Biomaterials Translational ›› 2023, Vol. 4 ›› Issue (4): 234-247.doi: 10.12336/biomatertransl.2023.04.004
• REVIEW • Previous Articles Next Articles
Chen-Hui Mi1#, Xin-Ya Qi1#, Yan-Wen Ding1#, Jing Zhou1, Jin-Wei Dao1,3, Dai-Xu Wei1,2,4,*( )
)
Received:2023-10-14
Revised:2023-11-03
Accepted:2023-11-29
Online:2023-12-27
Published:2023-12-28
Contact:
Dai-Xu Wei, daviddxwei@163.com, or weidaixu@nwu.edu.cn.
About author:#Author equally.
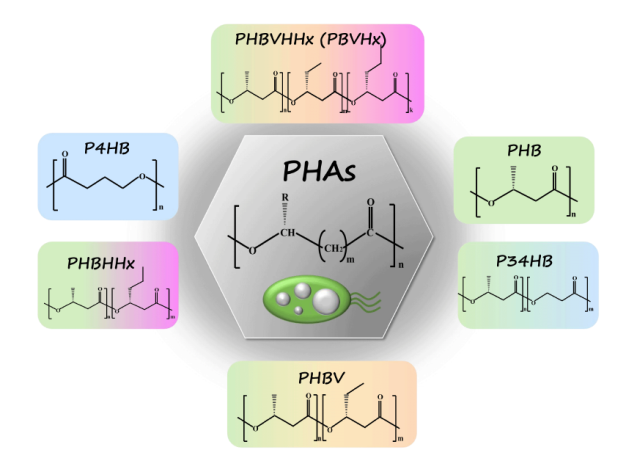
Figure 1. The general structure of PHAs and six commercial PHAs. Created with ChemDraw 2022 and Microsoft PowerPoint 2019. P34HB: poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate); P4HB: poly(4-hydroxybutyric acid); PHA: polyhydroxyalkanoate; PHB: poly(3-hydroxybutyric acid); PHBHHx: poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate); PHBV: poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate); PHBVHHx (PBVHx): poly(3-hydroxybutyric acid-co-3-hydroxyvaleric acid-co-3-hydroxyhexanoic acid trimer).
| Application | Material type | Fabrication method | Function | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bone | PHB/BC | Salt leaching technique | Promote bone formation in critical size calvarial defects in mice | |
| PHAs/Se-Sr-HA | Solvent casting | A high reduction of the number of Staphylococcus aureus 6538P and Escherichia coli 8739 bacterial cells | ||
| PHBV/PLGA | Computer-aided wet-spinning | Support murine preosteoblast cell colonisation and differentiation towards an osteoblastic phenotype | ||
| TCP/PHO | Soaking and drying | Enhance the wettability towards more cell-friendly material, enhance the durability of the composites (stress-strain characteristics) | ||
| P(3HO-co-3HHX)/HA | Solvent casting‐particulate leaching | Allow migration and proliferation of osteoblasts and mesenchymal cells as well as vascularisation | ||
| IM-BM(PLLA+CPC+PHA) | Electrospinning | Reinforce and stabilise incomplete fractures with both mechanical testing and an animal experiment | ||
| βTCP/P(3HB) | Polyurethane sponge replica method followed by polymer infiltration | Provide cell-friendly environment, ensure high cell viability, and reduce surface hydrophobicity | ||
| PHBV/MBGN/CIN | Emulsion solvent extraction/evaporation | High biological activity and antibacterial performance applied simultaneously in bone tissue engineering | ||
| Cartilage and joint | Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate)/poly(3-hydroxyoctanoate) | Electrospinning | Allow to produce a cartilage repair kit for clinical use to reduce the risk of developing secondary osteoarthritis | |
| PLCL/PHBV | Emulsion solvent evaporation | Enhance the compressive modulus of PLCL scaffolds, but could also serve as scaffolding structures for cartilaginous tissue formation | ||
| PHB-CS/HNT | Electrospinning | Demonstrate a significant increase in cell viability of chondrocytes | ||
| PHB-starch/HNTs | Electrospinning | Improve the tensile strength, support cell growth and attachment without any toxicity for biomedical applications | ||
| PhaP-RGD/PHBHHx | Solvent evaporation | The biomaterial films of PHBHHx modified with PhaP-RGD fusion protein can promote its biocompatibility with chondrocytes | ||
| Promote the proliferation and chondrogenic differentiation of human umbilical-cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells seeded on PHBHHx films | ||||
| Lead to more homogeneous cell spreading, better cell adhesion, proliferation and chondrogenic differentiation in the scaffolds | ||||
| Skin | PHB/PHB-HV | Electrospinning | Improve vascularisation of engineered bone tissue | |
| PHB/CA | Electrospinning | Improve cell proliferation | ||
| PHB/HEAA | Grafting | Promote the proliferation of human fibroblasts | ||
| P(3HB-co-4HB) | Freeze-drying | Promote the adhesion of mouse fibroblasts | ||
| PHB | Electrospinning | Support the growth of normal human dermal fibroblasts and keratinocytes | ||
| Promote the healing of diabetic wounds | ||||
| PHBA/CA | Electrospinning | Improve fibroblast adhesion and growth | ||
| Tendon and ligament | PHB/PHBV/PHUE/PHOUE | Electrospinning | Promote cell adhesion and proliferation | |
| PHBHHX | Electrospinning | Promote tendon repair in vivo, which is conducive to restoring weight-bearing and motor function | ||
| Make thin films | Promote adhesion and migration of mesenchymal stem cells and tendon cells | |||
| PHA | Mesh-augmented single-row RCRs and nonaugmented RCRs | Improve the initial biomechanical repair strength of tears at risk of rupture | ||
| Cardiovascular | PHA | Electrospinning | Promote the fusion of scaffolds with cells | |
| PHB | Electrospinning | Promote the adhesion and growth of cardiomyocytes and cardiac fibroblasts | ||
| PHBHHx/SF | Make thin films | Promote cell adhesion and proliferation | ||
| P(3HO) | Cardiac patches | Promote the adhesion and proliferation of neonatal ventricular rat muscle cells | ||
| Nervous | PHB | Electrospinning | Have high biocompatibility with human mesenchymal stem cells | |
| Promotes the adhesion and differentiation of embryonic cells into nerve cells | ||||
| Support the survival and regeneration of neurons after spinal cord injury | ||||
| PHB/PHBV | Electrospinning | Promote the interaction between Schwann cells and scaffolds | ||
| Triggers the activity of Schwann cells | ||||
| PCL-PHB | Electrospinning | Pluripotent stem cells were induced to differentiate into neurons | ||
| PHBHHx | Porous nerve conduit | Have good nerve regeneration ability, which can promote the rapid functional recovery of damaged nerves | ||
| Electrospinning | Promote the differentiation of neural stem cells into neurons |
Table 1. Applications of PHAs in the musculoskeletal system
| Application | Material type | Fabrication method | Function | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bone | PHB/BC | Salt leaching technique | Promote bone formation in critical size calvarial defects in mice | |
| PHAs/Se-Sr-HA | Solvent casting | A high reduction of the number of Staphylococcus aureus 6538P and Escherichia coli 8739 bacterial cells | ||
| PHBV/PLGA | Computer-aided wet-spinning | Support murine preosteoblast cell colonisation and differentiation towards an osteoblastic phenotype | ||
| TCP/PHO | Soaking and drying | Enhance the wettability towards more cell-friendly material, enhance the durability of the composites (stress-strain characteristics) | ||
| P(3HO-co-3HHX)/HA | Solvent casting‐particulate leaching | Allow migration and proliferation of osteoblasts and mesenchymal cells as well as vascularisation | ||
