K. Nonleaching antibacterial concept demonstrated by in situ construction of 2D nanoflakes on magnesium. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2020, 7, 1902089. |
| 99. |
Janning, C.; Willbold, E.; Vogt, C.; Nellesen, J.; Meyer-Lindenberg, A.; Windhagen, H.; Thorey, F.; Witte, F. Magnesium hydroxide temporarily enhancing osteoblast activity and decreasing the osteoclast number in peri-implant bone remodelling. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 1861-1868.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2009.12.037 URL |
| 100. |
Pinho, L. C.; Alves, M. M.; Colaço, B.; Fernandes, M. H.; Santos, C. Green-synthesized magnesium hydroxide nanoparticles induced osteoblastic differentiation in bone co-cultured cells. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021, 14, 1281.
doi: 10.3390/ph14121281 URL |
| 101. |
Shive, M. S.; Anderson, J. M. Biodegradation and biocompatibility of PLA and PLGA microspheres. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 1997, 28, 5-24.
doi: 10.1016/S0169-409X(97)00048-3 URL |
| 102. | Niiranen, H.; Pyhältö, T.; Rokkanen, P.; Kellomäki, M.; Törmälä, P. In vitro and in vivo behavior of self-reinforced bioabsorbable polymer and self-reinforced bioabsorbable polymer/bioactive glass composites. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2004, 69, 699-708. |
| 103. |
Wang, X.; Liu, M.; Li, H.; Yin, A.; Xia, C.; Lou, X.; Wang, H.; Mo, X.; Wu, J. MgO-incorporated porous nanofibrous scaffold promotes osteogenic differentiation of pre-osteoblasts. Mater Lett. 2021, 299, 130098.
doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2021.130098 URL |
| 104. |
Ji, J.; Dong, X.; Ma, X.; Tang, S.; Wu, Z.; Xia, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wei, J. Preparation and characterization of bioactive and degradable composites containing ordered mesoporous calcium-magnesium silicate and poly(l-lactide). Appl Surf Sci. 2014, 317, 1090-1099.
doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.09.024 URL |
| 105. |
Wang, C.; Meng, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, Q. 3D printing of polycaprolactone/bioactive glass composite scaffolds for in situ bone repair. Ceram Int. 2022, 48, 7491-7499.
doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.11.293 URL |
| 106. | Niknam, Z.; Golchin, A.; Rezaei-Tavirani, M.; Ranjbarvan, P.; Zali, H.; Omidi, M.; Mansouri, V. Osteogenic differentiation potential of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured on magnesium oxide/polycaprolactone nanofibrous scaffolds for improving bone tissue reconstruction. Adv Pharm Bull. 2022, 12, 142-154. |
| 107. |
Salaris, V.; Leonés, A.; López, D.; Kenny, J. M.; Peponi, L. A comparative study on the addition of MgO and Mg(OH)2 nanoparticles into PCL electrospun fibers. Macromol Chem Phys. 2023, 224, 2200215.
doi: 10.1002/macp.v224.1 URL |
| 108. | Vidhya, E.; Vijayakumar, S.; Nilavukkarasi, M.; Punitha, V. N.; Snega, S.; Praseetha, P. K. Green fabricated MgO nanoparticles as antimicrobial agent: characterization and evaluation. Mater Today Proc. 2021, 45, 5579-5583. |
| 109. |
Dong, Y.; Yao, L.; Cai, L.; Jin, M.; Forouzanfar, T.; Wu, L.; Liu, J.; Wu, G. Antimicrobial and pro-osteogenic coaxially electrospun magnesium oxide nanoparticles-polycaprolactone /parathyroid hormone-polycaprolactone composite barrier membrane for guided bone regeneration. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023, 18, 369-383.
doi: 10.2147/IJN.S395026 URL |
| 110. | Fan, L.; Chen, S.; Yang, M.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J. Metallic materials for bone repair. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024, 13, e2302132. |
| 111. |
Alipour, S.; Nour, S.; Attari, S. M.; Mohajeri, M.; Kianersi, S.; Taromian, F.; Khalkhali, M.; Aninwene, G. E., 2nd; Tayebi, L. A review on in vitro/in vivo response of additively manufactured Ti-6Al-4V alloy. J Mater Chem B. 2022, 10, 9479-9534.
doi: 10.1039/D2TB01616H URL |
| 112. |
Rondanelli, M.; Faliva, M. A.; Tartara, A.; Gasparri, C.; Perna, S.; Infantino, V.; Riva, A.; Petrangolini, G.; Peroni, G. An update on magnesium and bone health. Biometals. 2021, 34, 715-736.
