Biomaterials Translational ›› 2021, Vol. 2 ›› Issue (3): 257-271.doi: 10.12336/biomatertransl.2021.03.008
• REVIEW • Previous Articles Next Articles
Aditya Joshi1, George Dias2, Mark P. Staiger1,*( )
)
Received:2021-09-06
Revised:2021-09-10
Accepted:2021-09-13
Online:2021-09-28
Published:2021-09-28
Contact:
Mark P. Staiger
E-mail:mark.staiger@canterbury.ac.nz
About author:Mark P. Staiger, mark.staiger@canterbury.ac.nz.#Author Equally.
Joshi, A.; Dias, G.; Staiger, M. P. In silico modelling of the corrosion of biodegradable magnesium-based biomaterials: modelling approaches, validation and future perspectives. Biomater Transl. 2021, 2(3), 257-271.
| Time (hour) | ε (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2.7 | 8.4 | |
| 0﹣24 | 0.368 | 2.190 | 5.830 |
| 24﹣48 | 1.287 | 1.265 | 1.264 |
| 48﹣96 | 1.000 | 0.632 | 0.360 |
| 96﹣144 | 1.035 | 1.092 | 1.149 |
| 144﹣192 | 0.862 | 1.149 | 1.093 |
| 192﹣240 | 0.875 | 1.095 | 1.148 |
Table 1 фe as a function of pre-strain and immersion corrosion time.
| Time (hour) | ε (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2.7 | 8.4 | |
| 0﹣24 | 0.368 | 2.190 | 5.830 |
| 24﹣48 | 1.287 | 1.265 | 1.264 |
| 48﹣96 | 1.000 | 0.632 | 0.360 |
| 96﹣144 | 1.035 | 1.092 | 1.149 |
| 144﹣192 | 0.862 | 1.149 | 1.093 |
| 192﹣240 | 0.875 | 1.095 | 1.148 |
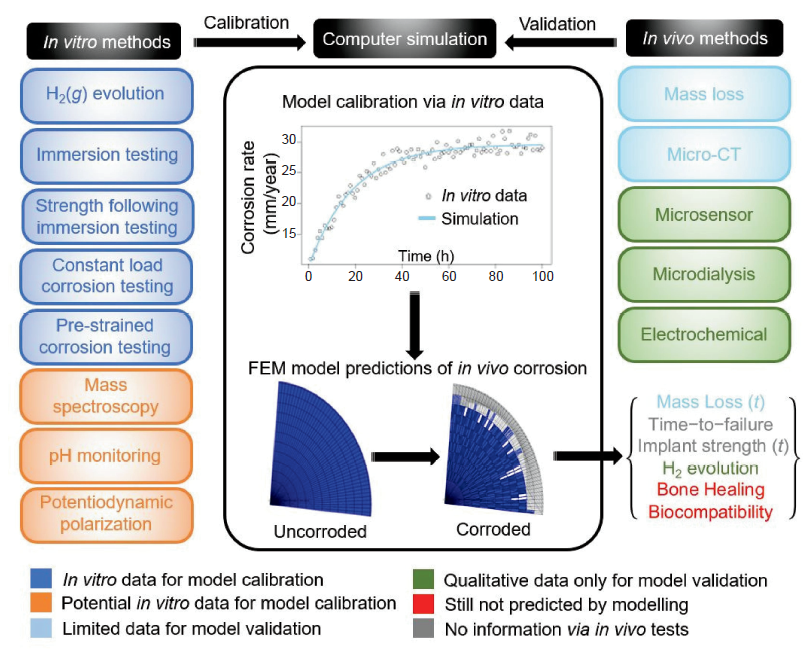
Figure 1. An overview of the potential of currently-available experimental in vitro and in vivo techniques for the calibration and validation of mathematical corrosion models. µCT: micro-computed tomography; H2(g): hydrogen gas.
| [1] |
Geetha, M.; Singh, A. K.; Asokamani, R.; Gogia, A. K. Ti based biomaterials, the ultimate choice for orthopaedic implants - A review. Prog Mater Sci. 2009, 54, 397-425.
doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2008.06.004 URL |
| [2] |
Nagels, J.; Stokdijk, M.; Rozing, P. M. Stress shielding and bone resorption in shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2003, 12, 35-39.
doi: 10.1067/mse.2003.22 URL |
| [3] |
Orringer, J. S.; Barcelona, V.; Buchman, S. R. Reasons for removal of rigid internal fixation devices in craniofacial surgery. J Craniofac Surg. 1998, 9, 40-44.
doi: 10.1097/00001665-199801000-00009 URL |
| [4] |
Francel, T. J.; Birely, B. C.; Ringelman, P. R.; Manson, P. N. The fate of plates and screws after facial fracture reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1992, 90, 568-573.
doi: 10.1097/00006534-199210000-00004 URL |
| [5] |
Fearon, J. A.; Munro, I. R.; Bruce, D. A. Observations on the use of rigid fixation for craniofacial deformities in infants and young children. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1995, 95, 634-637; discussion 638.
doi: 10.1097/00006534-199504000-00002 URL |
| [6] |
Yu, J. C.; Bartlett, S. P.; Goldberg, D. S.; Gannon, F.; Hunter, J.; Habecker, P.; Whitaker, L. A. An experimental study of the effects of craniofacial growth on the long-term positional stability of microfixation. J Craniofac Surg. 1996, 7, 64-68.
doi: 10.1097/00001665-199601000-00014 URL |
| [7] |
Puleo, D. A.; Huh, W. W. Acute toxicity of metal ions in cultures of osteogenic cells derived from bone marrow stromal cells. J Appl Biomater. 1995, 6, 109-116.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1549-9316 URL |
| [8] |
Jacobs, J. J.; Gilbert, J. L.; Urban, R. M. Corrosion of metal orthopaedic implants. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998, 80, 268-282.