| IM-BM(PLLA+CPC+PHA) | Electrospinning | Reinforce and stabilise incomplete fractures with both mechanical testing and an animal experiment | ||
| βTCP/P(3HB) | Polyurethane sponge replica method followed by polymer infiltration | Provide cell-friendly environment, ensure high cell viability, and reduce surface hydrophobicity | ||
| PHBV/MBGN/CIN | Emulsion solvent extraction/evaporation | High biological activity and antibacterial performance applied simultaneously in bone tissue engineering | ||
| Cartilage and joint | Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate)/poly(3-hydroxyoctanoate) | Electrospinning | Allow to produce a cartilage repair kit for clinical use to reduce the risk of developing secondary osteoarthritis | |
| PLCL/PHBV | Emulsion solvent evaporation | Enhance the compressive modulus of PLCL scaffolds, but could also serve as scaffolding structures for cartilaginous tissue formation | ||
| PHB-CS/HNT | Electrospinning | Demonstrate a significant increase in cell viability of chondrocytes | ||
| PHB-starch/HNTs | Electrospinning | Improve the tensile strength, support cell growth and attachment without any toxicity for biomedical applications | ||
| PhaP-RGD/PHBHHx | Solvent evaporation | The biomaterial films of PHBHHx modified with PhaP-RGD fusion protein can promote its biocompatibility with chondrocytes | ||
| Promote the proliferation and chondrogenic differentiation of human umbilical-cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells seeded on PHBHHx films | ||||
| Lead to more homogeneous cell spreading, better cell adhesion, proliferation and chondrogenic differentiation in the scaffolds | ||||
| Skin | PHB/PHB-HV | Electrospinning | Improve vascularisation of engineered bone tissue | |
| PHB/CA | Electrospinning | Improve cell proliferation | ||
| PHB/HEAA | Grafting | Promote the proliferation of human fibroblasts | ||
| P(3HB-co-4HB) | Freeze-drying | Promote the adhesion of mouse fibroblasts | ||
| PHB | Electrospinning | Support the growth of normal human dermal fibroblasts and keratinocytes | ||
| Promote the healing of diabetic wounds | ||||
| PHBA/CA | Electrospinning | Improve fibroblast adhesion and growth | ||
| Tendon and ligament | PHB/PHBV/PHUE/PHOUE | Electrospinning | Promote cell adhesion and proliferation | |
| PHBHHX | Electrospinning | Promote tendon repair in vivo, which is conducive to restoring weight-bearing and motor function | ||
| Make thin films | Promote adhesion and migration of mesenchymal stem cells and tendon cells | |||
| PHA | Mesh-augmented single-row RCRs and nonaugmented RCRs | Improve the initial biomechanical repair strength of tears at risk of rupture | ||
| Cardiovascular | PHA | Electrospinning | Promote the fusion of scaffolds with cells | |
| PHB | Electrospinning | Promote the adhesion and growth of cardiomyocytes and cardiac fibroblasts | ||
| PHBHHx/SF | Make thin films | Promote cell adhesion and proliferation | ||
| P(3HO) | Cardiac patches | Promote the adhesion and proliferation of neonatal ventricular rat muscle cells | ||
| Nervous | PHB | Electrospinning | Have high biocompatibility with human mesenchymal stem cells | |
| Promotes the adhesion and differentiation of embryonic cells into nerve cells | ||||
| Support the survival and regeneration of neurons after spinal cord injury | ||||
| PHB/PHBV | Electrospinning | Promote the interaction between Schwann cells and scaffolds | ||
| Triggers the activity of Schwann cells | ||||
| PCL-PHB | Electrospinning | Pluripotent stem cells were induced to differentiate into neurons | ||
| PHBHHx | Porous nerve conduit | Have good nerve regeneration ability, which can promote the rapid functional recovery of damaged nerves | ||
| Electrospinning | Promote the differentiation of neural stem cells into neurons |
| 1. |
Barone, R.; Szychlinska, M. A. Highlights in pathophysiology of the musculoskeletal system. Int J Mol Sci. 2023, 24, 6412.
doi: 10.3390/ijms24076412 URL |
| 2. |
Christensen, L. V.Physiology and pathophysiology of skeletal muscle contractions. Part I. Dynamic activity. J Oral Rehabil. 1986, 13, 451-461.
doi: 10.1111/jor.1986.13.issue-5 URL |
| 3. |
Christensen, L. V.Physiology and pathophysiology of skeletal muscle contractions. Part II. Static activity. J Oral Rehabil. 1986, 13, 463-477.
doi: 10.1111/jor.1986.13.issue-5 URL |
| 4. |
Evans, C. H. Advances in regenerative orthopedics. Mayo Clin Proc. 2013, 88, 1323-1339.
doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2013.04.027 URL |
| 5. |
Evans, C. H.; Huard, J. Gene therapy approaches to regenerating the musculoskeletal system. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015, 11, 234-242.
doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2015.28 |
| 6. |
Gobbi, A.; Francisco, R. A.; Lubowitz, J. H.; Allegra, F.; Canata, G. Osteochondral lesions of the talus: randomized controlled trial comparing chondroplasty, microfracture, and osteochondral autograft transplantation. Arthroscopy. 2006, 22, 1085-1092.
doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2006.05.016 URL |
| 7. |
Jackson, D. W.; Grood, E. S.; Goldstein, J. D.; Rosen, M. A.; Kurzweil, P. R.; Cummings, J. F.; Simon, T. M. A comparison of patellar tendon autograft and allograft used for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction in the goat model. Am J Sports Med. 1993, 21, 176-185.
doi: 10.1177/036354659302100203 URL |
| 8. |
Kolesky, D. B.; Truby, R. L.; Gladman, A. S.; Busbee, T. A.; Homan, K. A.; Lewis, J. A. 3D bioprinting of vascularized, heterogeneous cell-laden tissue constructs. Adv Mater. 2014, 26, 3124-3130.
doi: 10.1002/adma.v26.19 URL |
| 9. |
Ren, Z. W.; Wang, Z. Y.; Ding, Y. W.; Dao, J. W.; Li, H. R.; Ma, X.; Yang, X. Y.; Zhou, Z. Q.; Liu, J. X.; Mi, C. H.; Gao, Z. C.; Pei, H.; Wei, D. X. Polyhydroxyalkanoates: the natural biopolyester for future medical innovations. Biomater Sci. 2023, 11, 6013-6034.
doi: 10.1039/D3BM01043K URL |
| 10. |
Zhao, X. H.; Niu, Y. N.; Mi, C. H.; Gong, H. L.; Yang, X. Y.; Cheng, J. S. Y.; Zhou, Z. Q.; Liu, J. X.; Peng, X. L.; Wei, D. X. Electrospinning nanofibers of microbial polyhydroxyalkanoates for applications in medical tissue engineering. J Polym Sci. 2021, 59, 1994-2013.
doi: 10.1002/pola.v59.18 URL |
| 11. | Wang, Z. Y.; Zhang, X. W.; Ding, Y. W.; Ren, Z. W.; Wei, D. X. Natural biopolyester microspheres with diverse structures and surface topologies as micro-devices for biomedical applications. Smart Mater Med. 2023, 4, 15-36. |
| 12. |
Anderson, A. J.; Dawes, E. A. Occurrence, metabolism, metabolic role, and industrial uses of bacterial polyhydroxyalkanoates. Microbiol Rev. 1990, 54, 450-472.