doi: 10.1007/s10534-021-00305-0 |
| 113. |
Dorozhkin, S. V. Calcium orthophosphate bioceramics. Ceram Int. 2015, 41, 13913-13966.
doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.08.004 URL |
| 114. |
Wu, C.; Chang, J. A review of bioactive silicate ceramics. Biomed Mater. 2013, 8, 032001.
doi: 10.1088/1748-6041/8/3/032001 URL |
| 115. |
Zhang, M.; Yang, N.; Dehghan-Manshadi, A.; Venezuela, J.; Bermingham, M. J.; Dargusch, M. S. Fabrication and properties of biodegradable akermanite-reinforced Fe35Mn alloys for temporary orthopedic implant applications. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2023, 9, 1261-1273.
doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.2c01228 URL |
| 116. |
Siahmard, P.; Amini Najafabadi, R.; Meysami, A.; Meysami, M.; Isfahani, T. Investigation of structural properties of forsterite coating on AZ91 magnesium alloy by sol-gel method. Results Eng. 2023, 18, 101138.
doi: 10.1016/j.rineng.2023.101138 URL |
| 117. |
Bose, S.; Roy, M.; Bandyopadhyay, A. Recent advances in bone tissue engineering scaffolds. Trends Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 546-554.
doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2012.07.005 URL |
| 118. | Lewns, F. K.; Tsigkou, O.; Cox, L. R.; Wildman, R. D.; Grover, L. M.; Poologasundarampillai, g. hydrogels and bioprinting in bone tissue engineering: creating artificial stem-cell niches for in vitro models. Adv Mater. 2023, 35, e2301670. |
| 119. | Sarian, M. N.; Iqbal, N.; Sotoudehbagha, P.; Razavi, M.; Ahmed, Q. U.; Sukotjo, C.; Hermawan, H. Potential bioactive coating system for high-performance absorbable magnesium bone implants. Bioact Mater. 2022, 12, 42-63. |
| 120. |
El-Rashidy, A. A.; Roether, J. A.; Harhaus, L.; Kneser, U.; Boccaccini, A. R. Regenerating bone with bioactive glass scaffolds: a review of in vivo studies in bone defect models. Acta Biomater. 2017, 62, 1-28.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2017.08.030 URL |
| 121. | Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Qiang, L.; Ren, Y.; Lin, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, Q.; Gao, S.; Yang, X.; Zhang, C.; Fan, M.; Zheng, P.; Li, S.; Wang, J. Multifunctional 3D-printed bioceramic scaffolds: recent strategies for osteosarcoma treatment. J Tissue Eng. 2023, 14, 20417314231170371. |
| 122. |
Ma, H.; Feng, C.; Chang, J.; Wu, C. 3D-printed bioceramic scaffolds: from bone tissue engineering to tumor therapy. Acta Biomater. 2018, 79, 37-59.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2018.08.026 URL |
| 123. | McWilliam, R. H.; Chang, W.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Han, F.; Black, R. A.; Wu, J.; Luo, X.; Li, B.; Shu, W. Three-dimensional biofabrication of nanosecond laser micromachined nanofibre meshes for tissue engineered scaffolds. Biomater Transl. 2023, 4, 104-114. |
| 124. |
He, F.; Yuan, X.; Lu, T.; Wang, Y.; Feng, S.; Shi, X.; Wang, L.; Ye, J.; Yang, H. Preparation and characterization of novel lithium magnesium phosphate bioceramic scaffolds facilitating bone generation. J Mater Chem B. 2022, 10, 4040-4047.
doi: 10.1039/D2TB00471B URL |
| 125. |
Mouriño, V.; Boccaccini, A. R. Bone tissue engineering therapeutics: controlled drug delivery in three-dimensional scaffolds. J R Soc Interface. 2010, 7, 209-227.
doi: 10.1098/rsif.2009.0379 URL |
| 126. |
Alegrete, N.; Sousa, S. R.; Peleteiro, B.; Monteiro, F. J.; Gutierres, M. Local antibiotic delivery ceramic bone substitutes for the treatment of infected bone cavities and bone regeneration: a systematic review on what we have learned from animal models. Materials (Basel). 2023, 16, 2387.
doi: 10.3390/ma16062387 URL |
| 127. |
Radwan, N. H.; Nasr, M.; Ishak, R. A. H.; Awad, G. A. S. Moxifloxacin-loaded in situ synthesized bioceramic/poly(L-lactide-co-ε-caprolactone) composite scaffolds for treatment of osteomyelitis and orthopedic regeneration. Int J Pharm. 2021, 602, 120662.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2021.120662 URL |
| 128. |
Soundrapandian, C.; Datta, S.; Kundu, B.; Basu, D.; Sa, B. Porous bioactive glass scaffolds for local drug delivery in osteomyelitis: development and in vitro characterization. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2010, 11, 1675-1683.