doi: 10.2106/00004623-199802000-00015 URL |
| [9] |
Lhotka, C.; Szekeres, T.; Steffan, I.; Zhuber, K.; Zweymüller, K. Four-year study of cobalt and chromium blood levels in patients managed with two different metal-on-metal total hip replacements. J Orthop Res. 2003, 21, 189-195.
doi: 10.1016/S0736-0266(02)00152-3 URL |
| [10] |
Jacobs, J. J.; Skipor, A. K.; Patterson, L. M.; Hallab, N. J.; Paprosky, W. G.; Black, J.; Galante, J. O. Metal release in patients who have had a primary total hip arthroplasty. A prospective, controlled, longitudinal study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998, 80, 1447-1458.
doi: 10.2106/00004623-199810000-00006 URL |
| [11] | Park, J. B.; Kim, Y. K. Metallic Biomaterials. In Biomaterials, Wong, J. Y.; Bronzino, J. D., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, 2007; pp 1-22. |
| [12] |
Gilardino, M. S.; Chen, E.; Bartlett, S. P. Choice of internal rigid fixation materials in the treatment of facial fractures. Craniomaxillofac Trauma Reconstr. 2009, 2, 49-60.
doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1202591 URL |
| [13] |
Grünewald, T. A.; Rennhofer, H.; Hesse, B.; Burghammer, M.; Stanzl-Tschegg, S. E.; Cotte, M.; Löffler, J. F.; Weinberg, A. M.; Lichtenegger, H. C. Magnesium from bioresorbable implants: Distribution and impact on the nano- and mineral structure of bone. Biomaterials. 2016, 76, 250-260.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.10.054 URL |
| [14] |
Chen, Y.; Xu, Z.; Smith, C.; Sankar, J. Recent advances on the development of magnesium alloys for biodegradable implants. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 4561-4573.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2014.07.005 URL |
| [15] |
Rahim, M. I.; Ullah, S.; Mueller, P. P. Advances and challenges of biodegradable implant materials with a focus on magnesium-alloys and bacterial infections. Metals. 2018, 8, 532.
doi: 10.3390/met8070532 URL |
| [16] |
Staiger, M. P.; Pietak, A. M.; Huadmai, J.; Dias, G. Magnesium and its alloys as orthopedic biomaterials: a review. Biomaterials. 2006, 27, 1728-1734.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2005.10.003 URL |
| [17] |
Witte, F.; Fischer, J.; Nellesen, J.; Crostack, H. A.; Kaese, V.; Pisch, A.; Beckmann, F.; Windhagen, H. In vitro and in vivo corrosion measurements of magnesium alloys. Biomaterials. 2006, 27, 1013-1018.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2005.07.037 URL |
| [18] |
McBride, E. D. Absorbable metal in bone surgery: A further report on the use of magnesium alloys. J Am Med Assoc. 1938, 111, 2464-2467.
doi: 10.1001/jama.1938.02790530018007 URL |
| [19] | Witte, F. Reprint of: The history of biodegradable magnesium implants: A review. Acta Biomater. 2015, 23 Suppl, S28-40. |
| [20] |
Badar, M.; Lünsdorf, H.; Evertz, F.; Rahim, M. I.; Glasmacher, B.; Hauser, H.; Mueller, P. P. The formation of an organic coat and the release of corrosion microparticles from metallic magnesium implants. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 7580-7589.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2013.03.012 URL |
| [21] |
Han, P.; Cheng, P.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, C.; Ni, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, W.; Hou, P.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Chai, Y. In vitro and in vivo studies on the degradation of high-purity Mg (99.99wt.%) screw with femoral intracondylar fractured rabbit model. Biomaterials. 2015, 64, 57-69.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.06.031 URL |
| [22] |
Plaass, C.; von Falck, C.; Ettinger, S.; Sonnow, L.; Calderone, F.; Weizbauer, A.; Reifenrath, J.; Claassen, L.; Waizy, H.; Daniilidis, K.; Stukenborg-Colsman, C.; Windhagen, H. Bioabsorbable magnesium versus standard titanium compression screws for fixation of distal metatarsal osteotomies - 3 year results of a randomized clinical trial. J Orthop Sci. 2018, 23, 321-327.
doi: 10.1016/j.jos.2017.11.005 URL |
| [23] |
Seitz, J.-M.; Lucas, A.; Kirschner, M. Magnesium-based compression screws: a novelty in the clinical use of implants. JOM. 2016, 68, 1177-1182.
doi: 10.1007/s11837-015-1773-1 URL |
| [24] |
Rapetto, C.; Leoncini, M. Magmaris: a new generation metallic sirolimus-eluting fully bioresorbable scaffold: present status and future perspectives. J Thorac Dis. 2017, 9, S903-s913.
doi: 10.21037/jtd URL |
| [25] |
Noviana, D.; Paramitha, D.; Ulum, M. F.; Hermawan, H. The effect of hydrogen gas evolution of magnesium implant on the postimplantation mortality of rats. J Orthop Translat. 2016, 5, 9-15.
doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2015.08.003 URL |
| [26] | Loukil, N. Alloying elements of magnesium alloys: a literature review. In Magnesium alloys structure and properties, Tański, T. A.; Jarka, P., eds.; IntechOpen Limited: London, 2021. |
| [27] |
Liu, C.; Xin, Y.; Tang, G.; Chu, P. K. Influence of heat treatment on degradation behavior of bio-degradable die-cast AZ63 magnesium alloy in simulated body fluid. Mater Sci Eng A. 2007, 456, 350-357.
doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2006.12.020 URL |
| [28] |
Wang, Y.; Liu, G.; Fan, Z. A new heat treatment procedure for rheo-diecast AZ91D magnesium alloy. Scripta Mater. 2006, 54, 903-908.
doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2005.10.073 URL |
| [29] |
Zeng, R. C.; Zhang, J.; Huang, W.J.; Dietzel, W.; Kainer, K. U.; Blawert, C.; Ke, W. Review of studies on corrosion of magnesium alloys. Trans Nonfer Metals Soc China. 2006, 16, s763-s771.
doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(06)60297-5 URL |
| [30] |
Hornberger, H.; Virtanen, S.; Boccaccini, A. R. Biomedical coatings on magnesium alloys - a review. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 2442-2455.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2012.04.012 URL |
| [31] |
Gray, J. E.; Luan, B. Protective coatings on magnesium and its alloys — a critical review. J Alloys Compd. 2002, 336, 88-113.
doi: 10.1016/S0925-8388(01)01899-0 URL |
| [32] | Gonzalez, J.; Hou, R. Q.; Nidadavolu, E. P. S.; Willumeit-Römer, R.; Feyerabend, F. Magnesium degradation under physiological conditions - Best practice. Bioact Mater. 2018, 3, 174-185. |
| [33] |
Barfield, W. R.; Colbath, G.; DesJardins, J. D.; An, Y. H.; Hartsock, L. A. The potential of magnesium alloy use in orthopaedic surgery. Curr Orthop Pract. 2012, 23, 146-150.
doi: 10.1097/BCO.0b013e31824a553b URL |
| [34] |
Martinez Sanchez, A. H.; Luthringer, B. J.; Feyerabend, F.; Willumeit, R. Mg and Mg alloys: how comparable are in vitro and in vivo corrosion rates? A review. Acta Biomater. 2015, 13, 16-31.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2014.11.048 URL |
| [35] | Baino, F.; Yamaguchi, S. The use of simulated body fluid (SBF) for assessing materials bioactivity in the context of tissue engineering: review and challenges. Biomimetics (Basel). 2020, 5, 57. |
| [36] |
Song, G. L.; Atrens, A. Corrosion mechanisms of magnesium alloys. Adv Eng Mater. 1999, 1, 11-33.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1527-2648 URL |
| [37] | Zeng, R. C.; Yin, Z. Z.; Chen, X. B.; Xu, D. K. Corrosion Types of Magnesium Alloys. In Magnesium Alloys, Tański, T.; Borek, W.; Król, M., eds.; IntechOpen Limited: London, 2018. |
| [38] |
Li, W.; Li, N.; Zheng, Y.; Yuan, G. Fretting properties of biodegradable Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr alloy in air and in Hank’s solution. Sci Rep. 2016, 6, 35803.
doi: 10.1038/srep35803 URL |
| [39] |
Ghali, E.; Dietzel, W.; Kainer, K. U. General and localized corrosion of magnesium alloys: A critical review. J Mater Eng Perform. 2004, 13, 7-23.
doi: 10.1361/10599490417533 URL |
| [40] | Choudhary, L.; Singh Raman, R. K.; Hofstetter, J.; Uggowitzer, P. J. In-vitro characterization of stress corrosion cracking of aluminium-free magnesium alloys for temporary bio-implant applications. Mater Sci Eng CMater Biol Appl. 2014, 42, 629-636. |
| [41] |
Song, R. G.; Blawert, C.; Dietzel, W.; Atrens, A. A study on stress corrosion cracking and hydrogen embrittlement of AZ31 magnesium alloy. Mater Sci Eng A. 2005, 399, 308-317.
doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2005.04.003 URL |
| [42] |
Galvin, E.; O’Brien, D.; Cummins, C.; Mac Donald, B. J.; Lally, C. A strain-mediated corrosion model for bioabsorbable metallic stents. Acta Biomater. 2017, 55, 505-517.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2017.04.020 URL |
| [43] |
Törne, K.; Örnberg, A.; Weissenrieder, J. Influence of strain on the corrosion of magnesium alloys and zinc in physiological environments. Acta Biomater. 2017, 48, 541-550.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.10.030 URL |
| [44] |
Winzer, N.; Atrens, A.; Dietzel, W.; Raja, V. S.; Song, G.; Kainer, K. U. Characterisation of stress corrosion cracking (SCC) of Mg-Al alloys. Mater Sci Eng A. 2008, 488, 339-351.
doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2007.11.064 URL |
| [45] |
Snir, Y.; Ben-Hamu, G.; Eliezer, D.; Abramov, E. Effect of compression deformation on the microstructure and corrosion behavior of magnesium alloys. J Alloys Compd. 2012, 528, 84-90.
doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.03.010 URL |
| [46] |
Sezer, N.; Evis, Z.; Kayhan, S. M.; Tahmasebifar, A.; Koç, M. Review of magnesium-based biomaterials and their applications. J Magnes Alloys. 2018, 6, 23-43.
doi: 10.1016/j.jma.2018.02.003 URL |
| [47] | Kutz, M. Handbook of Materials Selection. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: 2002. |
| [48] |
Song, G.; Atrens, A. Understanding magnesium corrosion—a framework for improved alloy performance. Adv Eng Mater. 2003, 5, 837-858.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1527-2648 URL |
| [49] | Yin Yee Chin, P.; Cheok, Q.; Glowacz, A.; Caesarendra, W. A review of in-vivo and in-vitro real-time corrosion monitoring systems of biodegradable metal implants. Appl Sci. 2020, 10. |
| [50] |
Yin Yee Chin, P.; Cheok, Q.; Glowacz, A.; Caesarendra, W. A review of in-vivo and in-vitro real-time corrosion monitoring systems of biodegradable metal implants. Appl Sci. 2020, 10, 3141.