doi: 10.1128/mr.54.4.450-472.1990 URL |
| 13. | Palencia, M.; Lerma, T. A.; Garcés, V.; Mora, M. A.; Martínez, J. M.; Palencia, S. L. Chapter 19 - Functional and eco-friendly polymers in textile applications. In Eco-friendly functional polymers, Palencia, M.; Lerma, T. A.; Garcés, V.; Mora, M. A.; Martínez, J. M.; Palencia, S. L., eds. Elsevier: 2021; pp 285-293. |
| 14. | Mastrogiacomo, M.; Muraglia, A.; Komlev, V.; Peyrin, F.; Rustichelli, F.; Crovace, A.; Cancedda, R. Tissue engineering of bone: search for a better scaffold. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2005, 8, 277-284. |
| 15. | Troschl, C.; Meixner, K.; Drosg, B. Cyanobacterial PHA production-review of recent advances and a summary of three years’ working experience running a pilot plant. Bioengineering (Basel). 2017, 4, 26. |
| 16. | Peng, X. L.; Cheng, J. S.; Gong, H. L.; Yuan, M. D.; Zhao, X. H.; Li, Z.; Wei, D. X. Advances in the design and development of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines. Mil Med Res. 2021, 8, 67. |
| 17. |
Liu, J.; Zhou, Z.; Li, H.; Yang, X.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, J.; Wei, D. X. Current status and challenges in the application of microbial PHA particles. Particuology. 2024, 87, 286-302.
doi: 10.1016/j.partic.2023.08.011 URL |
| 18. |
Li, X. T.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, G. Q. Nanofibrous polyhydroxyalkanoate matrices as cell growth supporting materials. Biomaterials. 2008, 29, 3720-3728.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2008.06.004 URL |
| 19. |
Bassas-Galià, M.; Gonzalez, A.; Micaux, F.; Gaillard, V.; Piantini, U.; Schintke, S.; Zinn, M.; Mathieu, M. Chemical modification of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) for the preparation of hybrid biomaterials. Chimia. 2015, 69, 627-630.
doi: 10.2533/chimia.2015.627 URL |
| 20. |
Ai, M.; Zhu, Y.; Jia, X. Recent advances in constructing artificial microbial consortia for the production of medium-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoates. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021, 37, 2.
doi: 10.1007/s11274-020-02986-0 |
| 21. |
Chen, S.; Liu, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhu, B.; Yu, F.; Chen, G. Q.; Inoue, Y. Polymorphic crystallization of fractionated microbial medium-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoates. Polymer. 2009, 50, 4378-4388.
doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2009.07.011 URL |
| 22. |
Grigore, M. E.; Grigorescu, R. M.; Iancu, L.; Ion, R. M.; Zaharia, C.; Andrei, E. R. Methods of synthesis, properties and biomedical applications of polyhydroxyalkanoates: a review. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2019, 30, 695-712.
doi: 10.1080/09205063.2019.1605866 URL |
| 23. |
Witholt, B.; Kessler, B. Perspectives of medium chain length poly(hydroxyalkanoates), a versatile set of bacterial bioplastics. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 1999, 10, 279-285.
doi: 10.1016/S0958-1669(99)80049-4 URL |
| 24. |
Ishak, K. A.; Velayutham, T. S.; Annuar, M. S. M.; Sirajudeen, A. A. O. Structure-property interpretation of biological polyhydroxyalkanoates with different monomeric composition: dielectric spectroscopy investigation. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021, 169, 311-320.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.12.090 URL |
| 25. |
Savenkova, L.; Gercberga, Z.; Nikolaeva, V.; Dzene, A.; Bibers, I.; Kalnin, M. Mechanical properties and biodegradation characteristics of PHB-based films. Process Biochem. 2000, 35, 573-579.
doi: 10.1016/S0032-9592(99)00107-7 URL |
| 26. |
Ciesielski, S.; Pokoj, T.; Mozejko, J.; Klimiuk, E. Molecular identification of polyhydroxyalkanoates-producing bacteria isolated from enriched microbial community. Pol J Microbiol. 2013, 62, 45-50.
doi: 10.33073/pjm- URL |
| 27. |
Wecker, P.; Moppert, X.; Simon-Colin, C.; Costa, B.; Berteaux-Lecellier, V. Discovery of a mcl-PHA with unexpected biotechnical properties: the marine environment of French Polynesia as a source for PHA-producing bacteria. AMB Express. 2015, 5, 74.
doi: 10.1186/s13568-015-0163-y URL |
| 28. |
Koller, M. Biodegradable and biocompatible polyhydroxy-alkanoates (PHA): auspicious microbial macromolecules for pharmaceutical and therapeutic applications. Molecules. 2018, 23, 362.
doi: 10.3390/molecules23020362 URL |
| 29. |
Williams, S. F.; Martin, D. P.; Horowitz, D. M.; Peoples, O. P.PHA applications: addressing the price performance issue: I. Tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol. 1999, 25, 111-121.
doi: 10.1016/S0141-8130(99)00022-7 URL |
| 30. |
Lim, J.; You, M.; Li, J.; Li, Z. Emerging bone tissue engineering via polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA)-based scaffolds. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017, 79, 917-929.
doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2017.05.132 URL |
| 31. |
Chen, G. Q.; Wu, Q. The application of polyhydroxyalkanoates as tissue engineering materials. Biomaterials. 2005, 26, 6565-6578.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2005.04.036 URL |
| 32. |
Wang, Y. W.; Wu, Q.; Chen, G. Q. Attachment, proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts on random biopolyester poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2004, 25, 669-675.
doi: 10.1016/S0142-9612(03)00561-1 URL |
| 33. |
Hu, Y. J.; Wei, X.; Zhao, W.; Liu, Y. S.; Chen, G. Q. Biocompatibility of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 1115-1125.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2008.09.021 URL |
| 34. | Wei, X.; Hu, Y. J.; Xie, W. P.; Lin, R. L.; Chen, G. Q. Influence of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) on growth and osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2009, 90, 894-905. |
| 35. |
Wu, Y. L.; Wang, H.; Qiu, Y. K.; Liow, S. S.; Li, Z.; Loh, X. J. PHB-based gels as delivery agents of chemotherapeutics for the effective shrinkage of tumors. Adv Healthc Mater. 2016, 5, 2679-2685.
doi: 10.1002/adhm.v5.20 URL |
| 36. |
Marcello, E.; Maqbool, M.; Nigmatullin, R.; Cresswell, M.; Jackson, P. R.; Basnett, P.; Knowles, J. C.; Boccaccini, A. R.; Roy, I. Antibacterial composite materials based on the combination of polyhydroxyalkanoates with selenium and strontium co-substituted hydroxyapatite for bone regeneration. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 647007.
doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.647007 URL |
| 37. |
Shishatskaya, E. I.; Volova, T. G. A comparative investigation of biodegradable polyhydroxyalkanoate films as matrices for in vitro cell cultures. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2004, 15, 915-923.
doi: 10.1023/B:JMSM.0000036280.98763.c1 URL |
| 38. |
Ji, G. Z.; Wei, X.; Chen, G. Q. Growth of human umbilical cord Wharton’s Jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells on the terpolyester poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate). J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2009, 20, 325-339.
doi: 10.1163/156856209X412191 URL |
| 39. |
Ahmed, T.; Marçal, H.; Lawless, M.; Wanandy, N. S.; Chiu, A.; Foster, L. J. Polyhydroxybutyrate and its copolymer with polyhydroxyvalerate as biomaterials: influence on progression of stem cell cycle. Biomacromolecules. 2010, 11, 2707-2715.
doi: 10.1021/bm1007579 URL |
| 40. |
Yang, M.; Zhu, S.; Chen, Y.; Chang, Z.; Chen, G.; Gong, Y.; Zhao, N.; Zhang, X. Studies on bone marrow stromal cells affinity of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate). Biomaterials. 2004, 25, 1365-1373.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2003.08.018 URL |
| 41. |
Tesema, Y.; Raghavan, D.; Stubbs Iii, J. Bone cell viability on collagen immobilized poly(3-hydroxybutrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) membrane: Effect of surface chemistry. J Appl Polym Sci. 2004, 93, 2445-2453.