doi: 10.1208/s12249-010-9550-5 URL |
| 129. |
Kundu, B.; Soundrapandian, C.; Nandi, S. K.; Mukherjee, P.; Dandapat, N.; Roy, S.; Datta, B. K.; Mandal, T. K.; Basu, D.; Bhattacharya, R. N. Development of new localized drug delivery system based on ceftriaxone-sulbactam composite drug impregnated porous hydroxyapatite: a systematic approach for in vitro and in vivo animal trial. Pharm Res. 2010, 27, 1659-1676.
doi: 10.1007/s11095-010-0166-y URL |
| 130. |
Soundrapandian, C.; Basu, D.; Sa, B.; Datta, S. Local drug delivery system for the treatment of osteomyelitis: In vitro evaluation. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2011, 37, 538-546.
doi: 10.3109/03639045.2010.528427 URL |
| 131. |
Thanyaphoo, S.; Kaewsrichan, J. Synthesis and evaluation of novel glass ceramics as drug delivery systems in osteomyelitis. J Pharm Sci. 2012, 101, 2870-2882.
doi: 10.1002/jps.23230 URL |
| 132. | Deng, C.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, M.; Li, T.; Chen, H.; Xu, C.; Feng, Q.; Wang, X.; Yin, F.; Cheng, Y.; Wu, C. Bioceramic scaffolds with antioxidative functions for ROS scavenging and osteochondral regeneration. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022, 9, e2105727. |
| 133. |
Zhao, Z.; Li, G.; Ruan, H.; Chen, K.; Cai, Z.; Lu, G.; Li, R.; Deng, L.; Cai, M.; Cui, W. Capturing magnesium ions via microfluidic hydrogel microspheres for promoting cancellous bone regeneration. ACS Nano. 2021, 15, 13041-13054.
doi: 10.1021/acsnano.1c02147 URL |
| 134. |
Zhang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Cao, L.; Wang, X.; Zheng, A.; Chang, J.; Wu, J.; Wen, J.; Jiang, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z. Alginate-aker injectable composite hydrogels promoted irregular bone regeneration through stem cell recruitment and osteogenic differentiation. J Mater Chem B. 2018, 6, 1951-1964.
doi: 10.1039/C7TB03315J URL |
| 135. |
Ostrowski, N.; Roy, A.; Kumta, P. N. Magnesium phosphate cement systems for hard tissue applications: a review. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2016, 2, 1067-1083.
doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.6b00056 URL |
| 136. |
Hu, J.; Shao, J.; Huang, G.; Zhang, J.; Pan, S. In vitro and in vivo applications of magnesium-enriched biomaterials for vascularized osteogenesis in bone tissue engineering: a review of literature. J Funct Biomater. 2023, 14, 326.
doi: 10.3390/jfb14060326 URL |
| 137. |
Yu, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, C.; Zhang, B.; Chen, H.; Guo, H.; Zhong, G.; Qu, W.; Jiang, S.; Huang, H. Evaluation of inherent toxicology and biocompatibility of magnesium phosphate bone cement. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2010, 76, 496-504.
doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2009.12.010 URL |
| 138. |
Wu, F.; Wei, J.; Guo, H.; Chen, F.; Hong, H.; Liu, C. Self-setting bioactive calcium-magnesium phosphate cement with high strength and degradability for bone regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 1873-1884.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2008.06.020 URL |
| 139. |
Cabrejos-Azama, J.; Alkhraisat, M. H.; Rueda, C.; Torres, J.; Pintado, C.; Blanco, L.; López-Cabarcos, E. Magnesium substitution in brushite cements: Efficacy of a new biomaterial loaded with vancomycin for the treatment of Staphylococcus aureus infections. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016, 61, 72-78.
doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2015.10.092 URL |
| 140. |
Mestres, G.; Ginebra, M. P. Novel magnesium phosphate cements with high early strength and antibacterial properties. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 1853-1861.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2010.12.008 URL |
| 141. |
Mestres, G.; Abdolhosseini, M.; Bowles, W.; Huang, S. H.; Aparicio, C.; Gorr, S. U.; Ginebra, M. P. Antimicrobial properties and dentin bonding strength of magnesium phosphate cements. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 8384-8393.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2013.05.032 URL |
| 142. |
Lin, Z.; Wu, J.; Qiao, W.; Zhao, Y.; Wong, K. H. M.; Chu, P. K.; Bian, L.; Wu, S.; Zheng, Y.; Cheung, K. M. C.; Leung, F.; Yeung, K. W. K. Precisely controlled delivery of magnesium ions thru sponge-like monodisperse PLGA/nano-MgO-alginate core-shell microsphere device to enable in-situ bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2018, 174, 1-16.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2018.05.011 URL |
| 143. |
Liu, C.; Yang, G.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, X.; Wu, X.; Wu, P.; Gu, X.; Jiang, X. Magnesium ammonium phosphate composite cell-laden hydrogel promotes osteogenesis and angiogenesis in vitro. ACS Omega. 2021, 6, 9449-9459.
doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c06083 URL |
| 144. |
Zhu, Y.; Deng, S.; Ma, Z.; Kong, L.; Li, H.; Chan, H. F. Macrophages activated by akermanite/alginate composite hydrogel stimulate migration of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Biomed Mater. 2021, 16, 045004.
doi: 10.1088/1748-605X/abe80a |
| 145. | Wang, J. L.; Xu, J. K.; Hopkins, C.; Chow, D. H.; Qin, L. Biodegradable magnesium-based implants in orthopedics-a general review and perspectives. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2020, 7, 1902443. |
| 146. |
Tao, Z. S.; Zhou, W. S.; He, X. W.; Liu, W.; Bai, B. L.; Zhou, Q.; Huang, Z. L.; Tu, K. K.; Li, H.; Sun, T.; Lv, Y. X.; Cui, W.; Yang, L. A comparative study of zinc, magnesium, strontium-incorporated hydroxyapatite-coated titanium implants for osseointegration of osteopenic rats. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016, 62, 226-232.
doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2016.01.034 URL |
| 147. |
Varshney, S.; Nigam, A.; Singh, A.; Samanta, S. K.; Mishra, N.; Tewari, R. P. Antibacterial, structural, and mechanical properties of MgO/ZnO nanocomposites and its ha-based bio-ceramics; synthesized via physio-chemical route for biomedical applications. Mater Technol. 2022, 37, 2503-2516.
doi: 10.1080/10667857.2022.2043661 URL |
| 148. |
Cui, J.; Xia, L.; Lin, K.; Wang, X. In situ construction of a nano-structured akermanite coating for promoting bone formation and osseointegration of Ti-6Al-4V implants in a rabbit osteoporosis model. J Mater Chem B. 2021, 9, 9505-9513.
doi: 10.1039/D1TB01917A URL |
| [1] | Ziwei Tao, Ziyang Yuan, Dong Zhou, Lang Qin, Lan Xiao, Shihao Zhang, Changsheng Liu, Jinzhong Zhao, Yulin Li. Fabrication of magnesium-doped porous polylactic acid microsphere for bone regeneration [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2023, 4(4): 280-290. |
| [2] | Guixin Yuan, Zan Li, Xixi Lin, Na Li, Ren Xu. New perspective of skeletal stem cells [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2022, 3(4): 280-294. |
| [3] | Ying Luo, Jue Wang, Michael Tim Yun Ong, Patrick Shu-hang Yung, Jiali Wang, Ling Qin. Update on the research and development of magnesium-based biodegradable implants and their clinical translation in orthopaedics [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2021, 2(3): 188-196. |
| [4] | Xirui Jing, Qiuyue Ding, Qinxue Wu, Weijie Su, Keda Yu, Yanlin Su, Bing Ye, Qing Gao, Tingfang Sun, Xiaodong Guo. Magnesium-based materials in orthopaedics: material properties and animal models [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2021, 2(3): 197-213. |
| [5] | Yu Lu, Subodh Deshmukh, Ian Jones, Yu-Lung Chiu. Biodegradable magnesium alloys for orthopaedic applications [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2021, 2(3): 214-235. |
| [6] | Jialin Niu, Hua Huang, Jia Pei, Zhaohui Jin, Shaokang Guan, Guangyin Yuan. Research and development strategy for biodegradable magnesium-based vascular stents: a review [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2021, 2(3): 236-247. |
| [7] | Qingchuan Wang, Weidan Wang, Yanfang Li, Weirong Li, Lili Tan, Ke Yang. Biofunctional magnesium coating of implant materials by physical vapour deposition [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2021, 2(3): 248-256. |
| [8] | Aditya Joshi, George Dias, Mark P. Staiger. In silico modelling of the corrosion of biodegradable magnesium-based biomaterials: modelling approaches, validation and future perspectives [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2021, 2(3): 257-271. |
| [9] | Jing Long, Bin Teng, Wei Zhang, Long Li, Ming Zhang, Yingqi Chen, Zhenyu Yao, Xiangbo Meng, Xinluan Wang, Ling Qin, Yuxiao Lai. Preclinical evaluation of acute systemic toxicity of magnesium incorporated poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) porous scaffolds by three-dimensional printing [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2021, 2(3): 272-284. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||