doi: 10.3390/app10093141 URL |
| [51] |
Wang, W.; Wu, H.; Zan, R.; Sun, Y.; Blawert, C.; Zhang, S.; Ni, J.; Zheludkevich, M. L.; Zhang, X. Microstructure controls the corrosion behavior of a lean biodegradable Mg-2Zn alloy. Acta Biomater. 2020, 107, 349-361.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.02.040 URL |
| [52] |
Walter, R.; Kannan, M. B. Influence of surface roughness on the corrosion behaviour of magnesium alloy. Mater Des. 2011, 32, 2350-2354.
doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2010.12.016 URL |
| [53] |
Mitchell, J.; Crow, N.; Nieto, A. Effect of surface roughness on pitting corrosion of AZ31 Mg alloy. Metals. 2020, 10, 651.
doi: 10.3390/met10050651 URL |
| [54] |
Jiang, P.; Blawert, C.; Zheludkevich, M. L. The corrosion performance and mechanical properties of Mg-Zn based alloys—a review. Corros Mater Degrad. 2020, 1, 92-158.
doi: 10.3390/cmd1010007 URL |
| [55] |
Eliezer, A.; Gutman, E. M.; Abramov, E.; Aghion, E. Corrosion fatigue and mechanochemical behavior of magnesium alloys. Corros Rev. 1998, 16, 1-26.
doi: 10.1515/CORRREV.1998.16.1-2.1 URL |
| [56] |
Melchers, R. E.; Jeffrey, R. J. Probabilistic models for steel corrosion loss and pitting of marine infrastructure. Reliab Eng Syst Saf. 2008, 93, 423-432.
doi: 10.1016/j.ress.2006.12.006 URL |
| [57] |
Li, S. X.; Yu, S. R.; Zeng, H. L.; Li, J. H.; Liang, R. Predicting corrosion remaining life of underground pipelines with a mechanically-based probabilistic model. J Pet Sci Eng. 2009, 65, 162-166.
doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2008.12.023 URL |
| [58] | Radouani, R.; Echcharqy, Y.; Essahli, M. Numerical simulation of galvanic corrosion between carbon steel and low alloy steel in a bolted joint. Int J Corros. 2017, 2017, 6174904. |
| [59] |
Deshpande, K. B. Validated numerical modelling of galvanic corrosion for couples: magnesium alloy (AE44)-mild steel and AE44-aluminium alloy (AA6063) in brine solution. Corros Sci. 2010, 52, 3514-3522.
doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2010.06.031 URL |
| [60] |
Xue, Y.; Horstemeyer, M. F.; McDowell, D. L.; El Kadiri, H.; Fan, J. Microstructure-based multistage fatigue modeling of a cast AE44 magnesium alloy. Int J Fatigue. 2007, 29, 666-676.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2006.07.005 URL |
| [61] |
Saito, K.; Kuniya, J. Mechanochemical model to predict stress corrosion crack growth of stainless steel in high temperature water. Corros Sci. 2001, 43, 1751-1766.
doi: 10.1016/S0010-938X(00)00173-6 URL |
| [62] |
Wenman, M. R.; Trethewey, K. R.; Jarman, S. E.; Chard-Tuckey, P. R. A finite-element computational model of chloride-induced transgranular stress-corrosion cracking of austenitic stainless steel. Acta Mater. 2008, 56, 4125-4136.
doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2008.04.068 URL |
| [63] |
da Costa-Mattos, H. S.; Bastos, I. N.; Gomes, J. A. C. P. A simple model for slow strain rate and constant load corrosion tests of austenitic stainless steel in acid aqueous solution containing sodium chloride. Corros Sci. 2008, 50, 2858-2866.
doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2008.07.020 URL |
| [64] |
Bolotin, V. V.; Shipkov, A. A. Mechanical aspects of corrosion fatigue and stress corrosion cracking. Int J Solids Struct. 2001, 38, 7297-7318.
doi: 10.1016/S0020-7683(01)00002-6 URL |
| [65] |
Garud, Y. S. Quantitative evaluation of environmentally assisted cracking: a survey of developments and application of modeling concepts. J Pressure Vessel Technol. 1991, 113, 1-9.
doi: 10.1115/1.2928722 URL |
| [66] | Gutman, E. M. Mechanochemistry of materials. Cambridge International Science Publishing Ltd: Cambridge, 1998. |
| [67] |
Movchan, T. G.; Esipova, N. E.; Eryukin, P. V.; Uriev, N. B.; Rusanov, A. I. Mechanochemical effects in processes of corrosion of metals. Russ J Gen Chem. 2005, 75, 1681-1686.
doi: 10.1007/s11176-005-0491-8 URL |
| [68] |
Gastaldi, D.; Sassi, V.; Petrini, L.; Vedani, M.; Trasatti, S.; Migliavacca, F. Continuum damage model for bioresorbable magnesium alloy devices - application to coronary stents. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2011, 4, 352-365.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2010.11.003 URL |
| [69] | Kachanov, L. M. Introduction to continuum damage mechanics. Springer Netherlands: 1986. |
| [70] |
Lévesque, J.; Hermawan, H.; Dubé, D.; Mantovani, D. Design of a pseudo-physiological test bench specific to the development of biodegradable metallic biomaterials. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 284-295.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2007.09.012 URL |
| [71] | Myrissa, A.; Agha, N. A.; Lu, Y.; Martinelli, E.; Eichler, J.; Szakács, G.; Kleinhans, C.; Willumeit-Römer, R.; Schäfer, U.; Weinberg, A. M. In vitro and in vivo comparison of binary Mg alloys and pure Mg. Mater Sci Eng CMater Biol Appl. 2016, 61, 865-874. |
| [72] |
Antoniac, I.; Adam, R.; Biță, A.; Miculescu, M.; Trante, O.; Petrescu, I. M.; Pogărășteanu, M. Comparative assessment of in vitro and in vivo biodegradation of Mg-1Ca magnesium alloys for orthopedic applications. Materials (Basel). 2020, 14, 84.