doi: 10.1002/app.v93:5 URL |
| 42. |
Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hu, P. Surface modification of polyhydroxyalkanoates by ion implantation. Characterization and cytocompatibility improvement. Polym J. 2003, 35, 148-154.
doi: 10.1295/polymj.35.148 URL |
| 43. |
Wu, T. P.; Hu, R.; Zhang, X. B.; Li, W.; Chen, F. Biocompatibility of modified poly-β-hydroxybutyric acid to adrenocortical cells. J Wuhan Univ Technol Mater Sci Ed. 2004, 19, 38-40.
doi: 10.1007/BF03000164 URL |
| 44. |
Yu, B. Y.; Chen, P. Y.; Sun, Y. M.; Lee, Y. T.; Young, T. H. Effects of the surface characteristics of polyhydroxyalkanoates on the metabolic activities and morphology of human mesenchymal stem cells. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2010, 21, 17-36.
doi: 10.1163/156856209X410139 URL |
| 45. |
Webb, W. R.; Dale, T. P.; Lomas, A. J.; Zeng, G.; Wimpenny, I.; El Haj, A. J.; Forsyth, N. R.; Chen, G. Q. The application of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) scaffolds for tendon repair in the rat model. Biomaterials. 2013, 34, 6683-6694.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.05.041 URL |
| 46. |
Volova, T. G.; Shishatskaya, E. I.; Nikolaeva, E. D.; Sinskey, A. J. In vivo study of 2D PHA matrices of different chemical compositions: tissue reactions and biodegradations. Mater Sci Technol. 2014, 30, 549-557.
doi: 10.1179/1743284713Y.0000000470 URL |
| 47. | Qu, X. H.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, K. Y.; Chen, G. Q. In vivo studies of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) based polymers: biodegradation and tissue reactions. Biomaterials. 2006, 27, 3540-3548. |
| 48. |
Fan, L.; Hu, L.; Xie, J.; He, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Wei, D.; Yao, D.; Su, F. Biosafe, self-adhesive, recyclable, tough, and conductive hydrogels for multifunctional sensors. Biomater Sci. 2021, 9, 5884-5896.
doi: 10.1039/D1BM00665G URL |
| 49. |
Li, Y.; Xiao, L.; Wei, D.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Lian, R.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, J.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Zhao, J. Injectable biomimetic hydrogel guided functional bone regeneration by adapting material degradation to tissue healing. Adv Funct Mater. 2023, 33, 2213047.
doi: 10.1002/adfm.v33.19 URL |
| 50. |
Dwivedi, R.; Pandey, R.; Kumar, S.; Mehrotra, D. Poly hydroxyalkanoates (PHA): role in bone scaffolds. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2020, 10, 389-392.
doi: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2019.10.004 URL |
| 51. |
Anjum, A.; Zuber, M.; Zia, K. M.; Noreen, A.; Anjum, M. N.; Tabasum, S. Microbial production of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) and its copolymers: A review of recent advancements. Int J Biol Macromol. 2016, 89, 161-174.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.04.069 URL |
| 52. | Arrington, E. D.; Smith, W. J.; Chambers, H. G.; Bucknell, A. L.; Davino, N. A. Complications of iliac crest bone graft harvesting. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996, 300-309. |
| 53. |
Hazer, B.; Steinbüchel, A. Increased diversification of polyhydroxyalkanoates by modification reactions for industrial and medical applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2007, 74, 1-12.
doi: 10.1007/s00253-006-0732-8 URL |
| 54. |
Sharma, V.; Sehgal, R.; Gupta, R. Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA): properties and modifications. Polymer. 2021, 212, 123161.
doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2020.123161 URL |
| 55. |
Sudesh, K.; Abe, H.; Doi, Y. Synthesis, structure and properties of polyhydroxyalkanoates: biological polyesters. Prog Polym Sci. 2000, 25, 1503-1555.
doi: 10.1016/S0079-6700(00)00035-6 URL |
| 56. |
Pryadko, A.; Surmeneva, M. A.; Surmenev, R. A. Review of hybrid materials based on polyhydroxyalkanoates for tissue engineering applications. Polymers (Basel). 2021, 13, 1738.
doi: 10.3390/polym13111738 URL |
| 57. | Velasco, M. A.; Narváez-Tovar, C. A.; Garzón-Alvarado, D. A. Design, materials, and mechanobiology of biodegradable scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomed Res Int. 2015, 2015, 729076. |
| 58. |
Mota, C.; Wang, S. Y.; Puppi, D.; Gazzarri, M.; Migone, C.; Chiellini, F.; Chen, G. Q.; Chiellini, E. Additive manufacturing of poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate-co-(R)-3-hydroxyhexanoate] scaffolds for engineered bone development. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2017, 11, 175-186.
doi: 10.1002/term.v11.1 URL |
| 59. |
Doyle, C.; Tanner, E. T.; Bonfield, W. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of polyhydroxybutyrate and of polyhydroxybutyrate reinforced with hydroxyapatite. Biomaterials. 1991, 12, 841-847.
doi: 10.1016/0142-9612(91)90072-I URL |
| 60. |
Wang, Y.; Jiang, X. L.; Yang, S. C.; Lin, X.; He, Y.; Yan, C.; Wu, L.; Chen, G. Q.; Wang, Z. Y.; Wu, Q. MicroRNAs in the regulation of interfacial behaviors of MSCs cultured on microgrooved surface pattern. Biomaterials. 2011, 32, 9207-9217.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.08.058 URL |
| 61. |
Ellis, G.; Cano, P.; Jadraque, M.; Martín, M.; López, L.; Núñez, T.; de la Peña, E.; Marco, C.; Garrido, L. Laser microperforated biodegradable microbial polyhydroxyalkanoate substrates for tissue repair strategies: an infrared microspectroscopy study. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2011, 399, 2379-2388.
doi: 10.1007/s00216-011-4653-8 URL |
| 62. |
Wei, D.; Zhang, X. Biosynthesis, bioactivity, biotoxicity and applications of antimicrobial peptides for human health. Biosaf Health. 2022, 4, 118-134.
doi: 10.1016/j.bsheal.2022.02.003 URL |
| 63. |
Codreanu, A.; Balta, C.; Herman, H.; Cotoraci, C.; Mihali, C. V.; Zurbau, N.; Zaharia, C.; Rapa, M.; Stanescu, P.; Radu, I. C.; Vasile, E.; Lupu, G.; Galateanu, B.; Hermenean, A. Bacterial cellulose-modified polyhydroxyalkanoates scaffolds promotes bone formation in critical size calvarial defects in mice. Materials (Basel). 2020, 13, 1433.
doi: 10.3390/ma13061433 URL |
| 64. |
Pecorini, G.; Braccini, S.; Parrini, G.; Chiellini, F.; Puppi, D. Additive manufacturing of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate)/poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide) biphasic scaffolds for bone tissue regeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2022, 23, 3895.
doi: 10.3390/ijms23073895 URL |
| 65. | Lezcano, M. F.; Álvarez, G.; Chuhuaicura, P.; Godoy, K.; Alarcón, J.; Acevedo, F.; Gareis, I.; Dias, F. J. Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) scaffolds for peripheral nerve regeneration: a systematic review of animal models. Biology (Basel). 2022, 11, 706. |
| 66. |
Ansari, N. F.; Annuar, M. S. M.; Murphy, B. P. A porous medium-chain-length poly(3-hydroxyalkanoates)/hydroxyapatite composite as scaffold for bone tissue engineering. Eng Life Sci. 2017, 17, 420-429.
doi: 10.1002/elsc.v17.4 URL |
| 67. |
Nishizuka, T.; Kurahashi, T.; Hara, T.; Hirata, H.; Kasuga, T. Novel intramedullary-fixation technique for long bone fragility fractures using bioresorbable materials. PLoS One. 2014, 9, e104603.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104603 URL |
| 68. |
Skibiński, S.; Czechowska, J. P.; Cichoń, E.; Seta, M.; Gondek, A.; Cudnoch-Jędrzejewska, A.; Ślósarczyk, A.; Guzik, M.; Zima, A. Study on βTCP/P(3HB) scaffolds-physicochemical properties and biological performance in low oxygen concentration. Int J Mol Sci. 2022, 23, 11587.
doi: 10.3390/ijms231911587 URL |
| 69. |
Chotchindakun, K.; Pekkoh, J.; Ruangsuriya, J.; Zheng, K.; Unalan, I.; Boccaccini, A. R. Fabrication and characterization of cinnamaldehyde-loaded mesoporous bioactive glass nanoparticles/PHBV-based microspheres for preventing bacterial infection and promoting bone tissue regeneration. Polymers (Basel). 2021, 13, 1794.
doi: 10.3390/polym13111794 URL |
| 70. |
Ching, K. Y.; Andriotis, O. G.; Li, S.; Basnett, P.; Su, B.; Roy, I.; Tare, R. S.; Sengers, B. G.; Stolz, M. Nanofibrous poly(3-hydroxybutyrate)/poly(3-hydroxyoctanoate) scaffolds provide a functional microenvironment for cartilage repair. J Biomater Appl. 2016, 31, 77-91.
doi: 10.1177/0885328216639749 URL |
| 71. |
Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Moran, S.; Khang, G.; Ge, Z. Poly (l-lactide-co-caprolactone) scaffolds enhanced with poly (β-hydroxybutyrate-co-β-hydroxyvalerate) microspheres for cartilage regeneration. Biomed Mater. 2013, 8, 025005.
doi: 10.1088/1748-6041/8/2/025005 URL |
| 72. | Gao, T.; Chang, H.; Fan, M.; Lu, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Jing, X.; Shi, Y.; Li, Z. Bio-modification of polyhydroxyalkanoates and its biocompatibility with chondrocytes. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2014, 28, 1023-1029. |
| 73. |
Movahedi, M.; Karbasi, S. Electrospun halloysite nanotube loaded polyhydroxybutyrate-starch fibers for cartilage tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022, 214, 301-311.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.06.072 URL |
| 74. |
Li, X.; Chang, H.; Luo, H.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, G.; Lu, X.; He, X.; Chen, F.; Wang, T.; Liang, J.; Xu, M. Poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) scaffolds coated with PhaP-RGD fusion protein promotes the proliferation and chondrogenic differentiation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015, 103, 1169-1175.
doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.v103.3 URL |
| 75. |
You, M.; Peng, G.; Li, J.; Ma, P.; Wang, Z.; Shu, W.; Peng, S.; Chen, G. Q. Chondrogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) scaffolds coated with PHA granule binding protein PhaP fused with RGD peptide. Biomaterials. 2011, 32, 2305-2313.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.12.009 URL |
| 76. |
Zonari, A.; Novikoff, S.; Electo, N. R.; Breyner, N. M.; Gomes, D. A.; Martins, A.; Neves, N. M.; Reis, R. L.; Goes, A. M. Endothelial differentiation of human stem cells seeded onto electrospun polyhydroxybutyrate/polyhydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate fiber mesh. PLoS One. 2012, 7, e35422.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035422 URL |
| 77. |
Zhijiang, C.; Yi, X.; Haizheng, Y.; Jia, J.; Liu, Y. Poly(hydroxybutyrate)/cellulose acetate blend nanofiber scaffolds: preparation, characterization and cytocompatibility. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016, 58, 757-767.
doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2015.09.048 URL |
| 78. |
Ochoa-Segundo, E. I.; González-Torres, M.; Cabrera-Wrooman, A.; Sánchez-Sánchez, R.; Huerta-Martínez, B. M.; Melgarejo-Ramírez, Y.; Leyva-Gómez, G.; Rivera-Muñoz, E. M.; Cortés, H.; Velasquillo, C.; Vargas-Muñoz, S.; Rodríguez-Talavera, R. Gamma radiation-induced grafting of n-hydroxyethyl acrylamide onto poly(3-hydroxybutyrate): A companion study on its polyurethane scaffolds meant for potential skin tissue engineering applications. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020, 116, 111176.
doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2020.111176 URL |
| 79. |
Kanimozhi, K.; Basha, S. K.; Kaviyarasu, K.; SuganthaKumari, V. Salt leaching synthesis, characterization and in vitro cytocompatibility of chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol)/methylcellulose - ZnO nanocomposites scaffolds using L929 fibroblast cells. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2019, 19, 4447-4457.
doi: 10.1166/jnn.2019.16359 URL |
| 80. |
Nagiah, N.; Madhavi, L.; Anitha, R.; Anandan, C.; Srinivasan, N. T.; Sivagnanam, U. T. Development and characterization of coaxially electrospun gelatin coated poly (3-hydroxybutyric acid) thin films as potential scaffolds for skin regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2013, 33, 4444-4452.
doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2013.06.042 URL |
| 81. |
Sanhueza, C.; Hermosilla, J.; Bugallo-Casal, A.; Da Silva-Candal, A.; Taboada, C.; Millán, R.; Concheiro, A.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C.; Acevedo, F. One-step electrospun scaffold of dual-sized gelatin/poly-3-hydroxybutyrate nano/microfibers for skin regeneration in diabetic wound. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021, 119, 111602.
doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2020.111602 URL |
| 82. |
Feng, J.; Niu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zuo, H.; Wang, S.; Liu, X. Ficus carica extract impregnated amphiphilic polymer scaffold for diabetic wound tissue regenerations. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2021, 49, 219-229.
doi: 10.1080/21691401.2021.1890610 URL |
| 83. |
Veleirinho, B.; Coelho, D. S.; Dias, P. F.; Maraschin, M.; Ribeiro-do-Valle, R. M.; Lopes-da-Silva, J. A. Nanofibrous poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate)/chitosan scaffolds for skin regeneration. Int J Biol Macromol. 2012, 51, 343-350.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2012.05.023 URL |
| 84. | Rathbone, S.; Furrer, P.; Lübben, J.; Zinn, M.; Cartmell, S. Biocompatibility of polyhydroxyalkanoate as a potential material for ligament and tendon scaffold material. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010, 93, 1391-1403. |
| 85. |
Lomas, A. J.; Chen, G. G.; El Haj, A. J.; Forsyth, N. R. Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) supports adhesion and migration of mesenchymal stem cells and tenocytes. World J Stem Cells. 2012, 4, 94-100.
doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v4.i9.94 URL |
| 86. | Tashjian, R. Z.; Kolz, C. W.; Suter, T.; Henninger, H. B. Biomechanics of polyhydroxyalkanoate mesh-augmented single-row rotator cuff repairs. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2016, 45, E527-E533. |
| 87. |
Sodian, R.; Sperling, J. S.; Martin, D. P.; Egozy, A.; Stock, U.; Mayer, J. E., Jr.; Vacanti, J. P. Fabrication of a trileaflet heart valve scaffold from a polyhydroxyalkanoate biopolyester for use in tissue engineering. Tissue Eng. 2000, 6, 183-188.
doi: 10.1089/107632700320793 URL |
| 88. |
Leor, J.; Amsalem, Y.; Cohen, S. Cells, scaffolds, and molecules for myocardial tissue engineering. Pharmacol Ther. 2005, 105, 151-163.
doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2004.10.003 URL |
| 89. |
Sun, M.; Zhou, P.; Pan, L. F.; Liu, S.; Yang, H. X. Enhanced cell affinity of the silk fibroin- modified PHBHHx material. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2009, 20, 1743-1751.