doi: 10.3390/ma14010084 URL |
| [73] |
Grogan, J. A.; O’Brien, B. J.; Leen, S. B.; McHugh, P. E. A corrosion model for bioabsorbable metallic stents. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 3523-3533.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2011.05.032 URL |
| [74] |
Abdalla, M.; Joplin, A.; Elahinia, M.; Ibrahim, H. Corrosion modeling of magnesium and its alloys for biomedical applications: review. Corros Mater Degrad. 2020, 1, 219-248.
doi: 10.3390/cmd1020011 URL |
| [75] | Oppeel, A. Experimental characterisation and finite element modeling of biodegradable magnesium stents. Ghent University: Ghent, 2014. |
| [76] |
Debusschere, N.; Segers, P.; Dubruel, P.; Verhegghe, B.; De Beule, M. A Computational framework to model degradation of biocorrodible metal stents using an implicit finite element solver. Ann Biomed Eng. 2016, 44, 382-390.
doi: 10.1007/s10439-015-1530-1 URL |
| [77] | Amerinatanzi, A.; Mehrabi, R.; Ibrahim, H.; Dehghan, A.; Shayesteh Moghaddam, N.; Elahinia, M. Predicting the biodegradation of magnesium alloy implants: modeling, parameter identification, and validation. Bioengineering (Basel, Switzerland). 2018, 5, 105. |
| [78] |
Wu, W.; Gastaldi, D.; Yang, K.; Tan, L.; Petrini, L.; Migliavacca, F. Finite element analyses for design evaluation of biodegradable magnesium alloy stents in arterial vessels. Mater Sci Eng B. 2011, 176, 1733-1740.
doi: 10.1016/j.mseb.2011.03.013 URL |
| [79] | Manivasagam, G.; Dhinasekaran, D.; Rajamanickam, A. Biomedical implants: corrosion and its prevention -a review. Recent Patents Corros Sci. 2010, 2, 40-54. |
| [80] | Kasemo, B.; Lausmaa, J. Surface science aspects on inorganic biomaterials. CRC Crit Rev Clin Neurobiol. 1986, 4, 335-380. |
| [81] |
Deshpande, K. B. Numerical modeling of micro-galvanic corrosion. Electrochim Acta. 2011, 56, 1737-1745.
doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2010.09.044 URL |
| [82] | Montoya, R.; Iglesias, C.; Escudero, M. L.; García-Alonso, M. C. Modeling in vivo corrosion of AZ31 as temporary biodegradable implants. Experimental validation in rats. Mater Sci Eng CMater Biol Appl. 2014, 41, 127-133. |
| [83] |
Scheiner, S.; Hellmich, C. Stable pitting corrosion of stainless steel as diffusion-controlled dissolution process with a sharp moving electrode boundary. Corros Sci. 2007, 49, 319-346.
doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2006.03.019 URL |
| [84] |
Grogan, J. A.; Leen, S. B.; McHugh, P. E. A physical corrosion model for bioabsorbable metal stents. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 2313-2322.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2013.12.059 URL |
| [85] | Dahms, M.; Höche, D.; Ahmad Agha, N.; Feyerabend, F.; Willumeit-Römer, R. A simple model for long-time degradation of magnesium under physiological conditions. Mater Corros. 2018, 69, 191-196. |
| [86] |
Bajger, P.; Ashbourn, J. M. A.; Manhas, V.; Guyot, Y.; Lietaert, K.; Geris, L. Mathematical modelling of the degradation behaviour of biodegradable metals. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2017, 16, 227-238.
doi: 10.1007/s10237-016-0812-3 URL |
| [87] |
Birbilis, N.; Easton, M. A.; Sudholz, A. D.; Zhu, S. M.; Gibson, M. A. On the corrosion of binary magnesium-rare earth alloys. Corros Sci. 2009, 51, 683-689.
doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2008.12.012 URL |
| [88] |
Shen, Z.; Zhao, M.; Bian, D.; Shen, D.; Zhou, X.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Guo, H.; Zheng, Y. Predicting the degradation behavior of magnesium alloys with a diffusion-based theoretical model and in vitro corrosion testing. J Mater Sci Technol. 2019, 35, 1393-1402.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmst.2019.02.004 URL |
| [89] | Ornelas-Tellez, F.; Rico-Melgoza, J. J.; Villafuerte, A. E.; Zavala-Mendoza, F. J. Chapter 3 - Neural networks: a methodology for modeling and control design of dynamical systems. In Artificial neural networks for engineering applications, Alanis, A. Y.; Arana-Daniel, N.; López-Franco, C., eds.; Academic Press: 2019; pp 21-38. |
| [90] | Bulutsuz, A. G.; Yetilmezsoy, K.; Durakbasa, N. Application of fuzzy logic methodology for predicting dynamic measurement errors related to process parameters of coordinate measuring machines. J Intell Fuzzy Syst. 2015, 29, 1619-1633. |
| [91] |
Kamrunnahar, M.; Urquidi-Macdonald, M. Prediction of corrosion behaviour of Alloy 22 using neural network as a data mining tool. Corros Sci. 2011, 53, 961-967.
doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2010.11.028 URL |
| [92] | Kirkland, N. T.; Staiger, M. P.; Nisbet, D.; Davies, C. H. J.; Birbilis, N. Performance-driven design of Biocompatible Mg alloys. JOM. 2011, 63, 28-34. |
| [93] |
Birbilis, N.; Cavanaugh, M. K.; Sudholz, A. D.; Zhu, S. M.; Easton, M. A.; Gibson, M. A. A combined neural network and mechanistic approach for the prediction of corrosion rate and yield strength of magnesium-rare earth alloys. Corros Sci. 2011, 53, 168-176.
doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2010.09.013 URL |
| [94] |
Willumeit, R.; Feyerabend, F.; Huber, N. Magnesium degradation as determined by artificial neural networks. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 8722-8729.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2013.02.042 URL |
| [95] |
Xia, X.; Nie, J. F.; Davies, C. H. J.; Tang, W. N.; Xu, S. W.; Birbilis, N. An artificial neural network for predicting corrosion rate and hardness of magnesium alloys. Mater Des. 2016, 90, 1034-1043.
doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2015.11.040 URL |
| [96] |
Alhumade, H.; Rezk, H.; Nassef, A. M.; Al-Dhaifallah, M. Fuzzy logic based-modeling and parameter optimization for improving the corrosion protection of stainless steel 304 by epoxy-graphene composite. IEEE Access. 2019, 7, 100899-100909.
doi: 10.1109/Access.6287639 URL |
| [97] | Nava-Dino, C. G.; Orozco-Carmona, V. M.; Monreal-Romero, H. A.; Martínez-García, E. A.; Bautista-Margulis; Neri-Flores, M. A.; Chacón-Nava, J. G.; Martínez-Villafañe, A. Fuzzy sets and electrochemical noise to predict corrosion behavior of Ti alloys. Int J Electrochem Sci. 2013, 8, 4996-5006. |
| [98] |
Bahmani, A.; Arthanari, S.; Shin, K. S. Formulation of corrosion rate of magnesium alloys using microstructural parameters. J Magnes Alloys. 2020, 8, 134-149.
doi: 10.1016/j.jma.2019.12.001 URL |
| [99] |
Mei, D.; Lamaka, S. V.; Lu, X.; Zheludkevich, M. L. Selecting medium for corrosion testing of bioabsorbable magnesium and other metals - a critical review. Corros Sci. 2020, 171, 108722.
doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2020.108722 URL |
| [100] | ASTM G31-21. Standard Guide for Laboratory Immersion Corrosion Testing of Metals. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, 2021. |
| [101] | ASTM G1-03(2017)e1. Standard Practice for Preparing, Cleaning, and Evaluating Corrosion Test Specimens. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, 2017. |
| [102] | Song, G.; Atrens, A.; StJohn, D. An hydrogen evolution method for the estimation of the corrosion rate of magnesium alloys. In Magnesium technology, Hryn, J. N., ed. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: 2001. |
| [103] |
Kray, R. H. Modified hydrogen evolution method for metallic magnesium, aluminum, and zinc. Ind Eng Chem Anal Ed. 1934, 6, 250-251.
doi: 10.1021/ac50090a007 URL |
| [104] |
Sekar, P.; S, N.; Desai, V. Recent progress in in vivo studies and clinical applications of magnesium based biodegradable implants - A review. J Magnes Alloys. 2021, 9, 1147-1163.
doi: 10.1016/j.jma.2020.11.001 URL |
| [105] | Gao, X.; Dai, C. Y.; Jia, Q.; Zhai, C.; Shi, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, B. C.; Cai, H.; Lee, E. S.; Jiang, H. B. In vivo corrosion behavior of biodegradable magnesium alloy by MAF treatment. Scanning. 2021, 2021, 5530788. |
| [106] |
Kawamura, N.; Nakao, Y.; Ishikawa, R.; Tsuchida, D.; Iijima, M. Degradation and biocompatibility of AZ31 magnesium alloy implants in vitro and in vivo: a micro-computed tomography study in rats. Materials (Basel). 2020, 13, 473.
doi: 10.3390/ma13020473 URL |
| [107] | Xu, Y.; Meng, H.; Yin, H.; Sun, Z.; Peng, J.; Xu, X.; Guo, Q.; Xu, W.; Yu, X.; Yuan, Z.; Xiao, B.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Lu, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, A. Quantifying the degradation of degradable implants and bone formation in the femoral condyle using micro-CT 3D reconstruction. Exp Ther Med. 2018, 15, 93-102. |
| [108] |
Wang, X.; Shao, X.; Dai, T.; Xu, F.; Zhou, J. G.; Qu, G.; Tian, L.; Liu, B.; Liu, Y. In vivo study of the efficacy, biosafety, and degradation of a zinc alloy osteosynthesis system. Acta Biomater. 2019, 92, 351-361.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.05.001 URL |
| [109] | Thorngren, K. G. Proceedings of the Swedish Orthopedic Society Helsingborg, June 1-2, 1987. Acta Orthop Scand. 1988, 59, 77-100. |
| [110] |
Wang, Z. L.; Yu, S.; Sether, L. A.; Haughton, V. M. Incidence of unfused ossicles in the lumbar facet joints: CT, MR, and cryomicrotomy study. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1989, 13, 594-597.
doi: 10.1097/00004728-198907000-00007 URL |
| [111] |
Kapadia, R. D.; Stroup, G. B.; Badger, A. M.; Koller, B.; Levin, J. M.; Coatney, R. W.; Dodds, R. A.; Liang, X.; Lark, M. W.; Gowen, M. Applications of micro-CT and MR microscopy to study pre-clinical models of osteoporosis and osteoarthritis. Technol Health Care. 1998, 6, 361-372.