doi: 10.1007/s10856-009-3739-8 URL |
| 90. |
Bagdadi, A. V.; Safari, M.; Dubey, P.; Basnett, P.; Sofokleous, P.; Humphrey, E.; Locke, I.; Edirisinghe, M.; Terracciano, C.; Boccaccini, A. R.; Knowles, J. C.; Harding, S. E.; Roy, I. Poly(3-hydroxyoctanoate), a promising new material for cardiac tissue engineering. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018, 12, e495-e512.
doi: 10.1002/term.2318 URL |
| 91. |
Köse, S.; Kaya, F. A.; Denkbaş, E. B.; Korkusuz, P.; Çetinkaya, F. D. Evaluation of biocompatibility of random or aligned electrospun polyhydroxybutyrate scaffolds combined with human mesenchymal stem cells. Turk J Biol. 2016, 40, 410-419.
doi: 10.3906/biy-1508-18 URL |
| 92. |
Khorasani, M. T.; Mirmohammadi, S. A.; Irani, S. Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) scaffolds as a model for nerve tissue engineering application: fabrication and in vitro assay. Int J Polym Mater Polym Biomater. 2011, 60, 562-575.
doi: 10.1080/00914037.2010.531809 URL |
| 93. |
Masaeli, E.; Morshed, M.; Nasr-Esfahani, M. H.; Sadri, S.; Hilderink, J.; van Apeldoorn, A.; van Blitterswijk, C. A.; Moroni, L. Fabrication, characterization and cellular compatibility of poly(hydroxy alkanoate) composite nanofibrous scaffolds for nerve tissue engineering. PLoS One. 2013, 8, e57157.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057157 URL |
| 94. | Masaeli, E.; Wieringa, P. A.; Morshed, M.; Nasr-Esfahani, M. H.; Sadri, S.; van Blitterswijk, C. A.; Moroni, L. Peptide functionalized polyhydroxyalkanoate nanofibrous scaffolds enhance Schwann cells activity. Nanomedicine. 2014, 10, 1559-1569. |
| 95. |
Kuo, Y. C.; Huang, M. J. Material-driven differentiation of induced pluripotent stem cells in neuron growth factor-grafted poly(ε-caprolactone)-poly(β-hydroxybutyrate) scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2012, 33, 5672-5682.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.04.046 URL |
| 96. |
Bian, Y. Z.; Wang, Y.; Aibaidoula, G.; Chen, G. Q.; Wu, Q. Evaluation of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) conduits for peripheral nerve regeneration. Biomaterials. 2009, 30, 217-225.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2008.09.036 URL |
| 97. |
Xu, X. Y.; Li, X. T.; Peng, S. W.; Xiao, J. F.; Liu, C.; Fang, G.; Chen, K. C.; Chen, G. Q. The behaviour of neural stem cells on polyhydroxyalkanoate nanofiber scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2010, 31, 3967-3975.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.01.132 URL |
| 98. | Rahman, M.; Peng, X. L.; Zhao, X. H.; Gong, H. L.; Sun, X. D.; Wu, Q.; Wei, D. X. 3D bioactive cell-free-scaffolds for in-vitro/in-vivo capture and directed osteoinduction of stem cells for bone tissue regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2021, 6, 4083-4095. |
| 99. |
Wei, D. X.; Dao, J. W.; Liu, H. W.; Chen, G. Q. Suspended polyhydroxyalkanoate microspheres as 3D carriers for mammalian cell growth. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 473-483.
doi: 10.1080/21691401.2018.1459635 URL |
| 100. | Wei, D. X.; Dao, J. W.; Chen, G. Q. A micro-ark for cells: highly open porous polyhydroxyalkanoate microspheres as injectable scaffolds for tissue regeneration. Adv Mater. 2018, 30, e1802273. |
| 101. |
Zhao, X. H.; Peng, X. L.; Gong, H. L.; Wei, D. X. Osteogenic differentiation system based on biopolymer nanoparticles for stem cells in simulated microgravity. Biomed Mater. 2021, 16, 044102.
doi: 10.1088/1748-605X/abe9d1 |
| 102. |
Armiento, A. R.; Stoddart, M. J.; Alini, M.; Eglin, D. Biomaterials for articular cartilage tissue engineering: Learning from biology. Acta Biomater. 2018, 65, 1-20.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2017.11.021 URL |
| 103. |
Decker, R. S. Articular cartilage and joint development from embryogenesis to adulthood. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017, 62, 50-56.
doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2016.10.005 URL |
| 104. |
Swieszkowski, W.; Tuan, B. H.; Kurzydlowski, K. J.; Hutmacher, D. W. Repair and regeneration of osteochondral defects in the articular joints. Biomol Eng. 2007, 24, 489-495.
doi: 10.1016/j.bioeng.2007.07.014 URL |
| 105. |
Asl, M. A.; Karbasi, S.; Beigi-Boroujeni, S.; Zamanlui Benisi, S.; Saeed, M. Evaluation of the effects of starch on polyhydroxybutyrate electrospun scaffolds for bone tissue engineering applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021, 191, 500-513.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.09.078 URL |
| 106. |
Wei, D. X.; Chen, C. B.; Fang, G.; Li, S. Y.; Chen, G. Q. Application of polyhydroxyalkanoate binding protein PhaP as a bio-surfactant. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2011, 91, 1037-1047.
doi: 10.1007/s00253-011-3258-7 URL |
| 107. |
Fan, L.; He, Z.; Peng, X.; Xie, J.; Su, F.; Wei, D. X.; Zheng, Y.; Yao, D. Injectable, intrinsically antibacterial conductive hydrogels with self-healing and pH stimulus responsiveness for epidermal sensors and wound healing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021, 13, 53541-53552.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c14216 URL |
| 108. |
Fan, L.; Xie, J.; Zheng, Y.; Wei, D.; Yao, D.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, T. Antibacterial, self-adhesive, recyclable, and tough conductive composite hydrogels for ultrasensitive strain sensing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020, 12, 22225-22236.
doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c06091 URL |
| 109. |
Dhania, S.; Bernela, M.; Rani, R.; Parsad, M.; Grewal, S.; Kumari, S.; Thakur, R. Scaffolds the backbone of tissue engineering: Advancements in use of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA). Int J Biol Macromol. 2022, 208, 243-259.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.03.030 URL |
| 110. |
Doral, M. N.; Alam, M.; Bozkurt, M.; Turhan, E.; Atay, O. A.; Dönmez, G.; Maffulli, N. Functional anatomy of the Achilles tendon. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010, 18, 638-643.
doi: 10.1007/s00167-010-1083-7 URL |
| 111. |
Ahmed, I. M.; Lagopoulos, M.; McConnell, P.; Soames, R. W.; Sefton, G. K. Blood supply of the Achilles tendon. J Orthop Res. 1998, 16, 591-596.
doi: 10.1002/jor.v16:5 URL |
| 112. |
Theobald, P.; Benjamin, M.; Nokes, L.; Pugh, N. Review of the vascularisation of the human Achilles tendon. Injury. 2005, 36, 1267-1272.
doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2005.02.012 URL |
| 113. |
Longo, U. G.; Lamberti, A.; Maffulli, N.; Denaro, V. Tendon augmentation grafts: a systematic review. Br Med Bull. 2010, 94, 165-188.
doi: 10.1093/bmb/ldp051 URL |
| 114. |
Wilkins, R.; Bisson, L. J. Operative versus nonoperative management of acute Achilles tendon ruptures: a quantitative systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Am J Sports Med. 2012, 40, 2154-2160.
doi: 10.1177/0363546512453293 URL |
| 115. |
Cetti, R.; Christensen, S. E.; Ejsted, R.; Jensen, N. M.; Jorgensen, U. Operative versus nonoperative treatment of Achilles tendon rupture. A prospective randomized study and review of the literature. Am J Sports Med. 1993, 21, 791-799.