doi: 10.3233/THC-1998-65-609 URL |
| [112] |
Ding, M.; Odgaard, A.; Hvid, I. Accuracy of cancellous bone volume fraction measured by micro-CT scanning. J Biomech. 1999, 32, 323-326.
doi: 10.1016/S0021-9290(98)00176-6 URL |
| [113] | Salmon, P. Micro-CT 3D image analysis techniques for orthopedic applications: metal implant-to-bone contact surface and porosity of biomaterials. In A practical manual for musculoskeletal research, World Scientific: 2008; pp 583-603. |
| [114] |
Rhee, Y.; Hur, J. H.; Won, Y. Y.; Lim, S. K.; Beak, M. H.; Cui, W. Q.; Kim, K. G.; Kim, Y. E. Assessment of bone quality using finite element analysis based upon micro-CT images. Clin Orthop Surg. 2009, 1, 40-47.
doi: 10.4055/cios.2009.1.1.40 URL |
| [115] |
Suen, P. K.; Zhu, T. Y.; Chow, D. H.; Huang, L.; Zheng, L. Z.; Qin, L. Sclerostin antibody treatment increases bone formation, bone mass, and bone strength of intact bones in adult male rats. Sci Rep. 2015, 5, 15632.
doi: 10.1038/srep15632 URL |
| [116] | Wang, J.; Bi, L.; Bai, J. P.; Lyu, R.; Yang, B. K. Comparative study of micro-CT and histological section in bone morphometry. Zhongguo Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 2009, 17, 381-384. |
| [117] |
Buie, H. R.; Campbell, G. M.; Klinck, R. J.; MacNeil, J. A.; Boyd, S. K. Automatic segmentation of cortical and trabecular compartments based on a dual threshold technique for in vivo micro-CT bone analysis. Bone. 2007, 41, 505-515.
doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2007.07.007 URL |
| [118] |
Doepke, A.; Kuhlmann, J.; Guo, X.; Voorhees, R. T.; Heineman, W. R. A system for characterizing Mg corrosion in aqueous solutions using electrochemical sensors and impedance spectroscopy. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 9211-9219.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2013.07.011 URL |
| [119] |
Wang, J.; Jang, Y.; Wan, G.; Giridharan, V.; Song, G. L.; Xu, Z.; Koo, Y.; Qi, P.; Sankar, J.; Huang, N.; Yun, Y. Flow-induced corrosion of absorbable magnesium alloy: In-situ and real-time electrochemical study. Corros Sci. 2016, 104, 277-289.
doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2015.12.020 URL |
| [120] |
Zhao, D.; Wang, T.; Nahan, K.; Guo, X.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, Z.; Chen, S.; Chou, D. T.; Hong, D.; Kumta, P. N.; Heineman, W. R. In vivo characterization of magnesium alloy biodegradation using electrochemical H(2) monitoring, ICP-MS, and XPS. Acta Biomater. 2017, 50, 556-565.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2017.01.024 URL |
| [121] |
Zhao, D.; Wang, T.; Kuhlmann, J.; Dong, Z.; Chen, S.; Joshi, M.; Salunke, P.; Shanov, V. N.; Hong, D.; Kumta, P. N.; Heineman, W. R. In vivo monitoring the biodegradation of magnesium alloys with an electrochemical H2 sensor. Acta Biomater. 2016, 36, 361-368.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.03.039 URL |
| [122] |
Zhao, D.; Wang, T.; Hoagland, W.; Benson, D.; Dong, Z.; Chen, S.; Chou, D. T.; Hong, D.; Wu, J.; Kumta, P. N.; Heineman, W. R. Visual H(2) sensor for monitoring biodegradation of magnesium implants in vivo. Acta Biomater. 2016, 45, 399-409.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.08.049 URL |
| [123] | Boutry, C. M.; Chandrahalim, H.; Streit, P.; Schinhammer, M.; Hänzi, A. C.; Hierold, C. Towards biodegradable wireless implants. Philos Trans R Soc AMath Phys Eng Sci. 2012, 370, 2418-2432. |
| [124] |
Su Natasha, M.; Malon, R. S. P.; Wicaksono, D. H. B.; Córcoles, E. P.; Hermawan, H. Monitoring magnesium degradation using microdialysis and fabric-based biosensors. Sci China Mater. 2018, 61, 643-651.
doi: 10.1007/s40843-017-9069-3 URL |
| [125] | Ulrich, A.; Ott, N.; Tournier-Fillon, A.; Homazava, N.; Schmutz, P. Investigation of corrosion behavior of biodegradable magnesium alloys using an online-micro-flow capillary flow injection inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry setup with electrochemical control. Spectrochim Acta Part BAt Spectrosc. 2011, 66, 536-545. |
| [126] |
Witte, F.; Kaese, V.; Haferkamp, H.; Switzer, E.; Meyer-Lindenberg, A.; Wirth, C. J.; Windhagen, H. In vivo corrosion of four magnesium alloys and the associated bone response. Biomaterials. 2005, 26, 3557-3563.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2004.09.049 URL |
| [127] | Ma, S.; Zhou, B.; Markert, B. Numerical simulation of the tissue differentiation and corrosion process of biodegradable magnesium implants during bone fracture healing. ZAngew Math Mech. 2018, 98, 2223-2238. |
| [128] |
Mehboob, H.; Chang, S. H. Evaluation of healing performance of biodegradable composite bone plates for a simulated fractured tibia model by finite element analysis. Compos Struct. 2014, 111, 193-204.
doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2013.12.013 URL |
| [129] |
Costantino, M. D.; Schuster, A.; Helmholz, H.; Meyer-Rachner, A.; Willumeit-Römer, R.; Luthringer-Feyerabend, B. J. C. Inflammatory response to magnesium-based biodegradable implant materials. Acta Biomater. 2020, 101, 598-608.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.10.014 URL |
| [130] |
Jin, L.; Wu, J.; Yuan, G.; Chen, T. In vitro study of the inflammatory cells response to biodegradable Mg-based alloy extract. PLoS One. 2018, 13, e0193276.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0193276 URL |
| [131] |
Tsakiris, V.; Tardei, C.; Clicinschi, F. M. Biodegradable Mg alloys for orthopedic implants - A review. J Magnes Alloys. 2021. doi: 10.1016/j.jma.2021.06.024.
doi: 10.1016/j.jma.2021.06.024 URL |
| [132] | Walker, J.; Shadanbaz, S.; Kirkland, N. T.; Stace, E.; Woodfield, T.; Staiger, M. P.; Dias, G. J. Magnesium alloys: predicting in vivo corrosion with in vitro immersion testing. J Biomed Mater Res BAppl Biomater. 2012, 100, 1134-1141. |
| [133] |
Baroncelli, G. I. Quantitative ultrasound methods to assess bone mineral status in children: technical characteristics, performance, and clinical application. Pediatr Res. 2008, 63, 220-228.
doi: 10.1203/PDR.0b013e318163a286 URL |
| [134] |
Gao, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, L.; Gu, X.; Zhang, K.; Xia, J.; Fan, Y. Effect of stress on corrosion of high-purity magnesium in vitro and in vivo. Acta Biomater. 2019, 83, 477-486.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2018.11.019 URL |
| [1] | Yiqiang Hu, Yuan Xiong, Ranyang Tao, Hang Xue, Lang Chen, Ze Lin, Adriana C. Panayi, Bobin Mi, Guohui Liu. Advances and perspective on animal models and hydrogel biomaterials for diabetic wound healing [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2022, 3(3): 188-200. |
| [2] | Dafna Benayahu. Mesenchymal stem cell differentiation and usage for biotechnology applications: tissue engineering and food manufacturing [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2022, 3(1): 17-23. |
| [3] | Shuqin Cao, Quan Yuan. An update of nanotopographical surfaces in modulating stem cell fate: a narrative review [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2022, 3(1): 55-64. |
| [4] | Emma Steijvers, Armaan Ghei, Zhidao Xia. Manufacturing artificial bone allografts: a perspective [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2022, 3(1): 65-80. |
| [5] | Ke Hu, Yuxuan Li, Zunxiang Ke, Hongjun Yang, Chanjun Lu, Yiqing Li, Yi Guo, Weici Wang. History, progress and future challenges of artificial blood vessels: a narrative review [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2022, 3(1): 81-98. |
| [6] | Yizhong Peng, Jinye Li, Hui Lin, Shuo Tian, Sheng Liu, Feifei Pu, Lei Zhao, Kaige Ma, Xiangcheng Qing, Zengwu Shao. Endogenous repair theory enriches construction strategies for orthopaedic biomaterials: a narrative review [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2021, 2(4): 343-360. |
| [7] | Ge Yan, Yuqi Liu, Minghui Xie, Jiawei Shi, Weihua Qiao, Nianguo Dong. Experimental and computational models for tissue-engineered heart valves: a narrative review [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2021, 2(4): 361-375. |
| [8] | Ying Luo, Jue Wang, Michael Tim Yun Ong, Patrick Shu-hang Yung, Jiali Wang, Ling Qin. Update on the research and development of magnesium-based biodegradable implants and their clinical translation in orthopaedics [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2021, 2(3): 188-196. |
| [9] | Xirui Jing, Qiuyue Ding, Qinxue Wu, Weijie Su, Keda Yu, Yanlin Su, Bing Ye, Qing Gao, Tingfang Sun, Xiaodong Guo. Magnesium-based materials in orthopaedics: material properties and animal models [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2021, 2(3): 197-213. |
| [10] | Yu Lu, Subodh Deshmukh, Ian Jones, Yu-Lung Chiu. Biodegradable magnesium alloys for orthopaedic applications [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2021, 2(3): 214-235. |
| [11] | Jialin Niu, Hua Huang, Jia Pei, Zhaohui Jin, Shaokang Guan, Guangyin Yuan. Research and development strategy for biodegradable magnesium-based vascular stents: a review [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2021, 2(3): 236-247. |
| [12] | Qingchuan Wang, Weidan Wang, Yanfang Li, Weirong Li, Lili Tan, Ke Yang. Biofunctional magnesium coating of implant materials by physical vapour deposition [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2021, 2(3): 248-256. |
| [13] | Jing Long, Bin Teng, Wei Zhang, Long Li, Ming Zhang, Yingqi Chen, Zhenyu Yao, Xiangbo Meng, Xinluan Wang, Ling Qin, Yuxiao Lai. Preclinical evaluation of acute systemic toxicity of magnesium incorporated poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) porous scaffolds by three-dimensional printing [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2021, 2(3): 272-284. |
| [14] | Kamolrat Metavarayuth, Esteban Villarreal, Hui Wang, Qian Wang. Surface topography and free energy regulate osteogenesis of stem cells: effects of shape-controlled gold nanoparticles [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2021, 2(2): 165-173. |
| [15] | Yizhong Peng, Xiangcheng Qing, Hongyang Shu, Shuo Tian, Wenbo Yang, Songfeng Chen, Hui Lin, Xiao Lv, Lei Zhao, Xi Chen, Feifei Pu, Donghua Huang, Xu Cao, Zengwu Shao. Proper animal experimental designs for preclinical research of biomaterials for intervertebral disc regeneration [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2021, 2(2): 91-142. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||