doi: 10.1177/036354659302100606 URL |
| 116. | García-Germán, D.; Rubio-Quevedo, R.; Lopez-Goenaga, J.; Martin-Guinea, J. Achilles tendon recurrent rupture following surgical repair: report on two cases. Foot Ankle Surg. 2009, 15, 152-154. |
| 117. |
Kusumbe, A. P.; Ramasamy, S. K.; Adams, R. H. Coupling of angiogenesis and osteogenesis by a specific vessel subtype in bone. Nature. 2014, 507, 323-328.
doi: 10.1038/nature13145 |
| 118. |
Straley, K. S.; Foo, C. W.; Heilshorn, S. C. Biomaterial design strategies for the treatment of spinal cord injuries. J Neurotrauma. 2010, 27, 1-19.
doi: 10.1089/neu.2009.0948 URL |
| 119. |
Novikov, L. N.; Novikova, L. N.; Mosahebi, A.; Wiberg, M.; Terenghi, G.; Kellerth, J. O. A novel biodegradable implant for neuronal rescue and regeneration after spinal cord injury. Biomaterials. 2002, 23, 3369-3376.
doi: 10.1016/S0142-9612(02)00037-6 URL |
| 120. |
Wang, L.; Wang, Z. H.; Shen, C. Y.; You, M. L.; Xiao, J. F.; Chen, G. Q. Differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells grown in terpolyesters of 3-hydroxyalkanoates scaffolds into nerve cells. Biomaterials. 2010, 31, 1691-1698.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2009.11.053 URL |
| 121. |
Zhang, C.; Zhao, L.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lin, J.; Chen, Z. Folate-mediated poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyoctanoate) nanoparticles for targeting drug delivery. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2010, 76, 10-16.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2010.05.005 URL |
| 122. |
Pramual, S.; Assavanig, A.; Bergkvist, M.; Batt, C. A.; Sunintaboon, P.; Lirdprapamongkol, K.; Svasti, J.; Niamsiri, N. Development and characterization of bio-derived polyhydroxyalkanoate nanoparticles as a delivery system for hydrophobic photodynamic therapy agents. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2016, 27, 40.
doi: 10.1007/s10856-015-5655-4 URL |
| 123. |
Li, Z.; Loh, X. J. Recent advances of using polyhydroxyalkanoate-based nanovehicles as therapeutic delivery carriers. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 9, e1429.
doi: 10.1002/wnan.2017.9.issue-3 URL |
| 124. |
Shah, M.; Ullah, N.; Choi, M. H.; Yoon, S. C. Nanoscale poly(4-hydroxybutyrate)-mPEG carriers for anticancer drugs delivery. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 8416-8421.
doi: 10.1166/jnn.2014.9924 URL |
| 125. |
Nobes, G. A.; Marchessault, R. H.; Maysinger, D. Polyhydroxyalkanoates: materials for delivery systems. Drug Deliv. 1998, 5, 167-177.
doi: 10.3109/10717549809052032 URL |
| 126. |
Elmowafy, E.; Abdal-Hay, A.; Skouras, A.; Tiboni, M.; Casettari, L.; Guarino, V. Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA): applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2019, 16, 467-482.
doi: 10.1080/17434440.2019.1615439 URL |
| 127. |
Hu, J.; Wang, M.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, B.; Xie, Q.; Xu, X.; Li, S.; Zheng, Z.; Wei, D.; Zhang, X. A novel long-acting azathioprine polyhydroxyalkanoate nanoparticle enhances treatment efficacy for systemic lupus erythematosus with reduced side effects. Nanoscale. 2020, 12, 10799-10808.
doi: 10.1039/D0NR01308K URL |
| 128. |
Yan, Y.; Wei, D.; Li, J.; Zheng, J.; Shi, G.; Luo, W.; Pan, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; He, X.; Liu, D. A poly(L-lysine)-based hydrophilic star block co-polymer as a protein nanocarrier with facile encapsulation and pH-responsive release. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 2113-2120.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2012.02.016 URL |
| 129. | Wei, D.; Qiao, R.; Dao, J.; Su, J.; Jiang, C.; Wang, X.; Gao, M.; Zhong, J. Soybean lecithin-mediated nanoporous PLGA microspheres with highly entrapped and controlled released BMP-2 as a stem cell platform. Small. 2018, 14, e1800063. |
| 130. |
Sendil, D.; Gürsel, I.; Wise, D. L.; Hasirci, V. Antibiotic release from biodegradable PHBV microparticles. J Control Release. 1999, 59, 207-217.
doi: 10.1016/S0168-3659(98)00195-3 URL |
| 131. |
Kassab, A. C.; Xu, K.; Denkbaş, E. B.; Dou, Y.; Zhao, S.; Pişkin, E. Rifampicin carrying polyhydroxybutyrate microspheres as a potential chemoembolization agent. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 1997, 8, 947-961.
doi: 10.1163/156856297X00119 URL |
| 132. |
Xiong, Y. C.; Yao, Y. C.; Zhan, X. Y.; Chen, G. Q. Application of polyhydroxyalkanoates nanoparticles as intracellular sustained drug-release vectors. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2010, 21, 127-140.
doi: 10.1163/156856209X410283 URL |
| 133. |
Türesin, F.; Gürsel, I.; Hasirci, V. Biodegradable polyhydroxyalkanoate implants for osteomyelitis therapy: in vitro antibiotic release. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2001, 12, 195-207.
doi: 10.1163/156856201750180924 URL |
| 134. |
Yagmurlu, M. F.; Korkusuz, F.; Gürsel, I.; Korkusuz, P.; Ors, U.; Hasirci, V. Sulbactam-cefoperazone polyhydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate (PHBV) local antibiotic delivery system: in vivo effectiveness and biocompatibility in the treatment of implant-related experimental osteomyelitis. J Biomed Mater Res. 1999, 46, 494-503.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1097-4636 URL |
| 135. |
Gürsel, I.; Korkusuz, F.; Türesin, F.; Alaeddinoglu, N. G.; Hasirci, V. In vivo application of biodegradable controlled antibiotic release systems for the treatment of implant-related osteomyelitis. Biomaterials. 2001, 22, 73-80.
doi: 10.1016/S0142-9612(00)00170-8 URL |
| 136. |
Scheithauer, E. C.; Li, W.; Ding, Y.; Harhaus, L.; Roether, J. A.; Boccaccini, A. R. Preparation and characterization of electrosprayed daidzein-loaded PHBV microspheres. Mater Lett. 2015, 158, 66-69.
doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2015.05.133 URL |
| 137. | Peng, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X. A long-acting BMP-2 release system based on poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) nanoparticles modified by amphiphilic phospholipid for osteogenic differentiation. Biomed Res Int. 2016, 2016, 5878645. |
| 138. |
Chen, R.; Yu, J.; Gong, H. L.; Jiang, Y.; Xue, M.; Xu, N.; Wei, D. X.; Shi, C. An easy long-acting BMP7 release system based on biopolymer nanoparticles for inducing osteogenic differentiation of adipose mesenchymal stem cells. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2020, 14, 964-972.
doi: 10.1002/term.v14.7 URL |
| 139. | Shrivastav, A.; Kim, H. Y.; Kim, Y. R. Advances in the applications of polyhydroxyalkanoate nanoparticles for novel drug delivery system. Biomed Res Int. 2013, 2013, 581684. |
| 140. |
Li, Z.; Yang, J.; Loh, X. J. Polyhydroxyalkanoates: opening doors for a sustainable future. NPG Asia Mater. 2016, 8, e265-e265.
doi: 10.1038/am.2016.48 |
| 141. |
Nelson, T.; Kaufman, E.; Kline, J.; Sokoloff, L. The extraneural distribution of gamma-hydroxybutyrate. J Neurochem. 1981, 37, 1345-1348.
doi: 10.1111/jnc.1981.37.issue-5 URL |
| 142. |
Wang, B. L.; Wu, J. F.; Xiao, D.; Wu, B.; Wei, D. X. 3-hydroxybutyrate in the brain: biosynthesis, function, and disease therapy. Brain‐X. 2023, 1, e6.
doi: 10.1002/brx2.v1.1 URL |
| 143. | Xiang, Y.; Wang, Q. Q.; Lan, X. Q.; Zhang, H. J.; Wei, D. X. Function and treatment strategies of β-hydroxybutyrate in aging. Smart Mater Med. 2023, 4, 160-172. |
| 144. |
Zhao, Y.; Zou, B.; Shi, Z.; Wu, Q.; Chen, G. Q. The effect of 3-hydroxybutyrate on the in vitro differentiation of murine osteoblast MC3T3-E1 and in vivo bone formation in ovariectomized rats. Biomaterials. 2007, 28, 3063-3073.
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2007.03.003 URL |
| 145. |
Czechowska, J.; Skibiński, S.; Guzik, M.; Zima, A. Silver decorated βTCP-poly(3hydroxybutyrate) scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Materials (Basel). 2021, 14, 4227.
doi: 10.3390/ma14154227 URL |
| 146. |
Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, H.; Pang, X.; Liu, Y.; Tao, W.; Chen, X.; Zhang, P.; Chen, G. Q. Mechanism of reduced muscle atrophy via ketone body (D)-3-hydroxybutyrate. Cell Biosci. 2022, 12, 94.
doi: 10.1186/s13578-022-00826-2 |
| 147. |
Wang, Z.; Ma, K.; Jiang, X.; Xie, J.; Cai, P.; Li, F.; Liang, R.; Zhao, J.; Zheng, L. Electrospun poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) /Octacalcium phosphate Nanofibrous membranes for effective guided bone regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020, 112, 110763.
doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2020.110763 URL |
| 148. |
Ang, S. L.; Shaharuddin, B.; Chuah, J. A.; Sudesh, K. Electrospun poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate)/silk fibroin film is a promising scaffold for bone tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020, 145, 173-188.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.12.149 URL |
| 149. | Kourmentza, C.; Plácido, J.; Venetsaneas, N.; Burniol-Figols, A.; Varrone, C.; Gavala, H. N.; Reis, M. A. M. Recent advances and challenges towards sustainable polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) production. Bioengineering (Basel). 2017, 4, 55. |
| 150. |
Xu, N.; Peng, X. L.; Li, H. R.; Liu, J. X.; Cheng, J. S.; Qi, X. Y.; Ye, S. J.; Gong, H. L.; Zhao, X. H.; Yu, J.; Xu, G.; Wei, D. X. Marine-derived collagen as biomaterials for human health. Front Nutr. 2021, 8, 702108.
doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.702108 URL |
| 151. |
Volova, T.; Shishatskaya, E.; Sevastianov, V.; Efremov, S.; Mogilnaya, O. Results of biomedical investigations of PHB and PHB/PHV fibers. Biochem Eng J. 2003, 16, 125-133.
doi: 10.1016/S1369-703X(03)00038-X URL |
| 152. |
Turkyilmaz, S.; Chen, W. H.; Mitomo, H.; Regen, S. L. Loosening and reorganization of fluid phospholipid bilayers by chloroform. J Am Chem Soc. 2009, 131, 5068-5069.
doi: 10.1021/ja9011468 URL |
| [1] | Zhangjie Li, Dingyuan Yu, Chenyang Zhou, Feifan Wang, Kangyi Lu, Yijun Liu, Jiaqi Xu, Lian Xuan, Xiaolin Wang. Engineering vascularised organoid-on-a-chip: strategies, advances and future perspectives [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2024, 5(1): 21-32. |
| [2] | Ross H. McWilliam, Wenlong Chang, Zhao Liu, Jiayuan Wang, Fengxuan Han, Richard A. Black, Junxi Wu, Xichun Luo, Bin Li, Wenmiao Shu. Three-dimensional biofabrication of nanosecond laser micromachined nanofibre meshes for tissue engineered scaffolds [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2023, 4(2): 104-114. |
| [3] | Ahlam A. Abdalla, Catherine J. Pendegrass. Biological approaches to the repair and regeneration of the rotator cuff tendon-bone enthesis: a literature review [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2023, 4(2): 85-103. |
| [4] | Rob Jess, Tao Ling, Yi Xiong, Chris J. Wright, Feihu Zhao. Mechanical environment for in vitro cartilage tissue engineering assisted by in silico models [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2023, 4(1): 18-26. |
| [5] | Chavee Laomeephol, Helena Ferreira, Sorada Kanokpanont, Jittima Amie Luckanagul, Nuno M Neves, Siriporn Damrongsakkul. Osteogenic differentiation of encapsulated cells in dexamethasone–loaded phospholipid–induced silk fibroin hydrogels [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2022, 3(3): 213-220. |
| [6] | Xin Huang, Haoyu Guo, Lutong Wang, Zengwu Shao. Engineered microorganism–based delivery systems for targeted cancer therapy: a narrative review [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2022, 3(3): 201-212. |
| [7] | Ricardo Donate, Maryam Tamaddon, Viviana Ribeiro, Mario Monzón, J. Miguel Oliveira, Chaozong Liu. Translation through collaboration: practice applied in BAMOS project in in vivo testing of innovative osteochondral scaffolds [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2022, 3(2): 102-104. |
| [8] | Melika Sahranavard, Soulmaz Sarkari, SeyedehMina Safavi, Farnaz Ghorbani. Three-dimensional bio-printing of decellularized extracellular matrix-based bio-inks for cartilage regeneration: a systematic review [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2022, 3(2): 105-115. |
| [9] | Panita Maturavongsadit, Weiwei Wu, Jingyu Fan, Igor B. Roninson, Taixing Cui, Qian Wang. Graphene-incorporated hyaluronic acid-based hydrogel as a controlled Senexin A delivery system [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2022, 3(2): 152-161. |
| [10] | Emma Steijvers, Armaan Ghei, Zhidao Xia. Manufacturing artificial bone allografts: a perspective [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2022, 3(1): 65-80. |
| [11] | Ke Hu, Yuxuan Li, Zunxiang Ke, Hongjun Yang, Chanjun Lu, Yiqing Li, Yi Guo, Weici Wang. History, progress and future challenges of artificial blood vessels: a narrative review [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2022, 3(1): 81-98. |
| [12] | Yizhong Peng, Jinye Li, Hui Lin, Shuo Tian, Sheng Liu, Feifei Pu, Lei Zhao, Kaige Ma, Xiangcheng Qing, Zengwu Shao. Endogenous repair theory enriches construction strategies for orthopaedic biomaterials: a narrative review [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2021, 2(4): 343-360. |
| [13] | Xirui Jing, Qiuyue Ding, Qinxue Wu, Weijie Su, Keda Yu, Yanlin Su, Bing Ye, Qing Gao, Tingfang Sun, Xiaodong Guo. Magnesium-based materials in orthopaedics: material properties and animal models [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2021, 2(3): 197-213. |
| [14] | Yiqing Wang, Xiangyu Chu, Bing Wang. Recombinant adeno-associated virus-based gene therapy combined with tissue engineering for musculoskeletal regenerative medicine [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2021, 2(1): 19-29. |
| [15] | Maryam Tamaddon, Helena Gilja, Ling Wang, J. Miguel Oliveira, Xiaodan Sun, Rongwei Tan, Chaozong Liu. Osteochondral scaffolds for early treatment of cartilage defects in osteoarthritic joints: from bench to clinic [J]. Biomaterials Translational, 2020, 1(1): 3-17. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||